Neighbor discovery method based on the greatest common divisor of cycle length
A technology of greatest common divisor and neighbor discovery, applied in network data management, wireless communication, broadcast service distribution, etc., can solve problems such as increasing the frequency of sending beacons, ignoring other costs of sending beacons, and increasing the average discovery delay.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
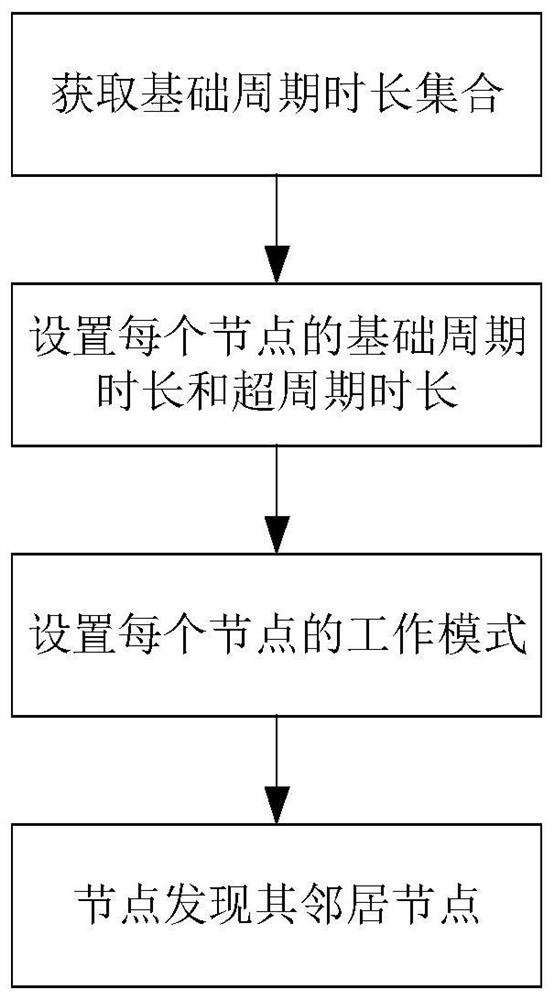
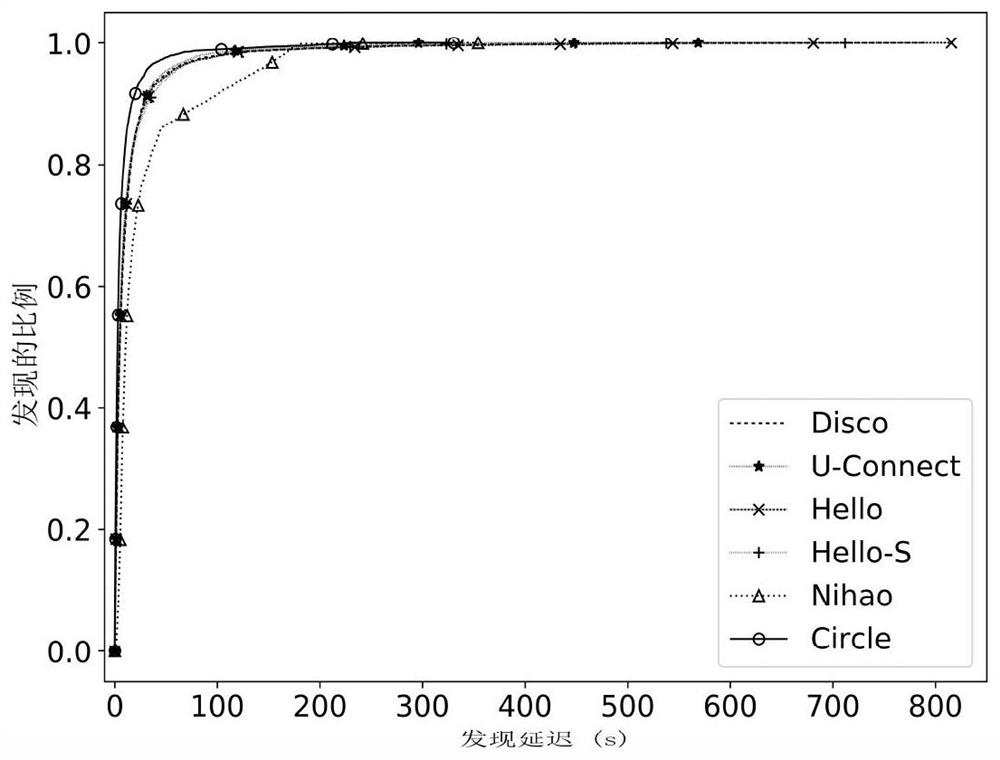
[0035]The invention is further described below with reference to the drawings. Specifically, the neighbor discovery method employed in the present invention is referred to as a Circle method.
[0036]Refer to the attachmentfigure 1 Further, the specific steps of the present invention are further described.
[0037]Step 1. Get the base period duration collection.
[0038]Suppose the user sets the minimum of the length of all nodes, the maximum value is 101 and 1001, respectively, and the alternate set of the basic period period is {101, 102, ..., 1000, 1001}.
[0039]Set the user to set the minimum of the length of the current period of all nodes, and the maximum value is re-entered into the maximum and minimum value of the duty cycle, respectively.
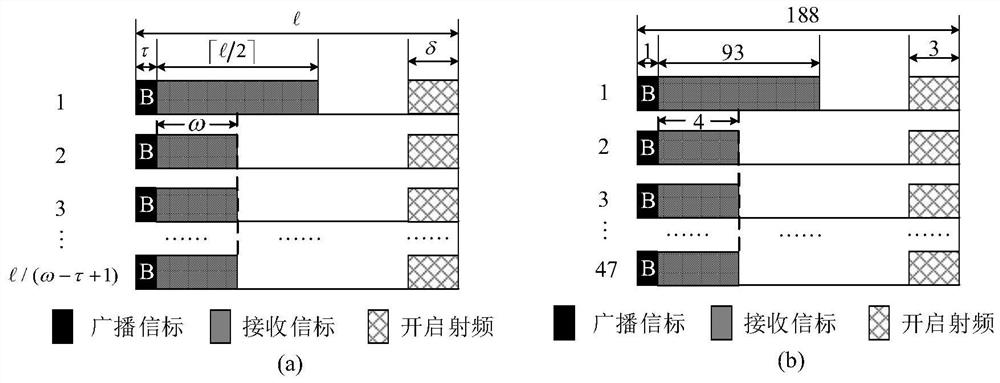
[0040]
[0041]Among them, the DC represents the duty cycle of the node, and τ represents the time length of the node broadcast beacon, ω represents the time long after the node broadcast beacon, δ indicates that the node broadcasts a beacon, and is star...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com