Shape memory articles and methods of controlling properties
A technology of memory alloy and fatigue performance, which is applied in the direction of medical formula, human tubular structure devices, blood vessels, etc., can solve the problems of plastic instability and nucleation difficulties, and achieve good sealing, enhanced device performance, easy function and durability. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0219] In this embodiment, the components or subassemblies are first shaped into their final geometry. A final heat treatment or series of multiple heat treatments is then performed while the (sub)assembly is in a relaxed state (ie, no deformation or load is applied to the target area). Zero stress / strain heat treatment can be performed either completely off the mandrel or using a holding or support fixture that does not impose additional stress or strain on the component at heat treatment temperatures.
[0220] Embodiment 1a - Low Temperature Zero Stress / Strain Conditioning
[0221] Time = 15 seconds - 600 seconds
[0222] ·Temperature = 300°C–525°C
[0223] ・Stress / strain = 0
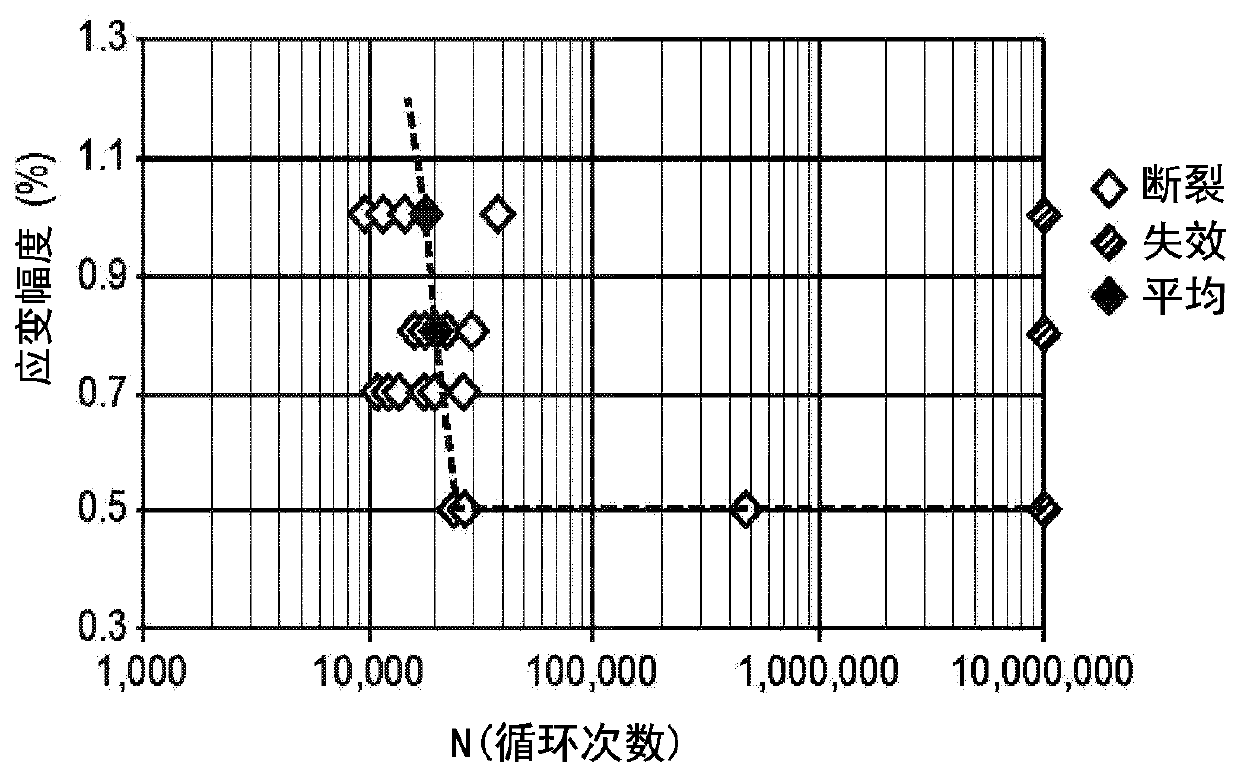
[0224] Zero stress / strain conditioning at low temperature promotes the separation of R′ and austenite phases, as assessed by DSC. This separation results in high flexural stiffness with low upper and lower platform stress values. In some embodiments, the separation of the R' phase and the austeni...
