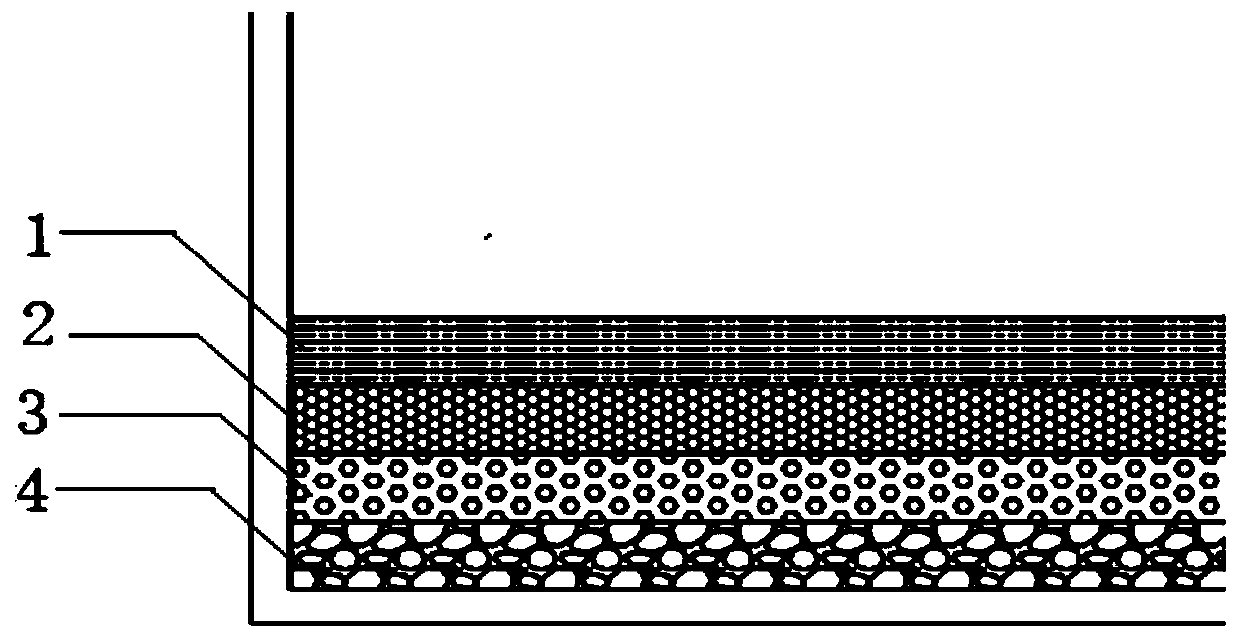
Domestication method for adapting scylla paramamosain seedlings to saline-alkali soil water area culture
A technology for simulating mud crabs and saline-alkali land, which is applied in the fields of climate change adaptation, application, fish farming, etc., can solve the problems of inability to widely promote and generate economic benefits, low survival rate of farming, etc., so as to improve the survival rate and increase economic effect of benefit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
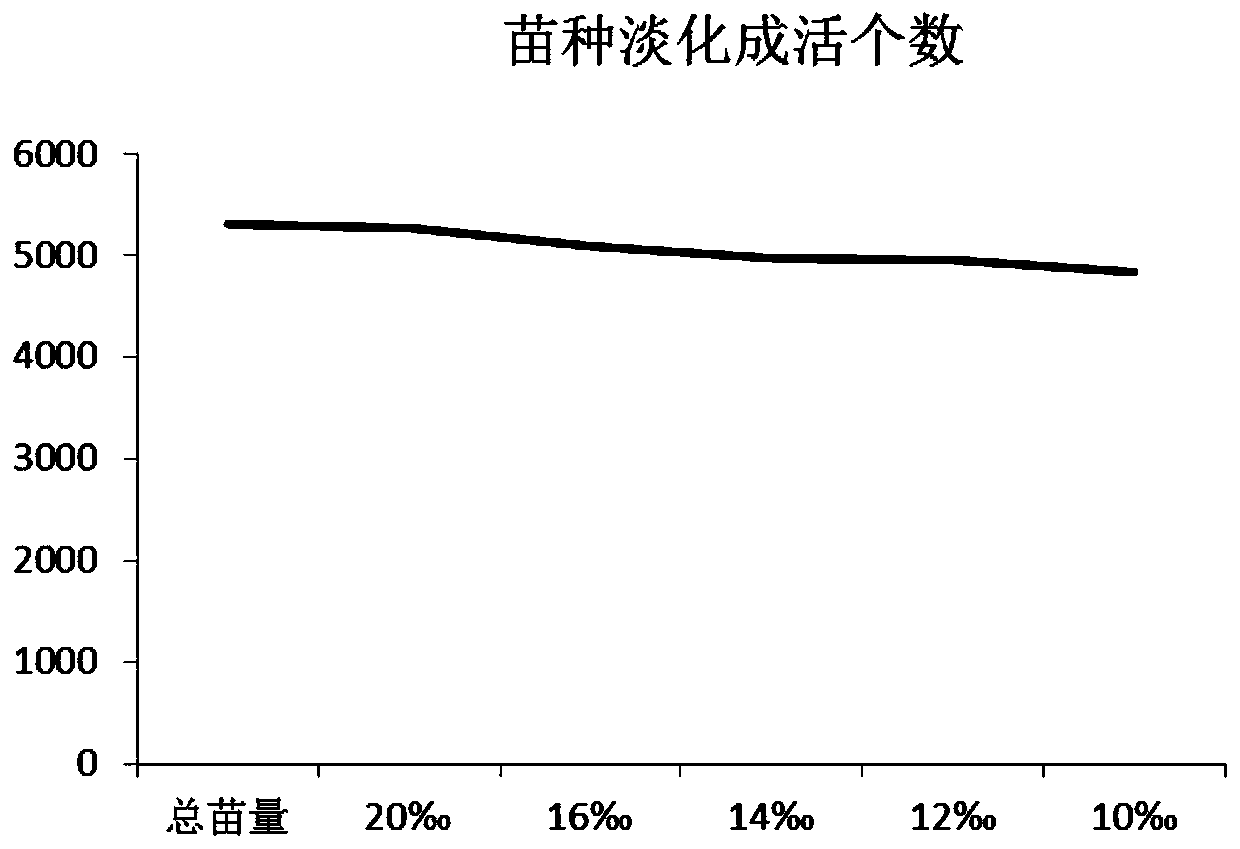
[0030] The pre-experiment was carried out with different developmental stages of mud crab seedlings, and it was found that the mortality rate of juvenile crabs at stage V was the lowest during the desalination process, so juvenile crabs at stage V were used for domestication. Taking the survival rate as the screening standard, the domestication method of the mud crab seedlings was finally determined, which also laid the foundation for the subsequent improvement of the survival rate of domesticated seedlings in low-alkalinity waters.
[0031] The high-efficiency domestication method of the large-scale seedlings (V stage juvenile crab) of the pseudo-cave blue crab suitable for cultivation in saline-alkali waters of alkalinity<10mM provided by the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0032] 1) Selection and disinfection of juvenile crab seedlings in stage V
[0033] Select stage V juvenile crabs with healthy limbs, strong physique, no disease, and strong vitality, a...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The domesticated crab seedlings are cultured in saline-alkali waters (7-8mM).
[0048] Salt-alkali domesticated crab seedlings are salvaged by aquatic plants and put into a foam box, shaken loose, and the foam box is covered with wet water sponge. The size of the foam box is 50cm×50cm. A small hole with a long (about 1 cM in size) is placed in the seedling shell, and 100 crab seedlings are placed.
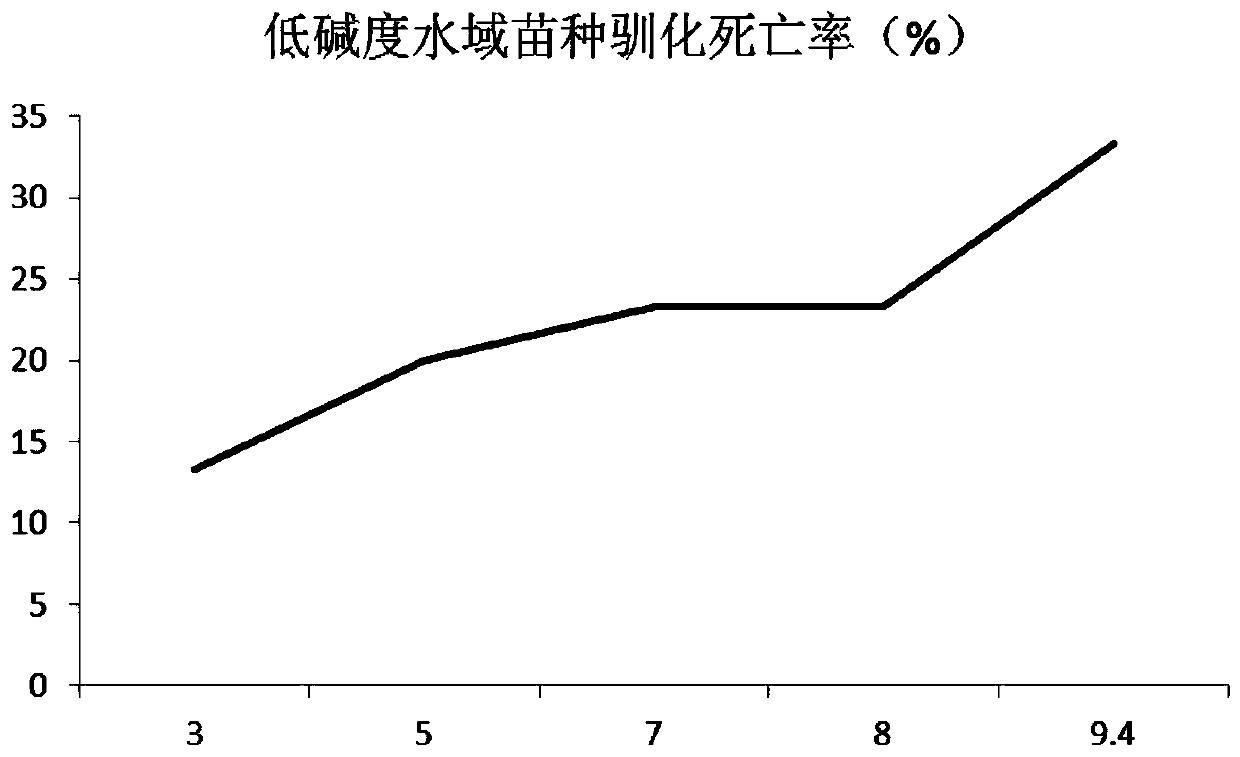
[0049] (7) Stocking of crab seedlings after domestication. In the process of alkalinity acclimatization, with the increase of alkalinity, the mortality rate increased, and when the alkalinity rose to 9.4mM, the mortality rate was 33.33% ( image 3 ), before putting the crab seedlings cultivated in salinization into the pond, pour part of the pond water into it, and then slowly pour it into the pond after adapting to the environment.
[0050] Compared with the cultivation of the salinity-alkalinity blue crab after domestication, the mortality rate of the crabs directly plac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com