Treatment method of zirconium alloy and application
A treatment method and technology of zirconium alloy, applied in the field of medical implant materials, can solve the problems of many micro-cracks and low density of the oxide ceramic layer of zirconium alloy, and achieve the effect of strong market competitiveness, low cost and reduction of raw material cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
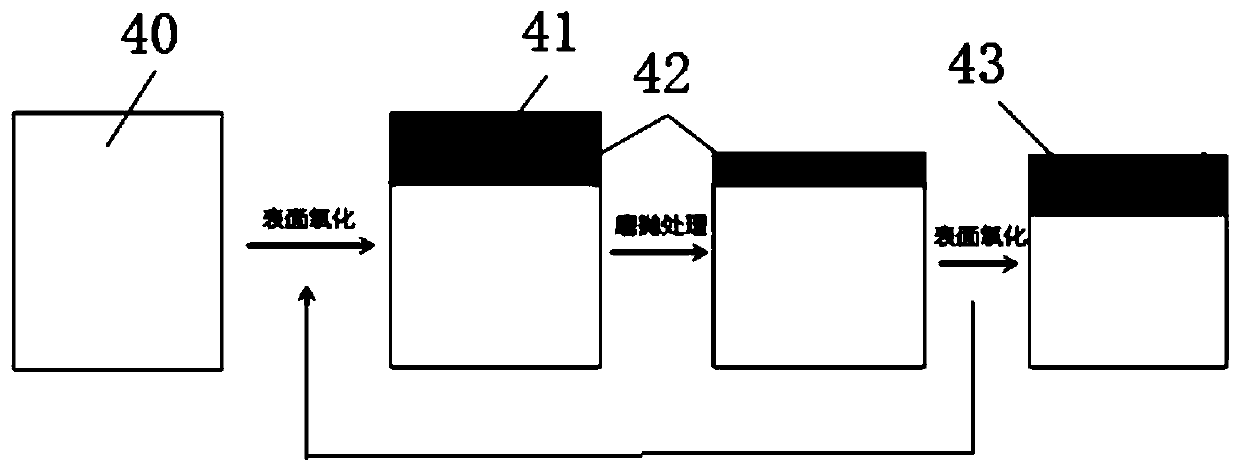
[0040] The preparation process of the material for medical implants is as follows: figure 2 The specific implementation steps are as follows:
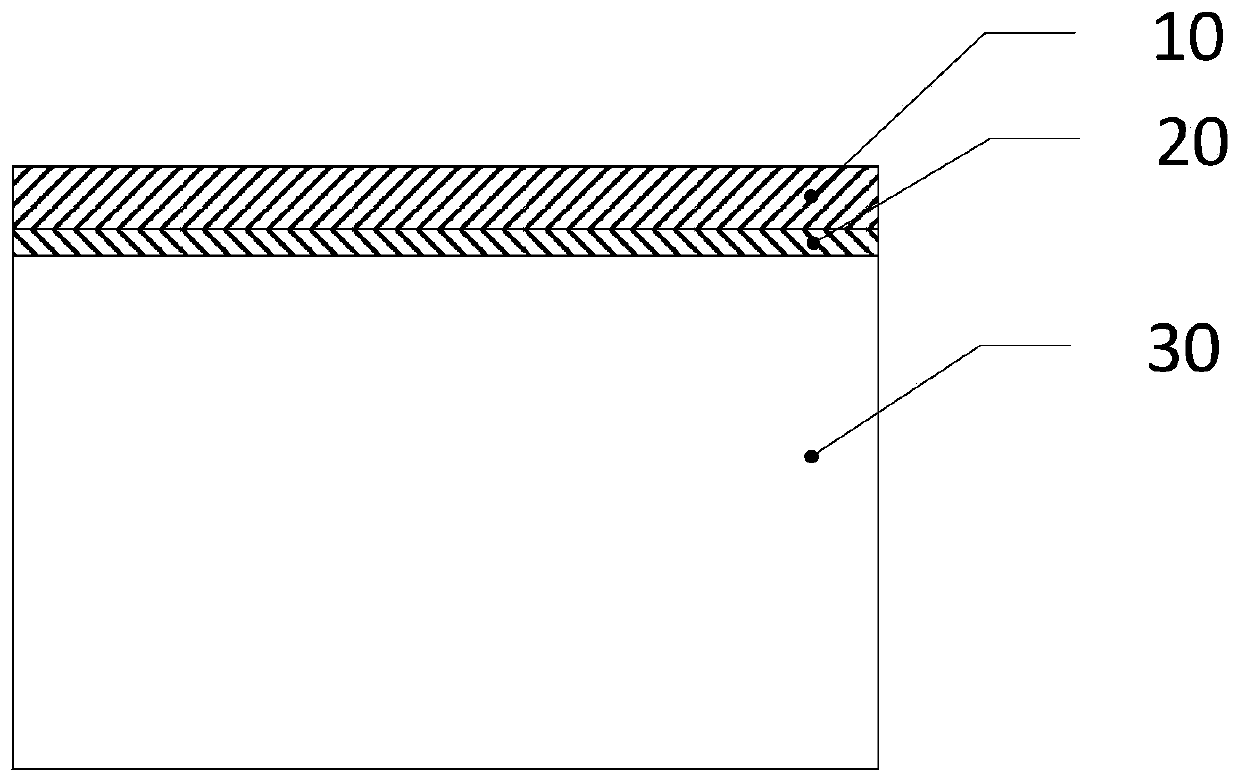
[0041] (1) Surface oxidation treatment is performed on the first surface layer 40 of the zirconium alloy metal substrate 30 with a hafnium element content of 0.5wt%-8wt%. Water bath or salt bath for surface oxidation, the oxidation temperature is 500℃-700℃, the treatment time is 0.5h-10h, the preferred oxidation temperature is 550℃-600℃, and the preferred treatment time is 4-6h, the surface of which is enriched with hafnium is formed. The first oxide surface layer 41 is composed of the oxygen-rich diffusion layer 20 and the oxide ceramic layer 10 .
[0042] (2) the first oxide surface layer 41 enriched with hafnium is removed by grinding, finishing, mechanical polishing, vibration polishing or any combination thereof, with a thickness of 1-20 μm, preferably a thickness of 3-12 μm, The second surface layer 42 having a reduced hafnium...
Embodiment 1
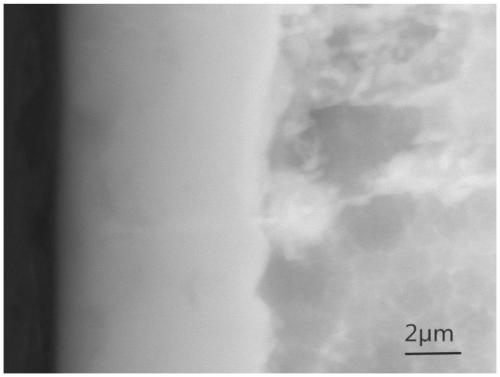