Embodiment approach 2
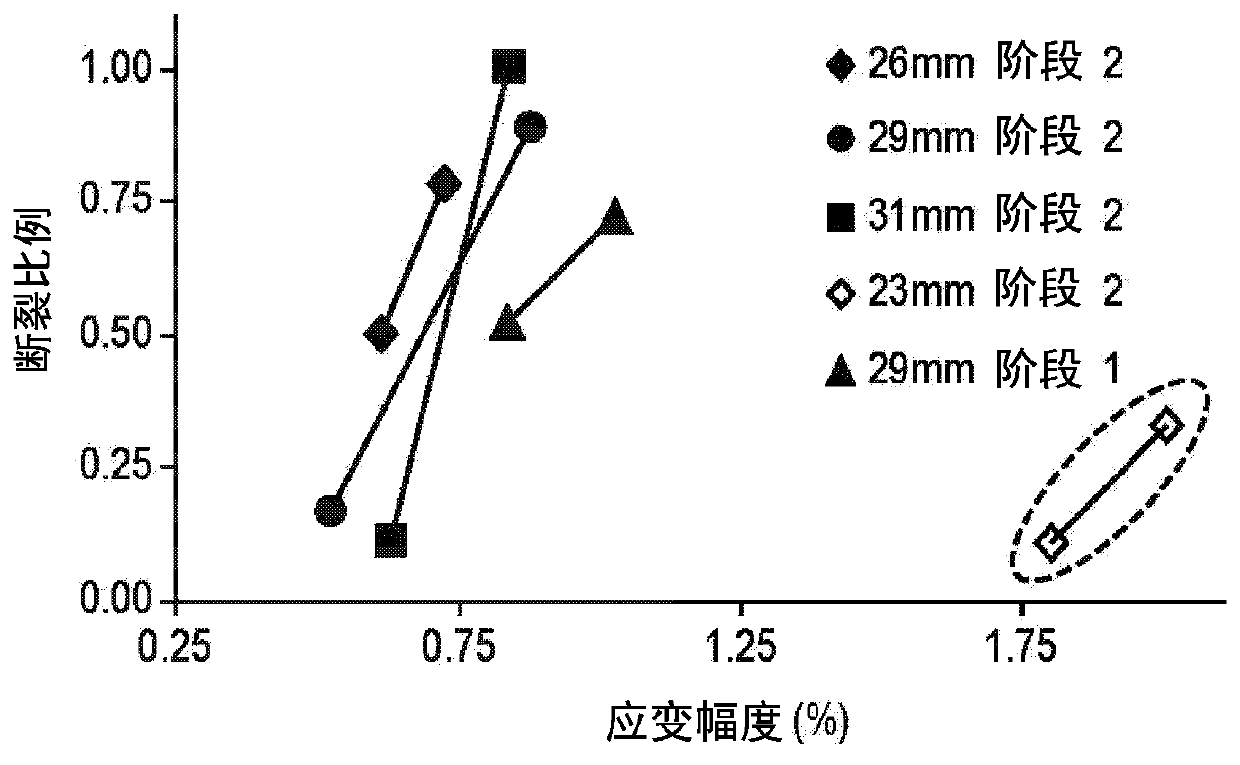
[0235] The nucleation barrier for the formation of Ni-rich precipitates in austenite is high, heterogeneous nucleation at grain boundaries during heat treatment of components and subassemblies under relaxed conditions (i.e. in the absence of externally applied loads) It is energetically favorable. Stress-assisted aging (aging under deviatoric stress / strain) can effectively produce uniformly distributed precipitates in slightly nickel-rich near-equiatomic Ni-Ti SMA. Thus, in this embodiment, the assembly or subassembly experiences non-zero stress / strain during the final heat treatment step. This non-zero stress / strain heat treatment is achieved by deforming the (sub)assembly using a mandrel or other constraining fixture.
