Path planning method based on mobile robot
A mobile robot, path planning technology, applied in the directions of instruments, non-electric variable control, two-dimensional position/channel control, etc. High efficiency and short time effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] 1. Environment Modeling
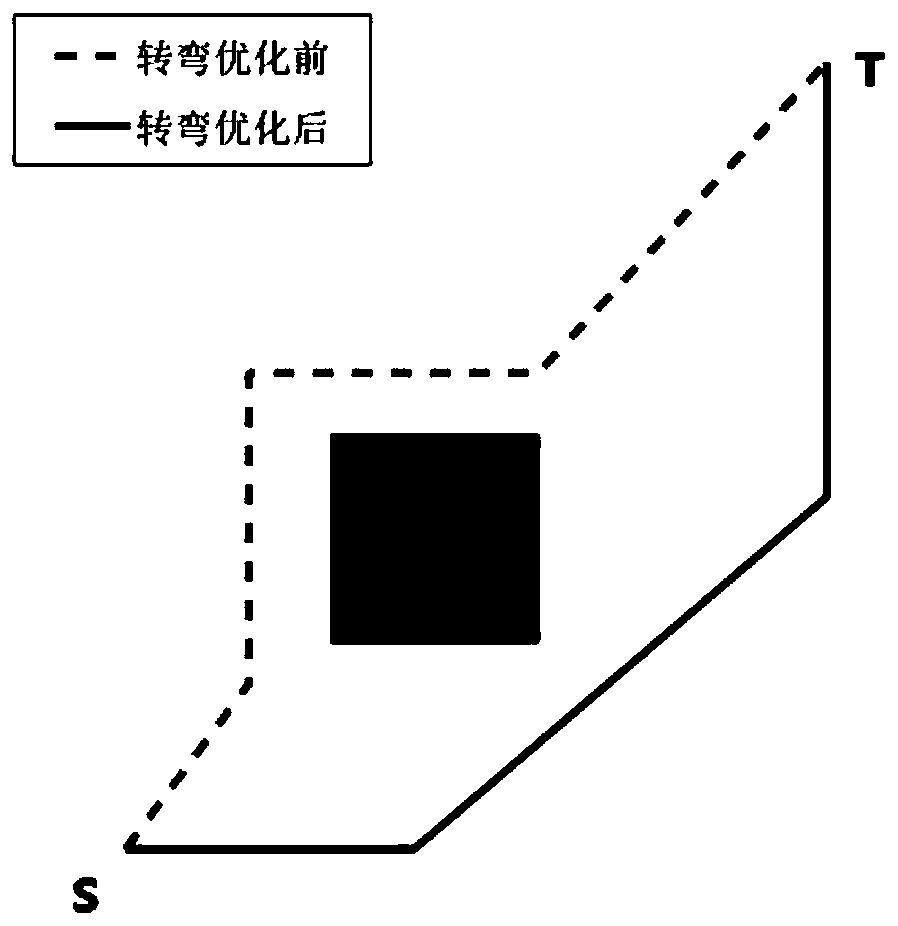
[0050] The environment in which the robot travels is a two-dimensional plane space, and the obstacles in the plane are set as static, random and known arbitrary irregular polygons, and its vertices (x, y) are represented by a ring list. Compared with the grid method, this method is easy to solve complex environmental information problems and occupies less resources.