[0048] For zirconium alloys with hafnium content image 3 and Figure 4 As shown, the oxide ceramic layer, the oxygen-rich diffusion layer, and the metal substrate are arranged from left to right. from image 3 It can be seen that the surface oxide ceramic film of sample 1 is dense and has fewer defects, while Figure 4 It shows that there are a lot of microcracks in the surface oxide ceramic layer of sample 2. From the results of elemental analysis, the surface oxide ceramic layer (position a, b) of sample 2 and the oxygen-rich diffusion layer (position c) have higher content The hafnium content is 1.53wt%, 1.80wt%, 2.09wt%, respectively, while the hafnium content (1.30wt%) near the substrate (position d) of the oxide ceramic layer is significantly lower than the initial hafnium of the alloy content (2.26 wt%). The oxidized ceramic layer on the surface of sample 2 was removed by mechanical grinding, polishing, etc., to a thickness of about 10 μm, that is, the oxidized cera...
Embodiment 2
[0052] For zirconium alloys with hafnium content Figure 9 and Figure 10 As shown, the oxidized ceramic layer, oxygen-rich diffusion layer and metal substrate are arranged from left to right. Compared with sample 5, the surface of the oxidized ceramic layer of sample 4 is dense and tightly bonded with the substrate, and the bonding interface has no gaps. The layer thickness is about 9.66 μm; the oxidized ceramic layer of sample 5 is slightly thicker, about 10.51 μm, but the inside of the oxidized ceramic layer is loose, and there are a lot of micro-cracks, and even the inside of the oxidized ceramic layer has a tendency to crack, and the interface with the substrate is also better. Poor, obvious gaps are visible. The oxidized ceramic layer and oxygen-rich diffusion layer on the surface of sample 5 were removed by mechanical grinding, polishing and other means to a thickness of about 12 μm. After that, they were kept in an air environment at 600 °C for 4 h to obtain sample 6. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com