Maker polypeptides and method for detecting non-edible meat from edible meat
A technology for eating meat and polypeptides, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as inaccuracy, interference with qualitative accuracy, false positive quantification, etc., and achieve the effect of improving food safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0090] Example 1. Obtainment of characteristic peptides of non-edible meat
[0091] 1. Obtaining of non-edible meat and edible meat samples
[0092] As shown in Table 1, 7 different non-edible meat samples and 4 different edible meat samples were taken, and the samples were fresh meat.
[0093] Table 1. Information of 11 kinds of meat samples
[0094]
[0095]
[0096] 2. Pretreatment of meat samples and acquisition of peptide groups
[0097] 1. Sample pretreatment steps:
[0098] (1) Weigh 1g of meat sample and homogenize it into a powder state, add 10mL protein extract (8M urea, 50mM NH 4 HCO 3 ) shake to extract protein, centrifuge at high speed and low temperature (20000rpm), take 400 μL of supernatant and transfer to 1mL EP tube to obtain protein solution;
[0099] (2) Add 8 mL of 1mol / L dithiothreitol (DTT) to 400 μL of the above protein solution and react at 37°C for 1 hour;
[0100] (3) Add 40 μL of 1 mol / L iodoacetamide (IAA) that has been prepared into th...
Embodiment 2
[0117] Embodiment 2, the detection of the edible meat sample that the market buys
[0118] 1. The steps of analyzing the edible meat to be tested include:
[0119] 1. Sample pretreatment steps:
[0120] Same as Steps 1 and 2 in Step 2 of Example 1.
[0121] 2. Mass spectrometry and liquid phase detection conditions:
