Dynamic reference point depth offset Z value compression algorithm
A technology of depth offset and compression algorithm, which is applied in computing, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of large memory data bandwidth, achieve high compressibility, good continuity, and improve the effect of compressibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
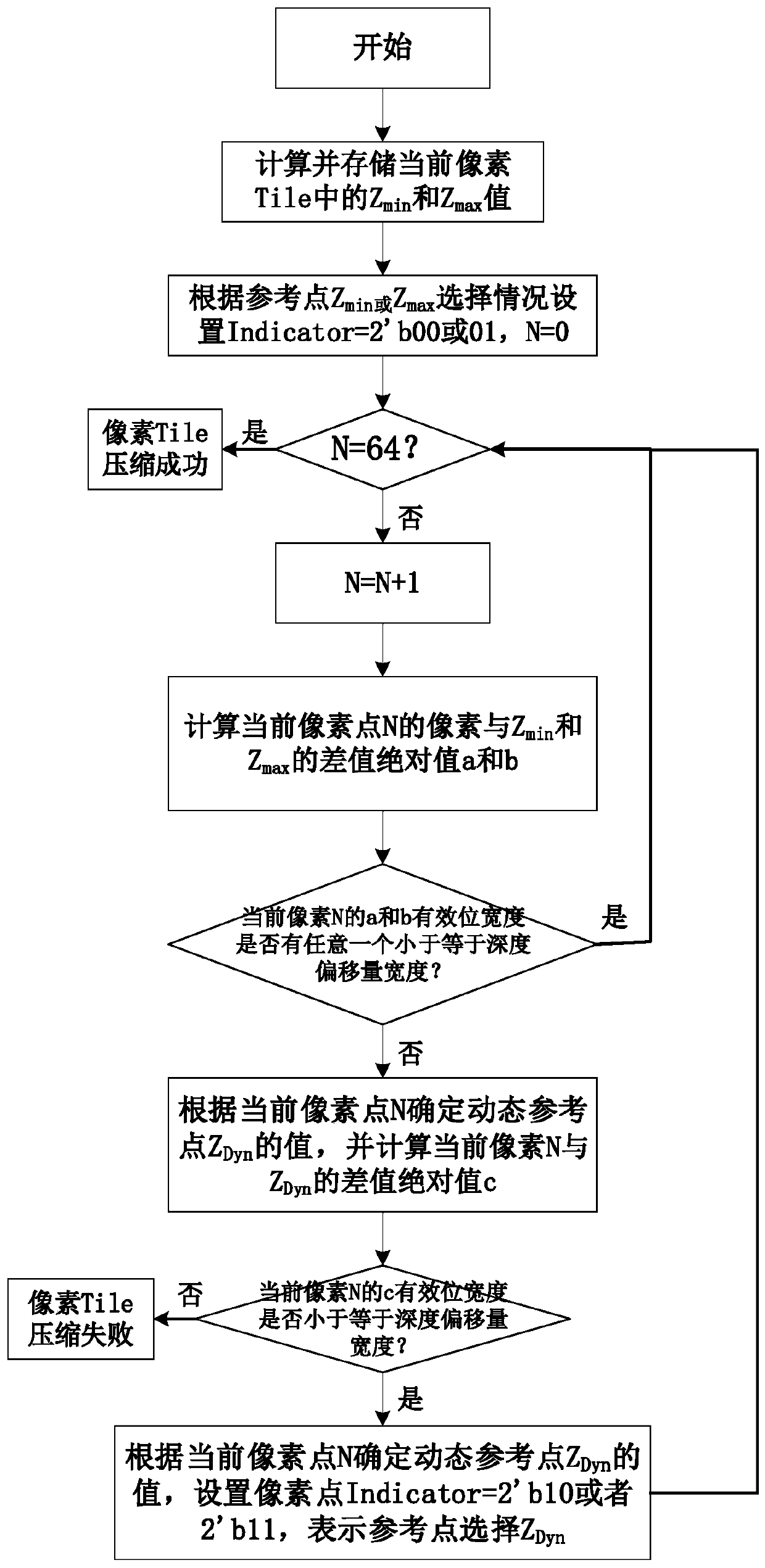
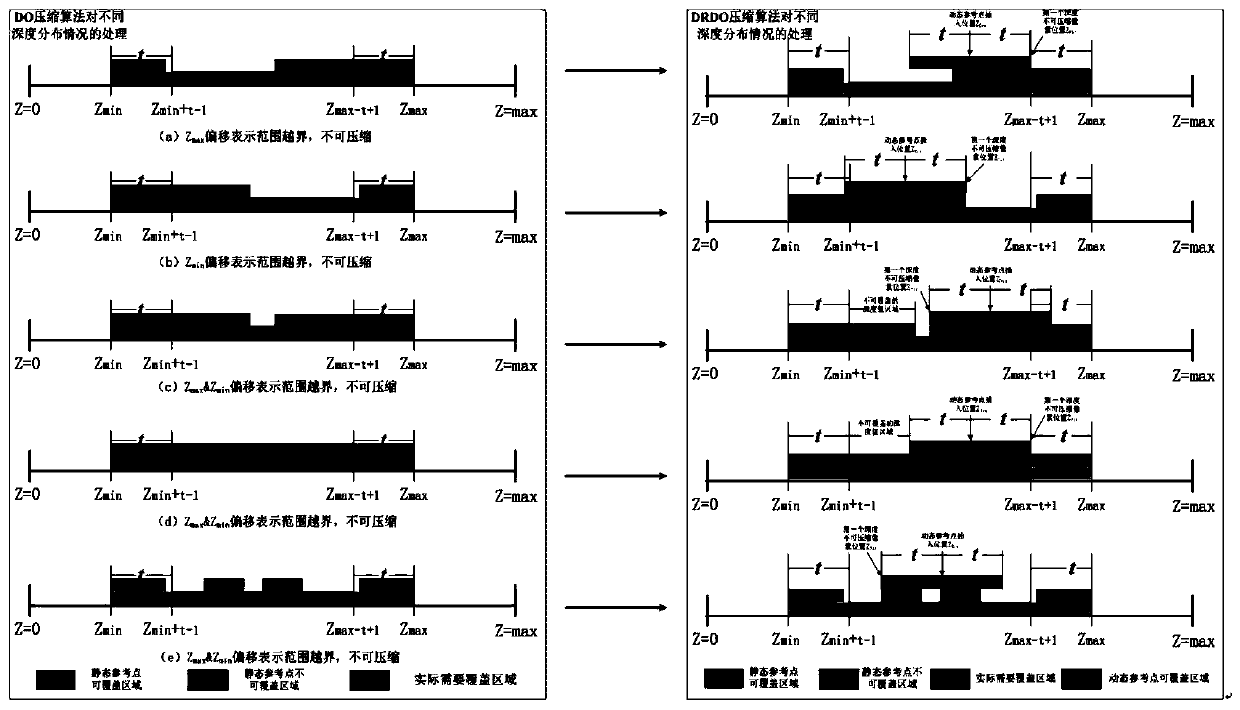
[0039] In DO algorithm original 2 static Z Min and Z Max Based on the reference point, add a dynamic reference point Z for each pixel Tile Dyn , when a certain pixel depth data in Tile is based on Z Min and Z Max When the compression of the reference point fails, the Z is dynamically determined according to the position of the pixel point of the current compression failure Dyn The insertion position, and at the same time increase the indicator associated with each offset from 1bit to 2bit, so that in Z Min ,Z Max and Z Dyn Choose between reference points to make the Z-based Dyn The reference point's offset coverage area relative to Z Min or Z Max Reference points doubled for better coverage Tile cannot be Z based Min and Z Max Discrete, non-uniformly distributed pixel depth values covered by the reference point offset, resulting in higher compressibility.
[0040] A dynamic reference point depth offset Z value compression algorithm, the algorithm includes the foll...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com