Cell culture method for inducing dental pulp stem cells to differentiate into bladder smooth muscle cells in vitro
A technology of smooth muscle cells and dental pulp stem cells, applied in the medical field, can solve the problems of limited application and poor in vitro proliferation ability of ADSCs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] A cell culture method for inducing dental pulp stem cells to differentiate into bladder smooth muscle cells in vitro, the cell culture method comprising the steps of:
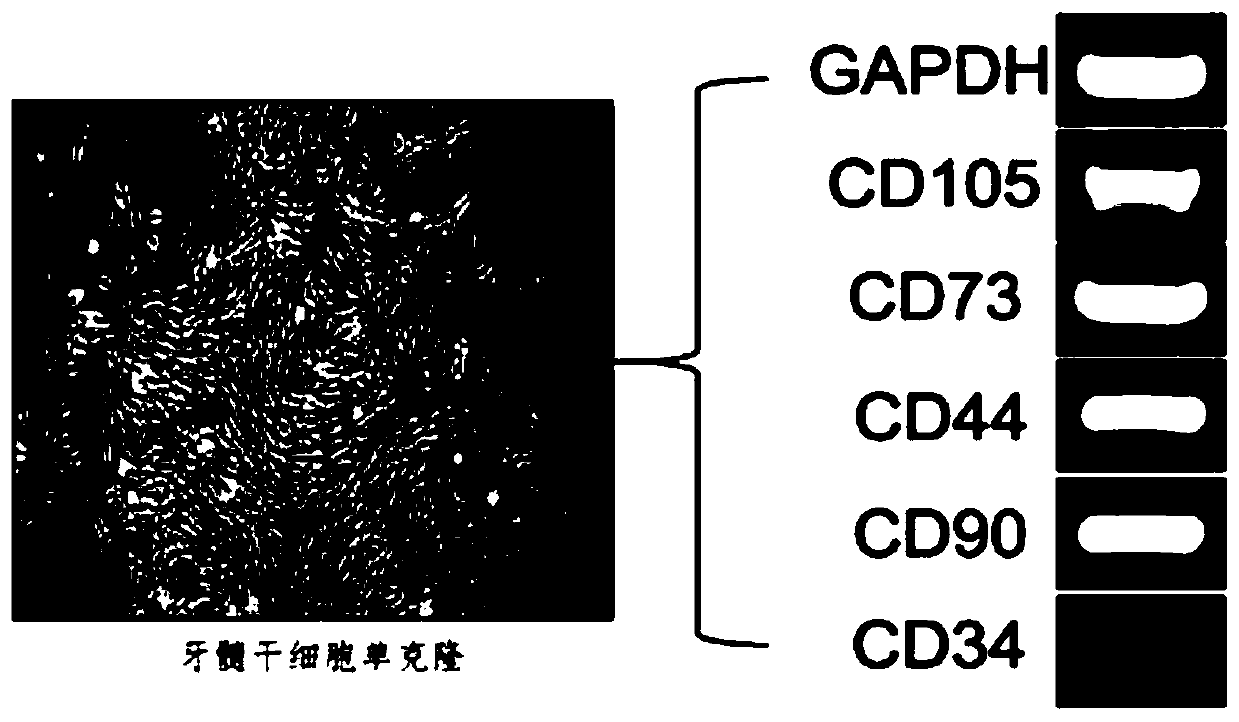
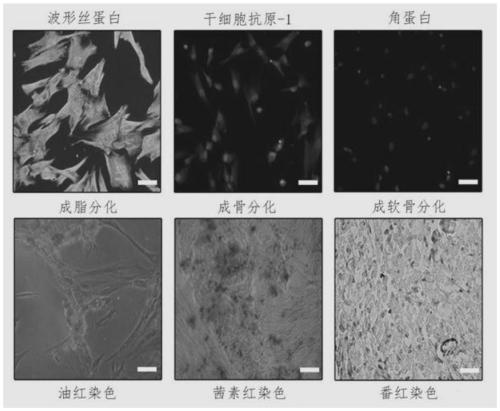
[0035] Step (1) Isolation and cultivation of dental pulp stem cells DPSCs;
[0036] Step (2) separation and cultivation of bladder smooth muscle cells SMCs;
[0037] Step (3) collecting bladder smooth muscle cell SMCs conditioned medium CM;
[0038] Step (4) screening bladder smooth muscle cell SMCs in vitro induction culture medium;
[0039] Step (5) inducing the differentiation of dental pulp stem cells DPSCs to bladder smooth muscle cells SMCs in vitro.
Embodiment 2
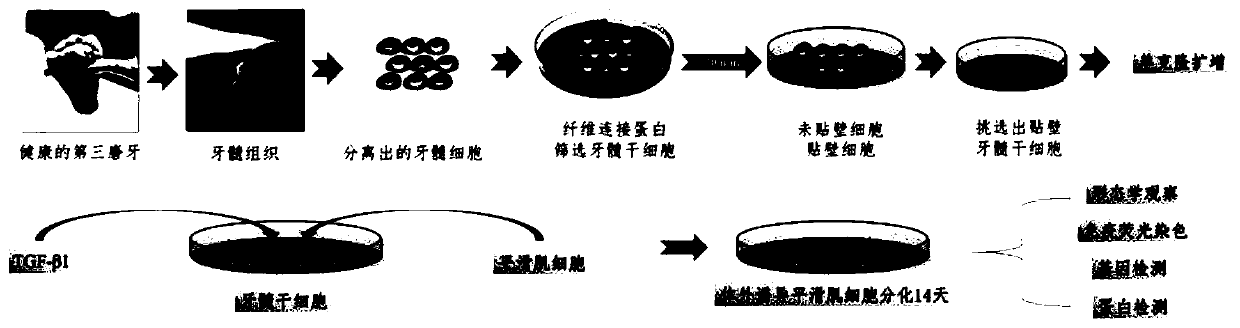
[0041] Such as figure 1 As shown, a cell culture method for inducing dental pulp stem cells to differentiate into bladder smooth muscle cells in vitro, the cell culture method includes the following steps:
[0042] Step (1) Isolation and cultivation of dental pulp stem cells DPSCs;
[0043] The step (1) the separation and cultivation of dental pulp stem cells DPSCs comprises the following steps:
[0044] 1) Under sterile conditions, take out the pulp tissue from the exfoliated tooth, put the pulp tissue in an EP tube, add 1ml of collagenase type Ⅰ with a concentration of 4μg / μl, and transfer the EP tube to CO 2 Digestion was carried out in the incubator, and the EP tube was fully shaken every 20 minutes to make the pulp tissue fully contact with the digestive enzymes; after 1 hour of full digestion, the contents of the EP tube were passed through a 70 μm cell sieve and transferred to a new EP tube. Obtain a single cell suspension; use PBS buffer to fully rinse the cell suspe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com