Method for multi-objective optimization opportunistic routing of underwater sensor network
A multi-objective optimization and underwater sensing technology, which is applied in the field of multi-objective optimization opportunity routing in underwater sensor networks, can solve the problems of falling into local optimal solutions, energy consumption, data redundancy, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
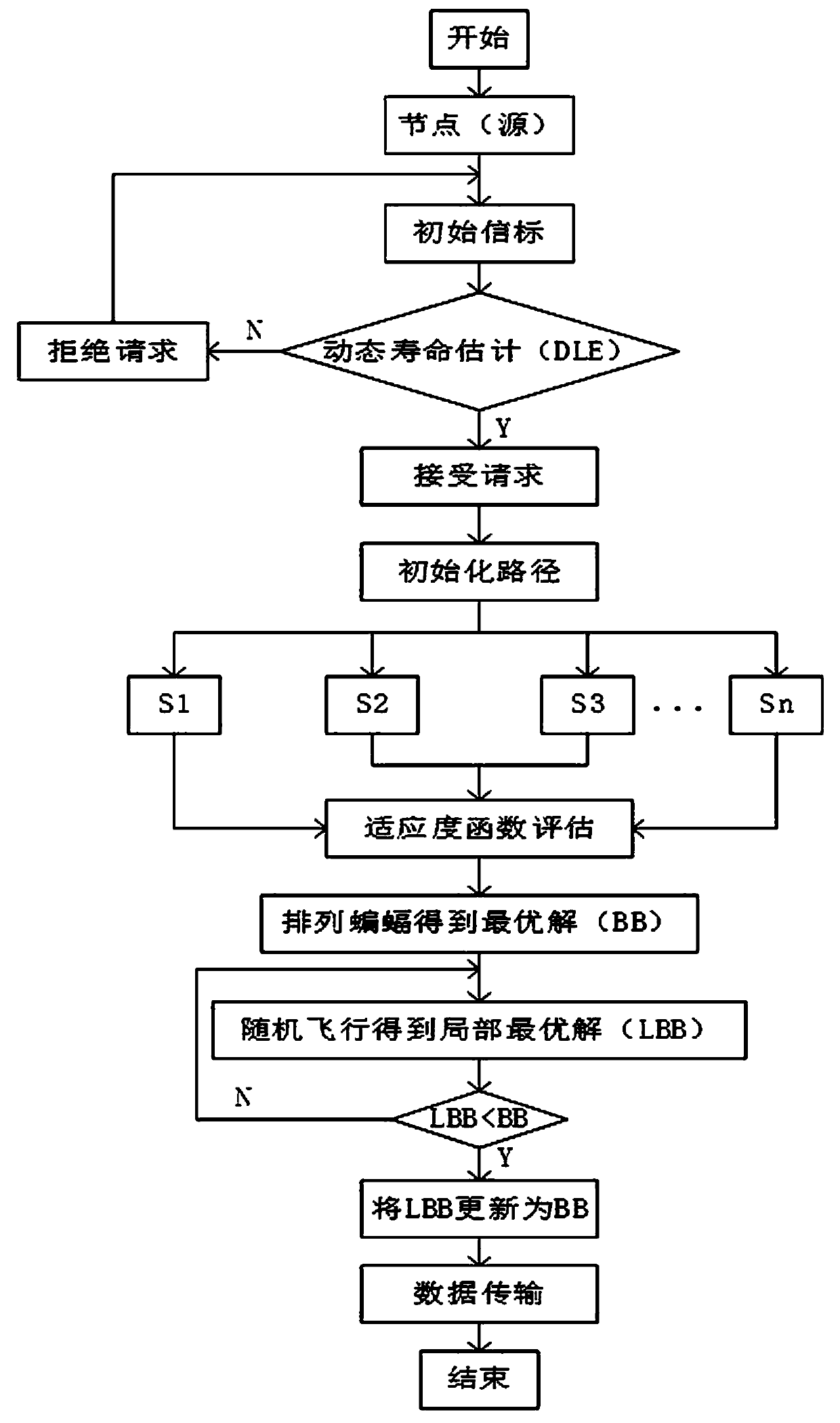
[0073] refer to image 3 , a method for multi-objective optimization opportunity routing in underwater sensor networks, including the following steps:
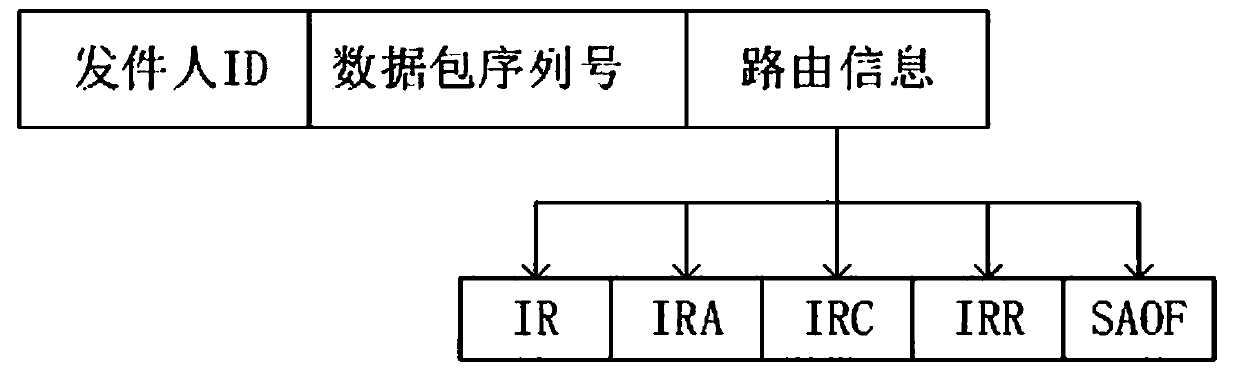
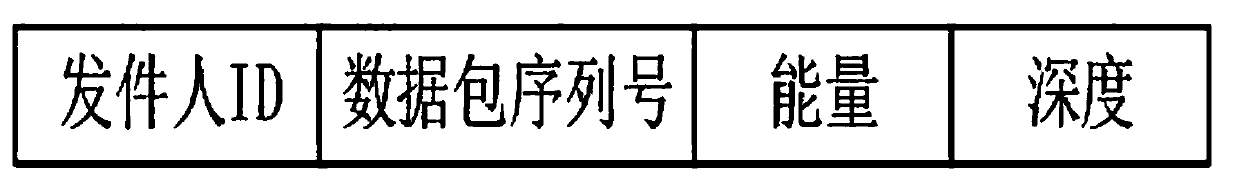
[0074] 1) Define multi-objective optimization opportunity routing MOO-BA: In the routing packet type and message format of MOO-BA, the packet header of any packet contains two fields: sender ID, packet sequence number, sender ID is the identifier of the underwater sensor node; the packet sequence number is the unique sequence number assigned to the packet by the underwater sensor node, the combination of the sender ID and the packet sequence number helps to avoid duplication in the routing process, routing information Including energy and depth, energy is the remaining energy of the beacon node, depth is the depth information of the current transponder, each node is automatically updated during the beacon sending phase, such as figure 1 shown;
[0075] Routing information includes five types of requests, namely invite reques...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com