[0236] Embodiment 2a - Low Temperature Non-Zero Stress / Strain Conditioning
[0237] Time = 15 seconds - 600 seconds
[0238] ·Temperature = 300°C–525°C
[0239] Stress / strain = non-zero
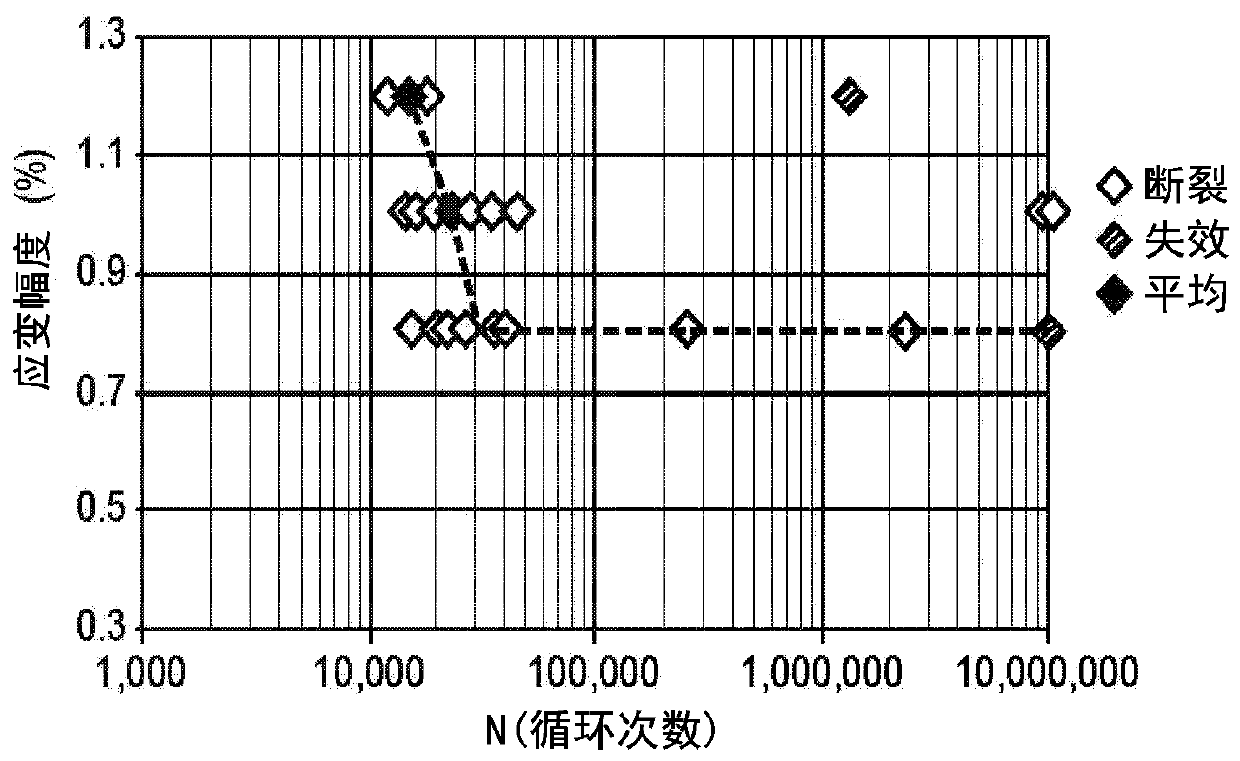
[0240] Non-zero stress / strain conditioning at low temperature prom...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com