SNP-based caps molecular markers for identification of single seeds of Palmer amaranthus, Amaranth amaranthus and Amaranthus sativus and its application
A molecular marker, Amaranthus amaranthus technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of hindering application, long detection time, high cost and high cost, and achieve the effect of accurate and effective identification method, accurate detection identification, and reliable detection method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
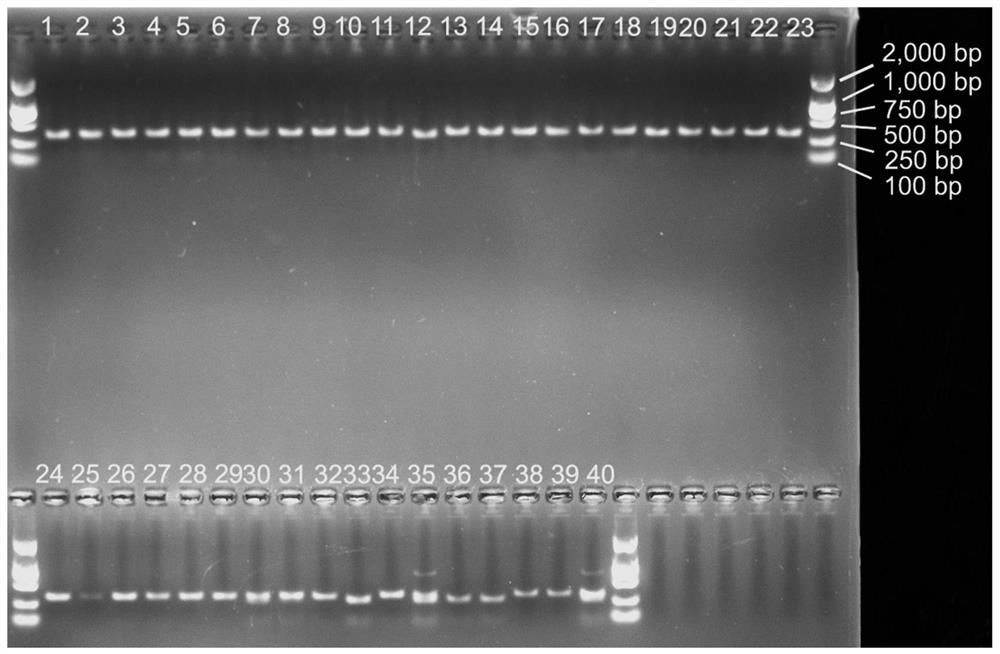
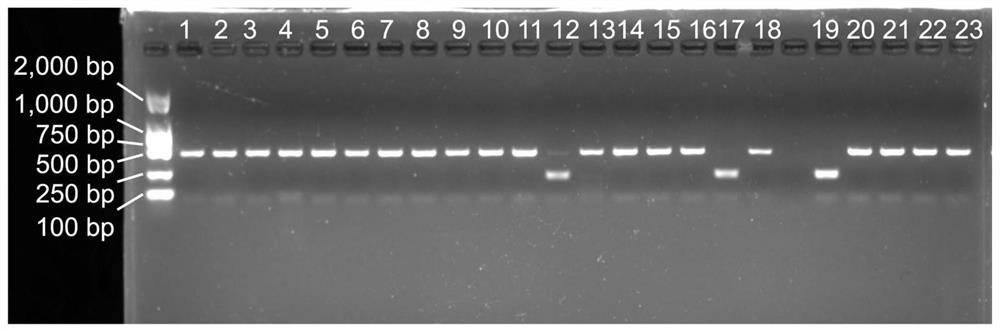
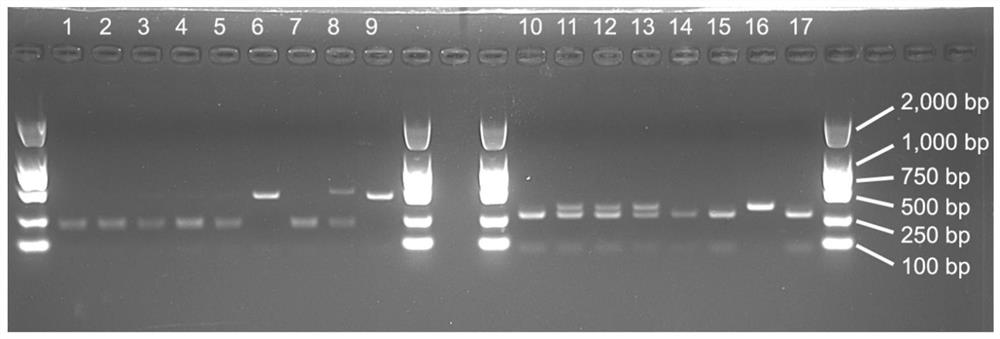
[0040] Example 1 SNP site and acquisition of SNP site-based CAPs molecular markers
[0041] By analyzing and aligning the sequences of 18S, ITS, 26S and other genes in 52 samples of 18 species of Amaranthus L., and analyzing their phylogenetic relationships and sequence differences, the results obtained for the distinction between Amaranthus amaranthus and Amaranthus amaranthus , SNP sites of Amaranthus serrata and other Amaranthus plants, wherein, the SNP site used to distinguish Amaranthus from other Amaranth plants is located at position 233 of the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. This site is A, and this site is C in other Amaranth species. The SNP site for distinguishing Amaranthus amaranthus / Amaranthus from other amaranth plants is located at the 200th position of the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. This site in plants is A / T.
[0042] The specific names and material sources of the 52 plant materials used for gene amplification and sequence analysis are shown in Table 1, and ...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Embodiment 2 The method for distinguishing and identifying the single seed of Amaranthus amaranthus, Amaranthus chinensis, Amaranthus serrata and other Amaranth plants
[0061] Utilize the CAPs molecular markers provided in Example 1 and their specific detection primers to identify Amaranthus amarantensis, Amaranth amaranthus, Amaranthus serrata, and the specific methods are as follows:
[0062] 1. DNA extraction
[0063] The single seed of the amaranth plant to be tested was ground and placed in a 1.5 ml centrifuge tube, and was then used in a water bath at 95° C. for 10 minutes with Lysase A, and then centrifuged for 2 minutes for use.
[0064] 2. PCR amplification
[0065] (1) Amplification of the CAPs molecular marker shown in SEQ ID NO.1
[0066] Using the DNA obtained in step 1 as a template, forward primer 78F: 5'-GTCCCTGCCCTTTGTACACA-3' and reverse primer 419R: 5'-GGGTTCGTTGTTGCATCGAG-3' were used for PCR amplification.
[0067] The PCR reaction system is cal...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Embodiment 3 Differentiation and identification of Amaranthus amaranthus, Amaranthus amaranthus, Amaranthus serrata
[0081] Taking the single seeds of 52 plant material samples shown in Table 1 as the sample to be tested, the method for distinguishing and identifying Amaranth, Amaranth serrata, Amaranth and other Amaranth plants provided in Example 2 was used to carry out Amaranth. , Distinctive identification of Amaranthus amaranthus and Amaranthus amaranthus seeds.
[0082] A mixed sample of single seeds of different plant materials in the 52 plant material samples shown in Table 1 was used as a control.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com