[0122] Same as Step 3 of Example 1.
[0123] 3. Analysis of results
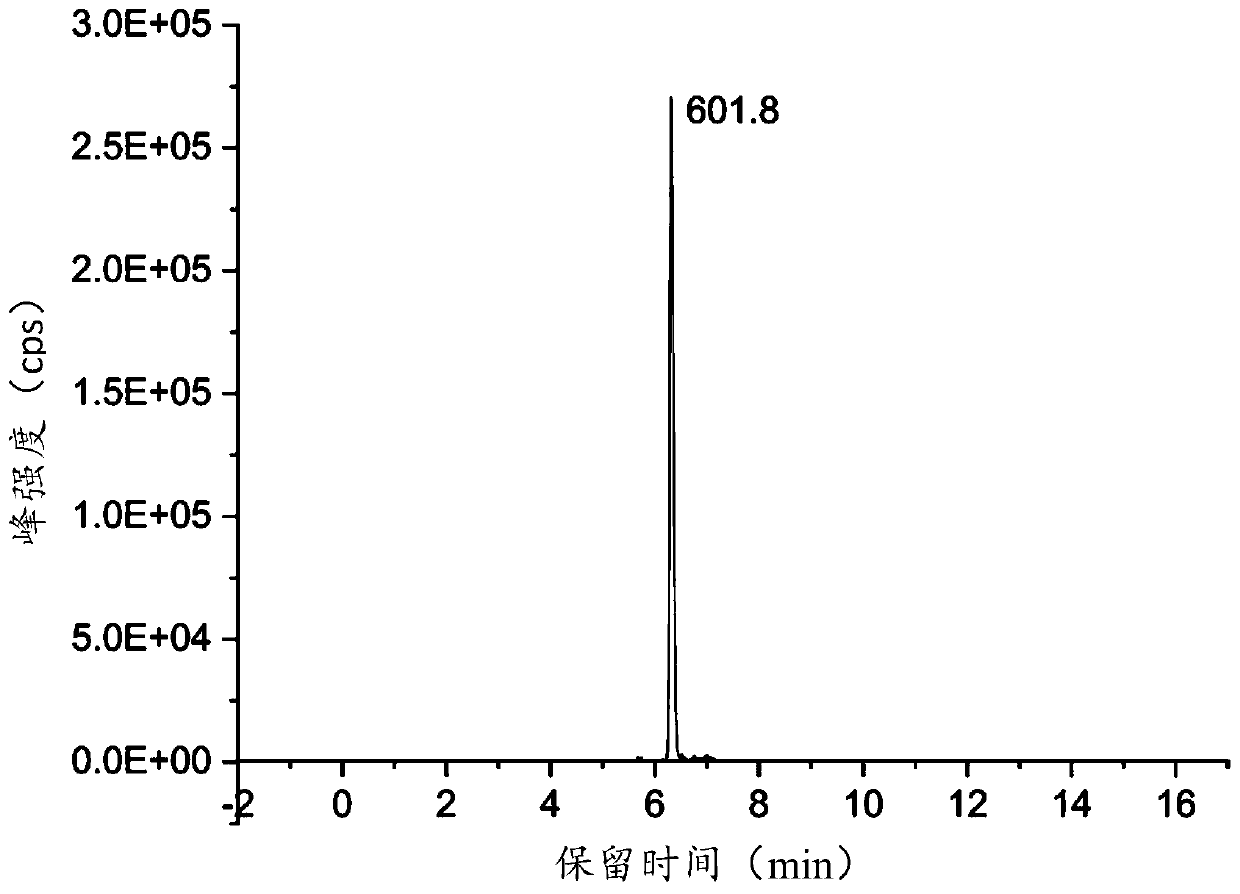
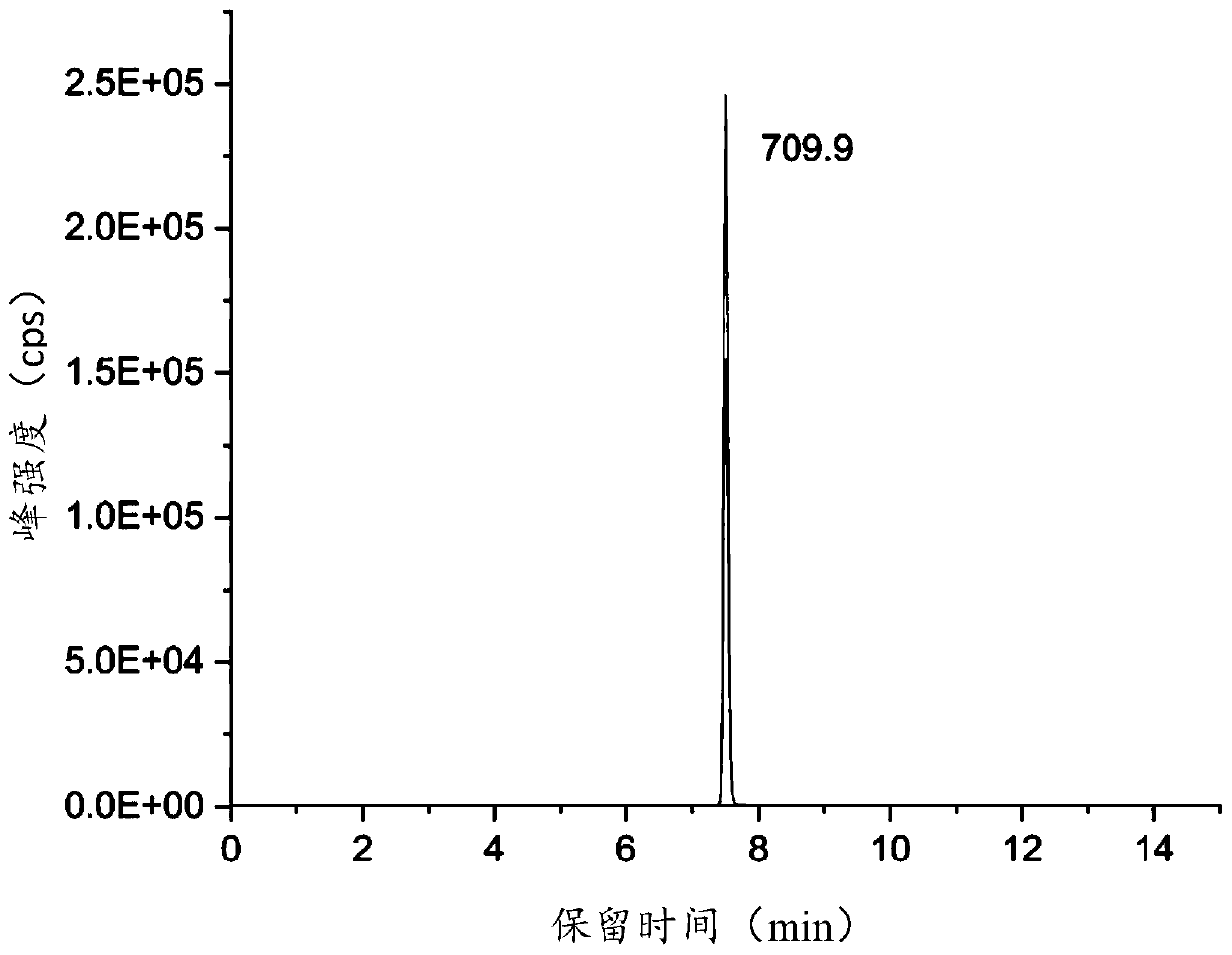
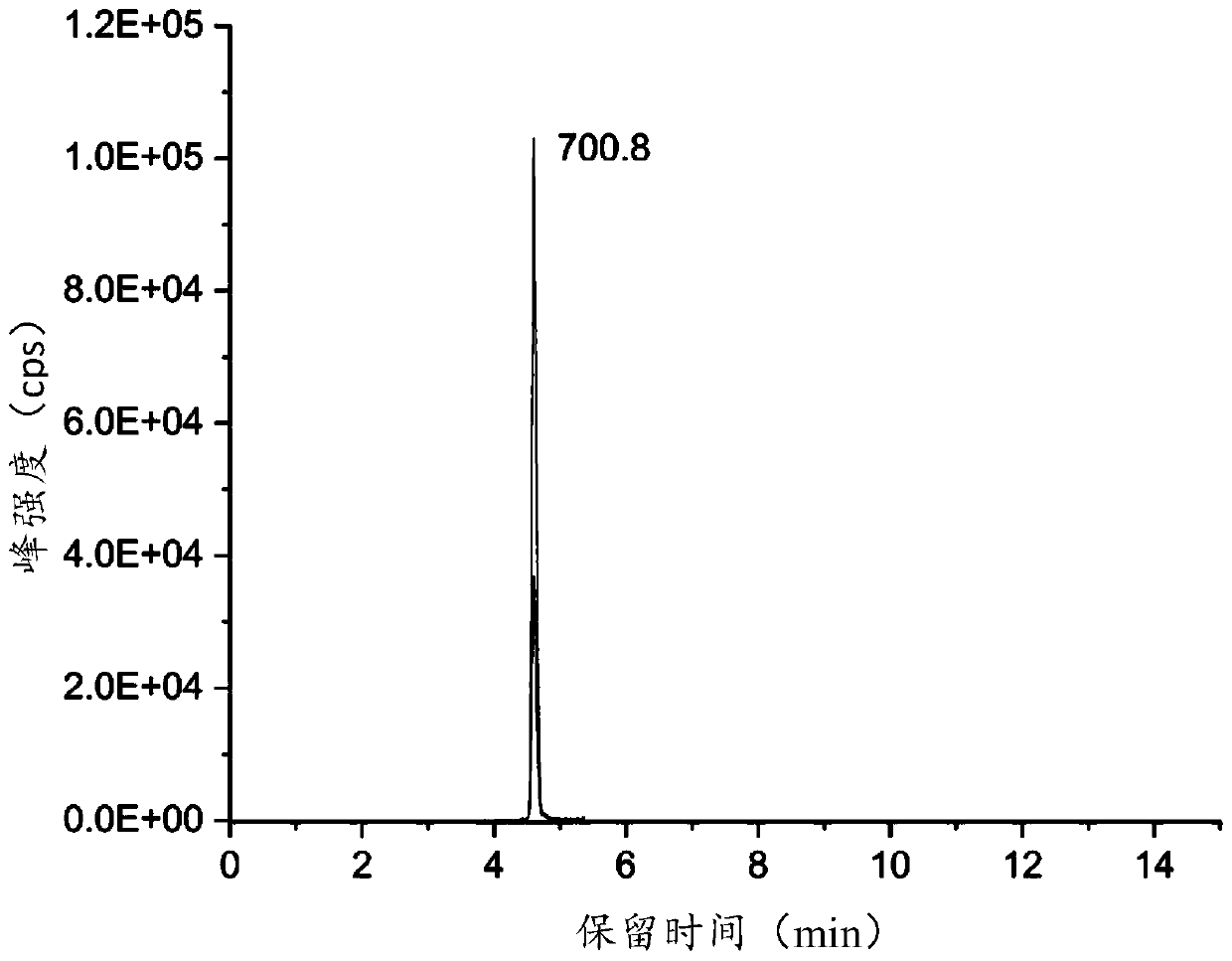
[0124] Comparing the detection results of step 2 with the chromatograms of each characteristic polypeptide shown in Table 2 in Example 1, when any of the chromatograms described in Example 1 appears, it can be judged that the edible meat to be tested contains the corresponding species of non-edible meat and edible meat.
[0125] 2. Testing of edible meat samples purchased in the market:
[0126] Randomly buy 3 beef samples (1 fresh meat, 2 cooked meat), 3 lamb samples (1 fresh meat, 2 cooked meat), 3 donkey meat samples (1 fresh meat, 2 cooked meat) randomly purchased from the market Coo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com