Method for designing length of straight section at end of high-speed rail driving motor hanging plate spring
A technology for driving motor and hanging plate, which is applied in the fields of electrical digital data processing, instruments, geometric CAD, etc., can solve the problems of not giving accurate and reliable high-speed rail driving motor hanging plate spring end straight section length, not considering and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
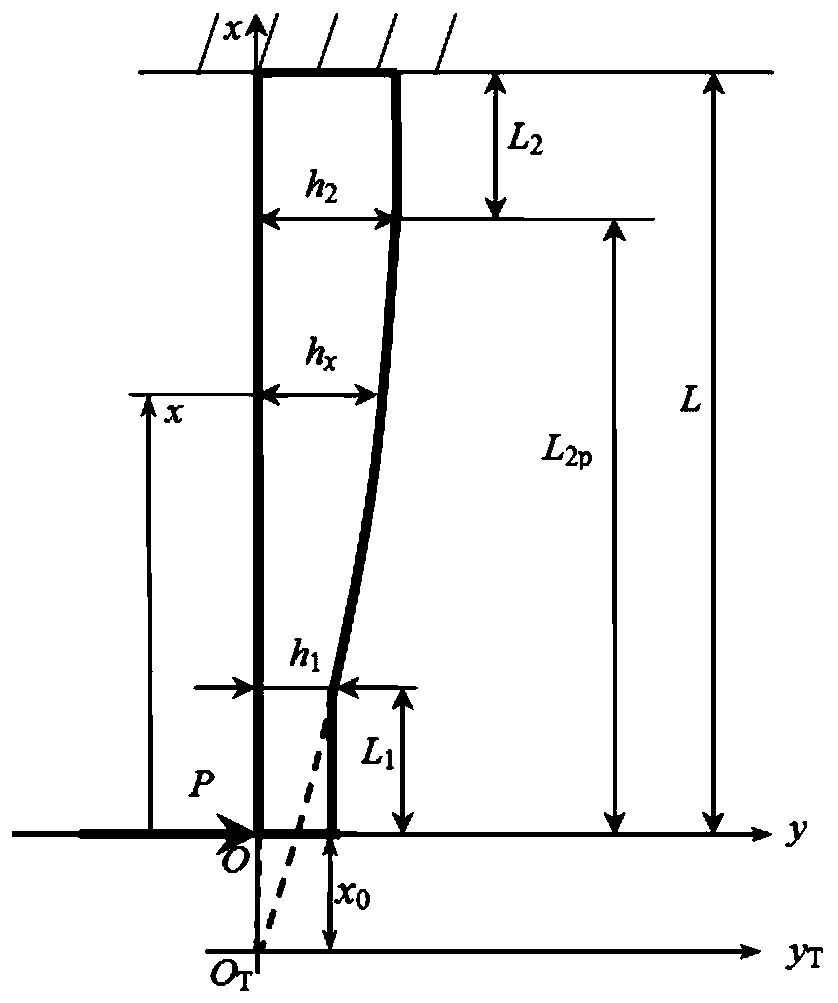
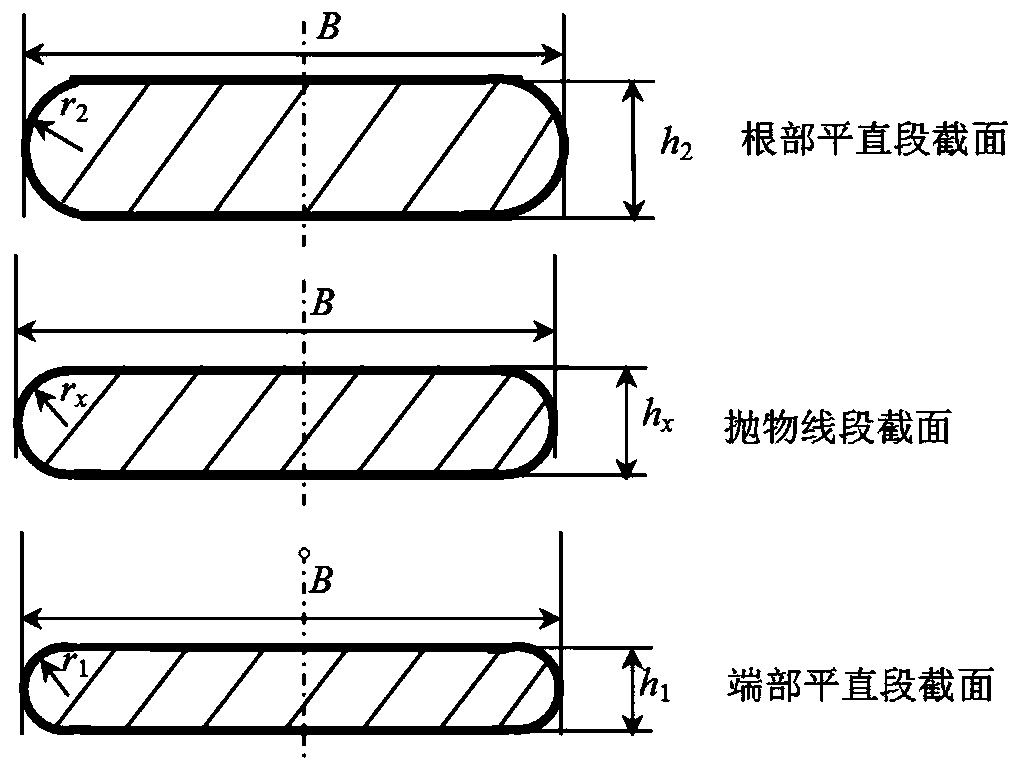
[0051] Example 1: It is known that the two ends of the cross-section of a leaf spring suspended by a high-speed rail drive motor are semicircular arcs, the width B=80mm, the elastic modulus E=206GPa, and the thickness h of the straight section at the root of the leaf spring 2 = 20mm, the thickness h of the straight section at the end 1 =8mm, the thickness ratio of the parabola segment β=h 1 / h 2 = 0.4; the effective length L of the hanging leaf spring = 550mm, the length L of the straight section at the root 2 =50mm, the length L from the root of the parabola segment to the end point of the leaf spring 2p =L-L 2 = 500mm. The design requirement value K of the lateral stiffness of the leaf spring for the drive motor of the high-speed rail y = 110.32 N / mm. According to the working length of the high-speed rail drive motor hanging leaf spring, the thickness and length of the straight section at the root, the thickness of the end straight section, the modulus of elasticity, a...
example 2
