Optimal control method for robot trajectory planning based on obstacle size homotopy strategy
An optimal control and trajectory planning technology, applied in the direction of program control manipulators, manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of robustness and efficiency dependence, affecting the progress of job tasks, limiting the application of optimal control methods, etc., to achieve strong reliability Operability and feasibility, the effect of facilitating practical application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0063] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with specific examples.
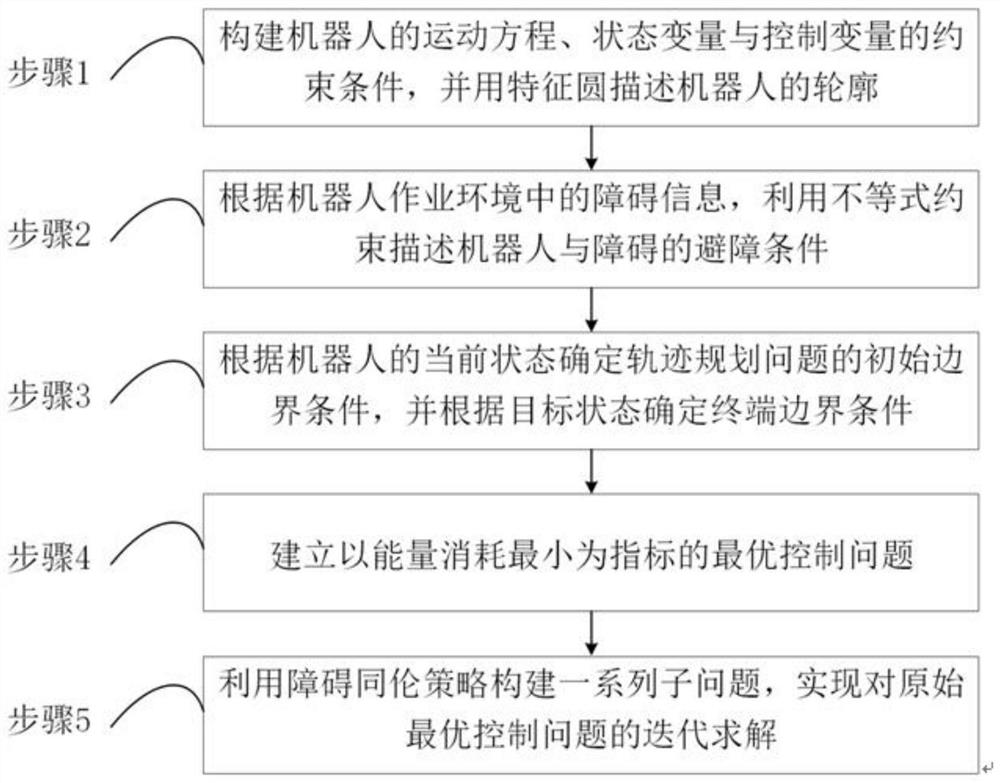
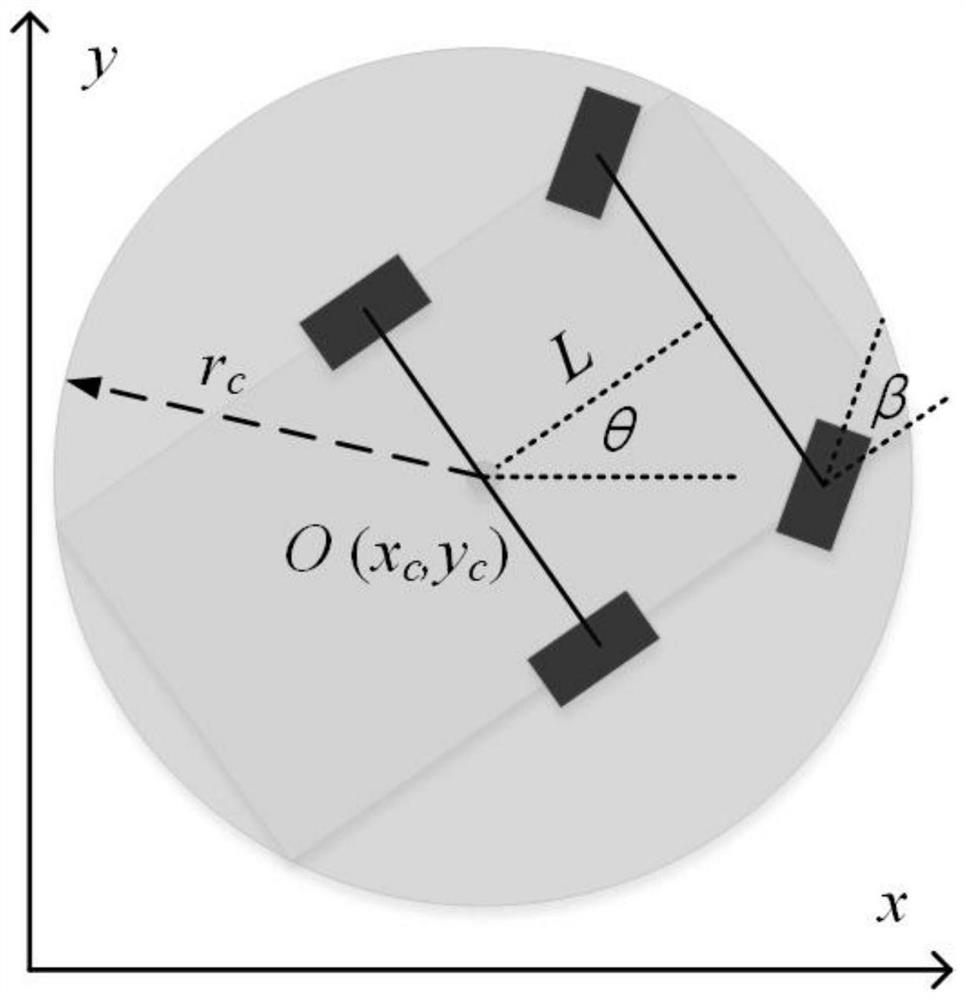
[0064] In the method of the present invention, the motion equation of the robot, the constraint conditions of the state variables and the control variables are first constructed, and the outline of the robot is described by a characteristic circle. Second, according to the obstacle information in the robot's working environment, the obstacle avoidance conditions of the robot and the obstacle are described by using inequality constraints. Third, the initial boundary conditions of the trajectory planning problem are determined according to the current state of the robot, and the terminal boundary conditions of the trajectory planning problem are determined according to the goal state. Fourth, establish the optimal control problem with the minimum energy consumption as the index. Fifth, a series of sub-problems are constructed using the homotopy strategy to realize the iterative...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com