[0051] 2. Dynamic parallel fitting strategy
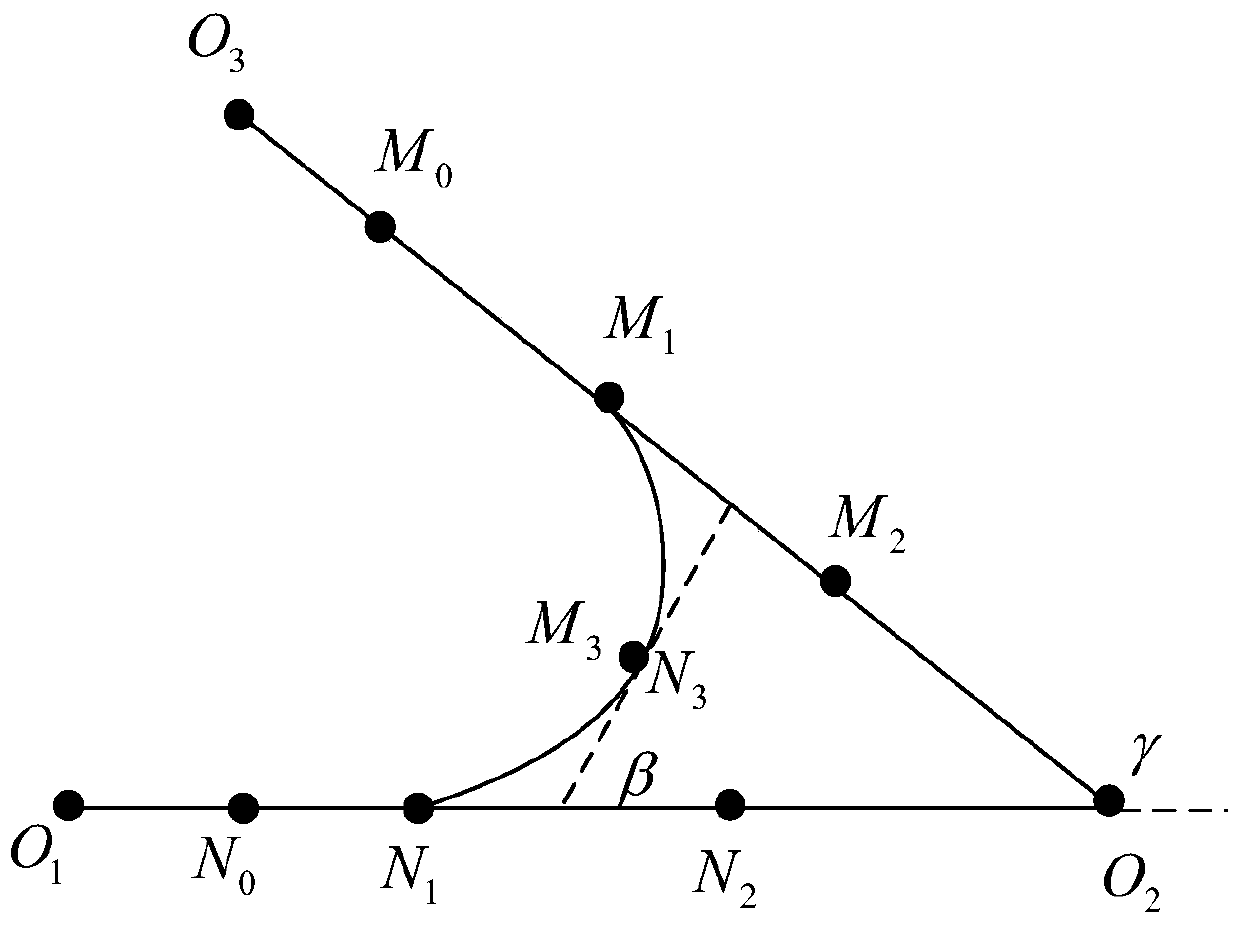
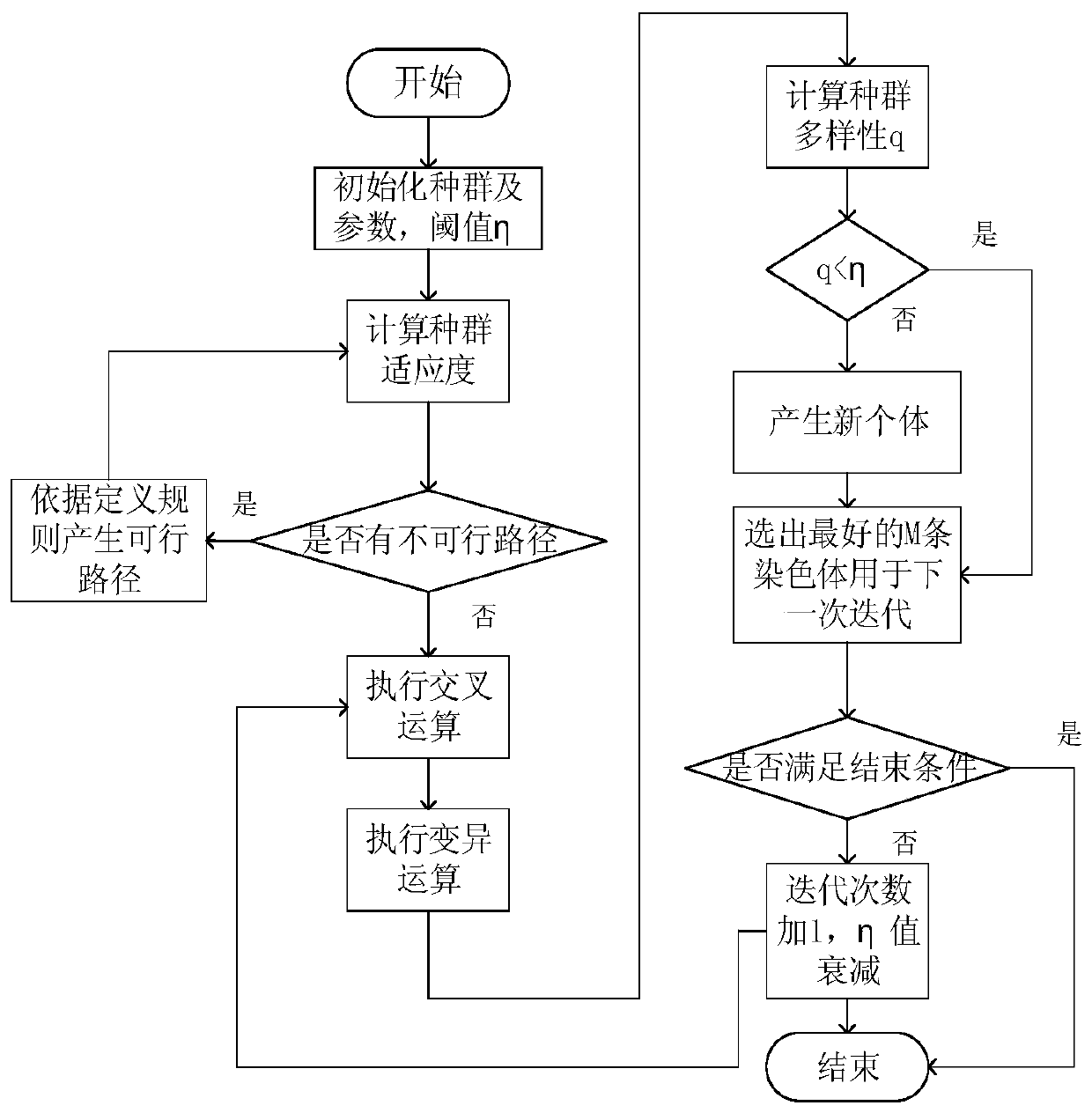
[0052] In previous studies, the process of using Bezier curve to smooth the path is an independent process, that is, after the optimal path is generated, the Bezier curve is used for static fitting, which will increase the calculation steps and make the algorithm cumbersome. Therefore, use Q-IGA to search for the most suitable control point P as the control point of the Bezier curve, and use the selected control point to generate a shorter optimal path.
[0053] The environment model established in the method of the present invention...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Before carrying out the simulation experiment, it is first necessary to set reasonable parameters to make the algorithm obtain the optimal solution. Figure 4 (a), (b), (c), and (d) are the relationship between population size and path length, calculation time, iteration number and path length, and calculation time, respectively. Combining the four performance diagrams, it can be seen that with the increase of the population size and the number of iterations, the execution time of the algorithm continues to increase, basically showing a linear upward trend, which is in line with the relationship between the running time and the complexity of the algorithm; As the number of times increases, the path length decreases for a period of time, and after a certain node, it tends to be stable and basically unchanged. It can be seen from Figures (a) and (c) that when the population size is 110, the path length reaches stability after 150 iterations. Therefore, for the first map, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com