[0087] Example 2: It is known that the two ends of the cross-section of a leaf spring suspended by a high-speed rail drive motor are semicircular arcs, except for the thickness h of the straight section at the root 2 =21mm and lateral rigidity design requirement value K y =117.36N / mm, other structural parameters are exactly the same as those of Embodiment 1, that is, the thickness h of the flat section at the root of the leaf spring 2 =21mm, the thickness h of the straight section at the end 1 =8mm, the thickness ratio of the parabola segment β=h 1 / h 2 =0.381; the average thickness h of the parabola segment p =(h 1 + h 2 ) / 2=14.5mm. Using the design steps of Embodiment 1, the length of the end straight section, the length of the parabolic section and the thickness of the parabolic section at different positions of the high-speed rail drive motor hanging leaf spring are designed, namely:
[0088] (1) Calculation of the equivalent width of each segment of the high-speed ...
example 3
[0123] Example 3: It is known that the two ends of the cross-section of the suspension plate spring of a high-speed rail drive motor are chamfered, except for the cross-sectional shape and the design requirement value of lateral stiffness K y =125.2N / mm, other structural parameters are exactly the same as those of the second embodiment. That is, the thickness h of the straight section of the root 2 =21mm, the thickness h of the straight section at the end 1 =8mm, the thickness ratio of the parabola segment β=h 1 / h 2 =0.381, the average thickness h of the parabola segment p =(h 1 + h 2 ) / 2=14.5mm; the ratio of the chamfer radius to the thickness of the straight section at the root k r2 = r 2 / h 2 = 1 / 5, the ratio of the chamfer radius to the thickness of the straight section at the end k r1 = r 1 / h 1 = 1 / 5, the ratio k of the average chamfer radius and thickness of the parabola segment rp = r p / h p = 1 / 5. According to the function length of the high-speed rail...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com