Laser frequency stabilization device and method, semiconductor laser component using same
A technology of semiconductors and lasers, which is applied in the field of laser frequency stabilization devices, can solve the problems of non-universality, small center frequency adjustment range, and low operating frequency, so as to avoid temperature drift and residual amplitude modulation noise, and is easy to adjust and enhance The effect of stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments and with reference to the accompanying drawings.
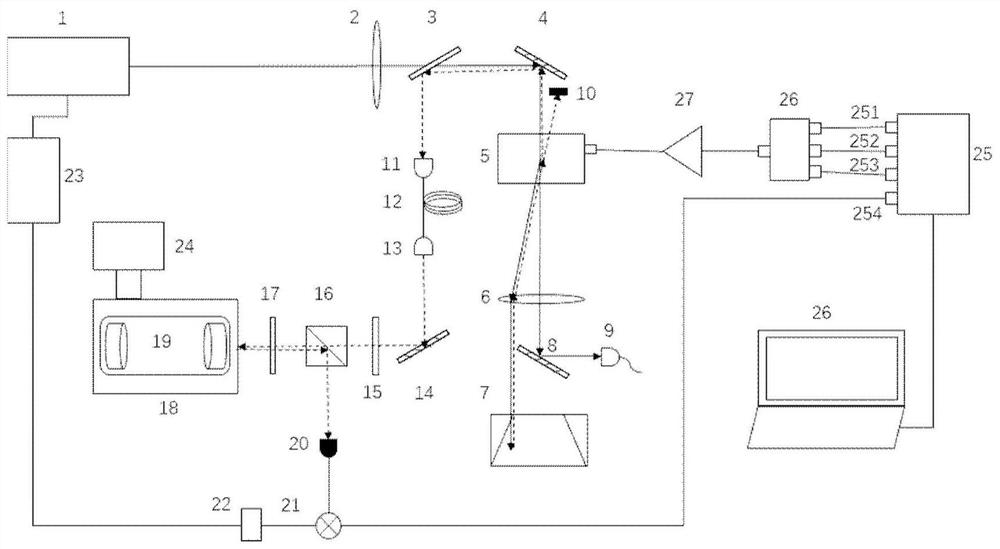
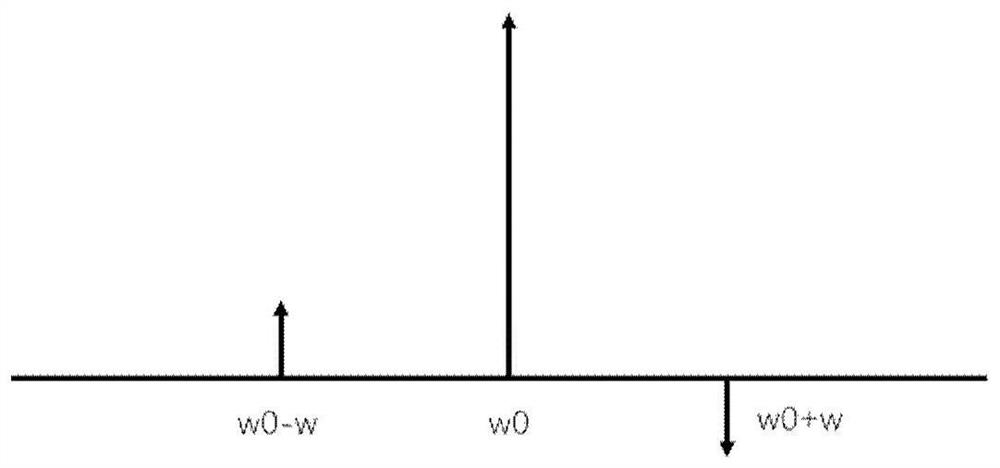
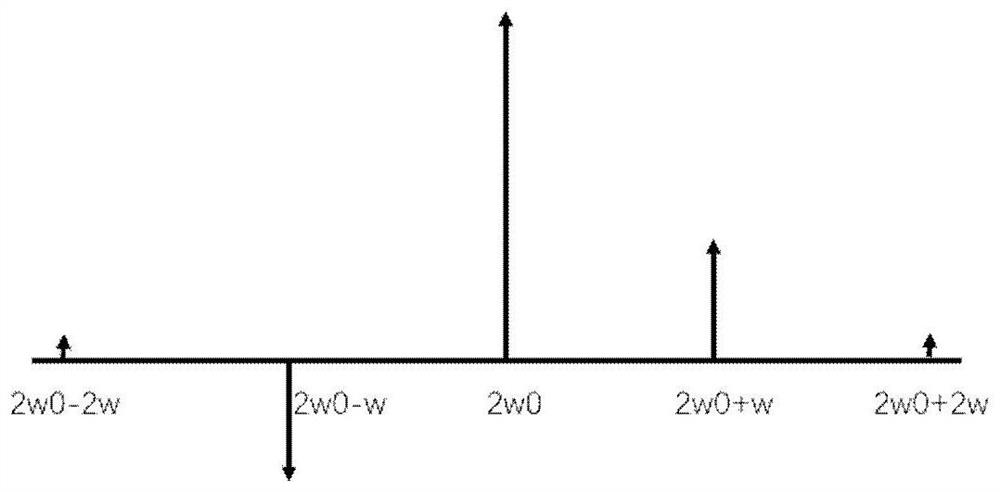
[0044] The invention discloses a laser frequency stabilization method and device, comprising a semiconductor laser, an acousto-optic modulator, a lens, a rectangular prism, a half glass slide, a polarization beam splitter, a quarter glass slide, and is arranged in a vacuum device Fabry-Perot cavity, multi-channel RF signal source, combiner, RF amplifier, photodetector, mixer, low-pass filter and servo system. Use multi-channel radio frequency signal source 25 to generate frequency respectively w 0 、w 0 -w,w 0 +w, RF signals with phases of 0 degrees, 0 degrees, and 180 degrees respectively, are amplified by the RF amplifier 27 to drive the acousto-optic modulator 5, and the laser light emitted by the semiconductor laser ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com