Method for producing intestinal organoid derived from pluripotent stem cells
A technology of pluripotent stem cells and a production method, which is applied in the field of making intestinal organoids from pluripotent stem cells, and can solve the problem of no pharmacokinetics and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0152]
[0153] In order to create a novel method for producing functional intestinal organoids, the following research was conducted.
[0154] 1. Method
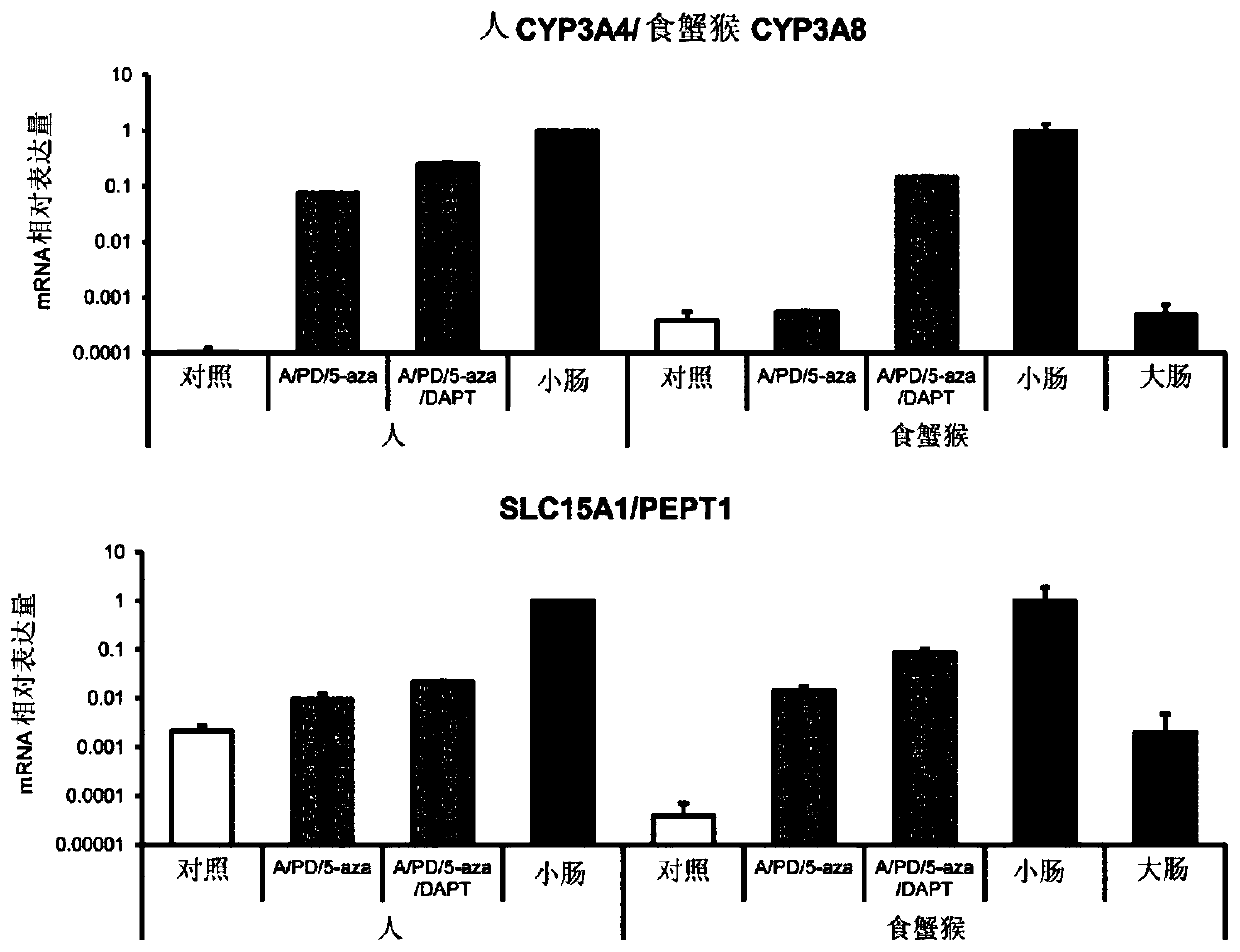
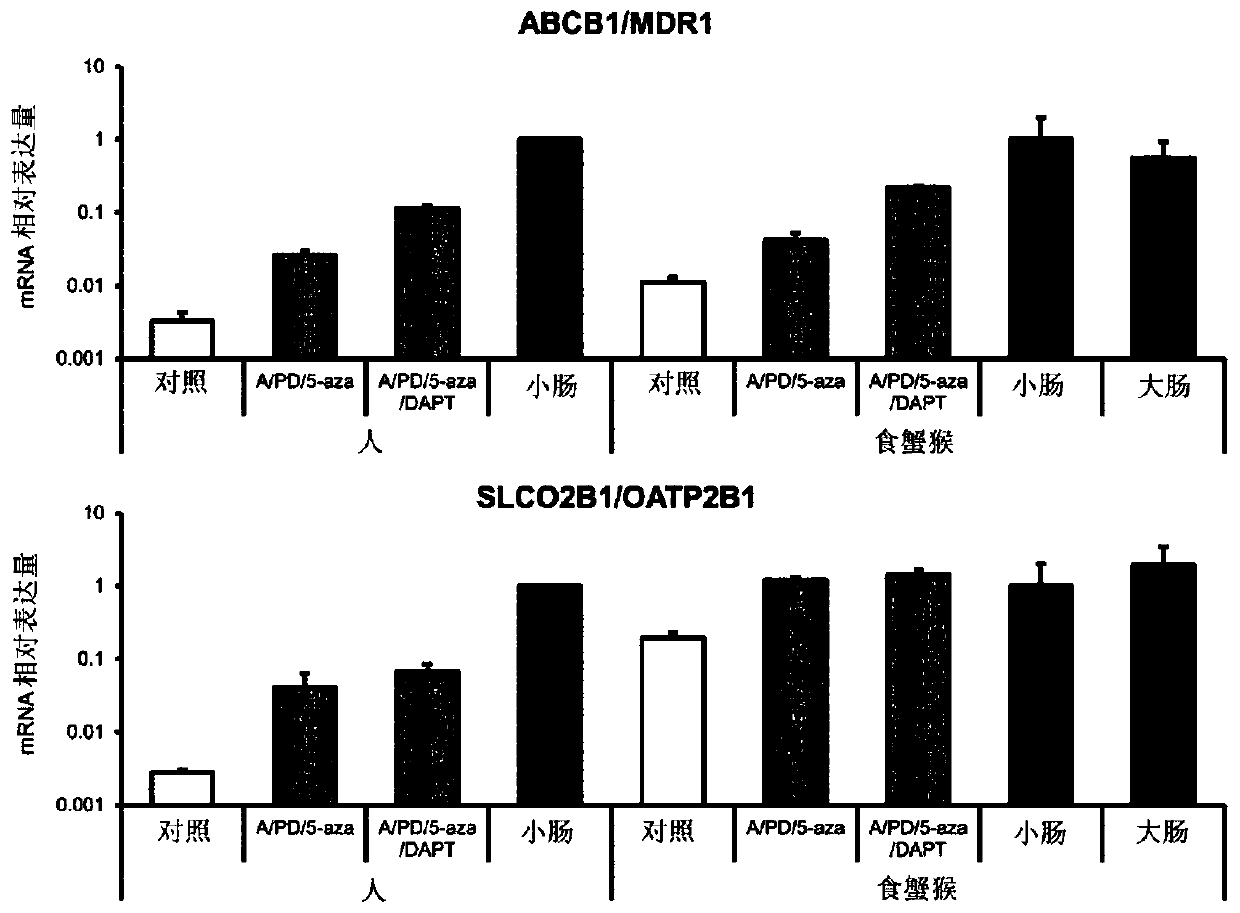
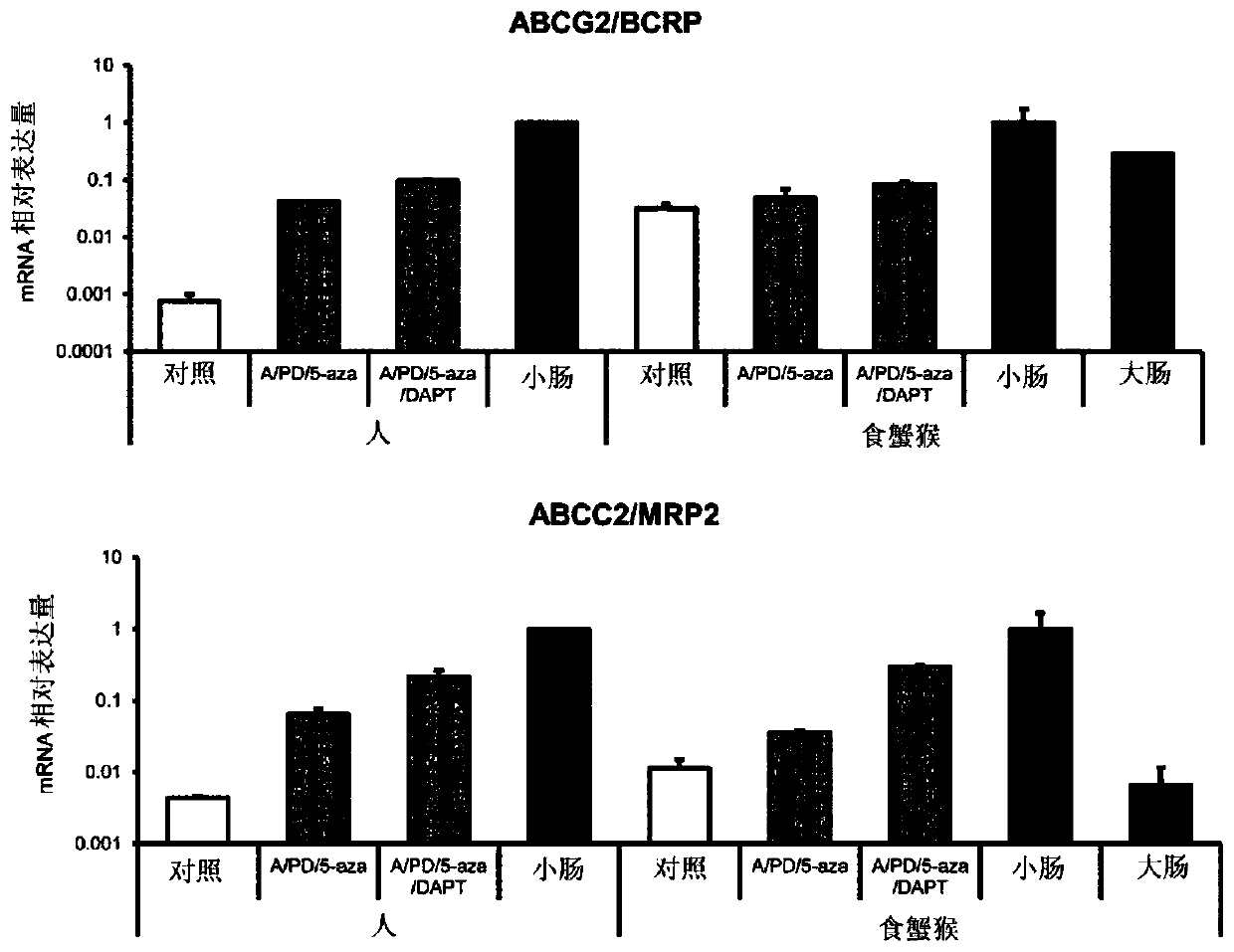
[0155] (1) cells
[0156]Human iPS cells (iPS-51: Windy) were transformed with octamer-binding protein 3 / 4 (OCT3 / 4), sex-determining region Y-box protein 2 (SOX2), kruppel-like factor 4 ( KLF4), v-myc myeloma virus oncogene homologue (avian) (c-MYC) was introduced into human fetal lung fibroblast MRC-5, and then cloned human ES cell-like colonies, obtained by the National Provided by Dr. Akihiro Umezawa, Center for Developmental Medical Research. Cynomolgus monkey iPS cells were introduced into fibroblasts cultured from cynomolgus monkey skin tissue with pCXLE-hOCT3 / 4-shp53-F, pCXLE-hSK, and pCXLE-hUL as episomal vectors by electroporation. Monkey ES cell-like colonies were cloned and established by the present inventors. As feeder cells, mouse fetal fibroblasts (MEFs) were used.
[0157] (2) culture medium
[0158]...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap