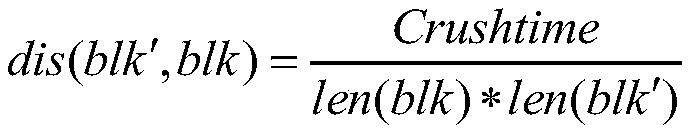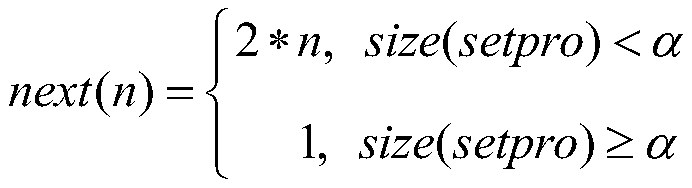Error code negotiation method of quantum key distribution system
A quantum key distribution and bit error technology, which is applied in the field of quantum communication, can solve problems such as reducing negotiation efficiency, and achieve the effects of improving negotiation efficiency, reducing collision phenomena, and increasing processing speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
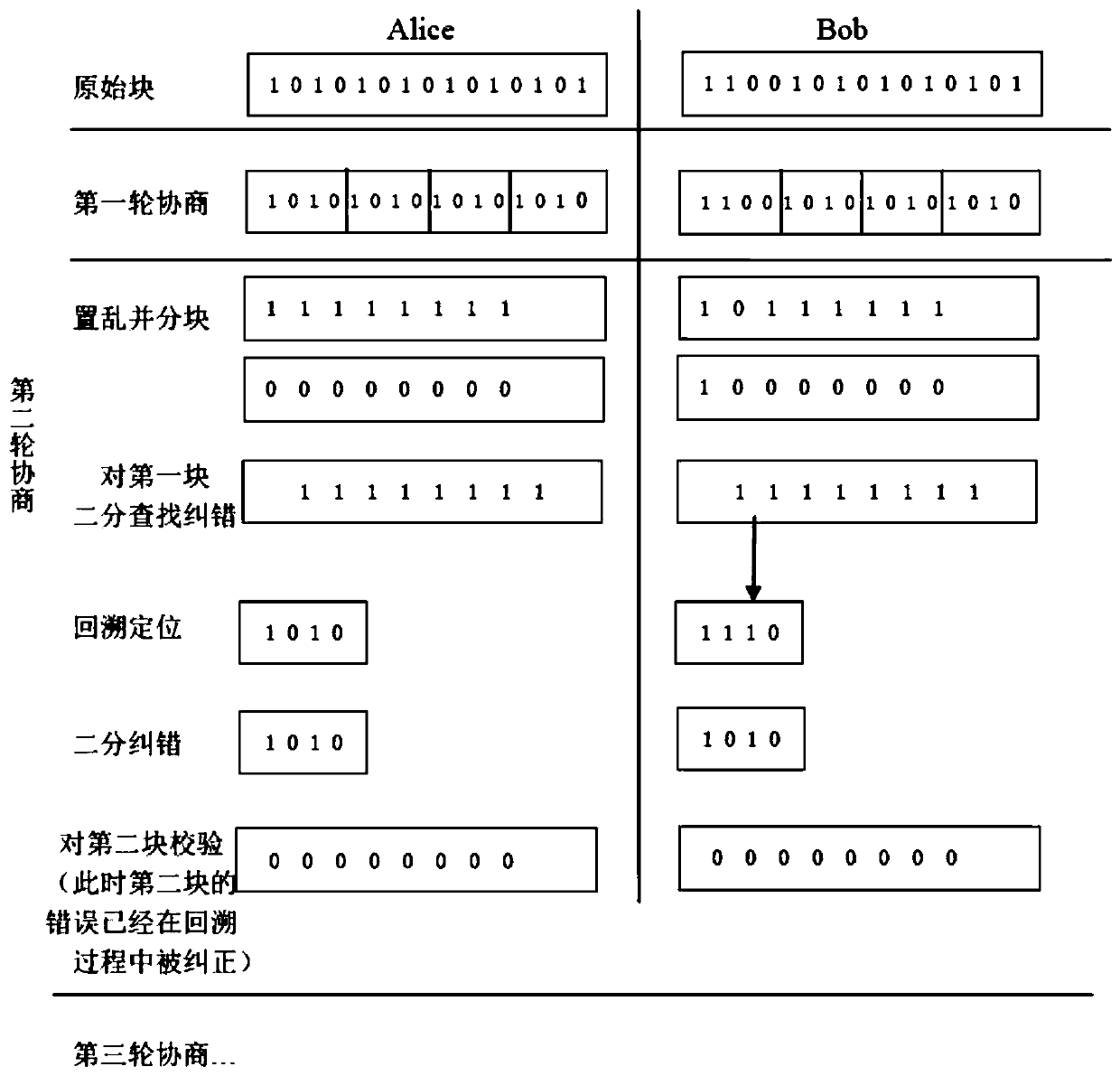
[0058] In the present embodiment, each frame is 64Kb long, and the bit error rate is 3%. 16 frames are set in parallel, α=64, and the negotiation process is:
[0059] 1) Determine the block length of each round according to the bit error rate. Here, the block length of the first round is 32, the block length of the second round is 256, and the 3rd-14th round is half of the entire data length, that is, 32Kb.
[0060] 2) In the first round, the data is divided into blocks according to the block length of 32, and binary search and error correction are performed on blocks with different parity checks. Since there is no backtracking in the first round, the processing is not related to other rounds. The first round works alone and provides data for the second round as data preprocessing.
[0061] 3) In the second round, Arnold scrambles the data of the first round of preprocessing according to 64Kb. The scramble table can be shared to save storage resources and placed in different f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com