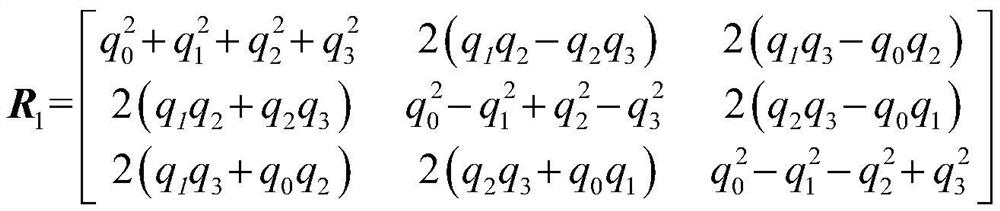A method for accurate alignment of parts based on pd-like algorithm combined with icp algorithm
An algorithmic and precise technology, applied in the computer and mechanical fields, can solve problems such as being unfavorable for algorithmic solution, reducing computational efficiency, and difficult to meet accurate alignment of parts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, a PD-like algorithm combined with an ICP algorithm for accurate part alignment method, including the steps of PD-like algorithm for rough registration and the ICP algorithm for fine registration;
[0060] The step of performing rough registration with the PD-like algorithm includes using the PD-like algorithm for rough matching of point cloud data, thereby providing an accurate initial position and attitude for the ICP algorithm;
[0061] The step of the ICP algorithm for fine registration includes the use of the ICP algorithm to fine-match the point cloud data to achieve the purpose of precise alignment.
[0062] The step of the rough registration of the PD-like algorithm is to use the machine learning algorithm of the PD-like adaptive step size adjustment to perform rough matching on the point cloud data.
[0063] The step of fine registration by ICP algorithm uses the ICP algorithm to fine match the matched point cl...
Embodiment 2
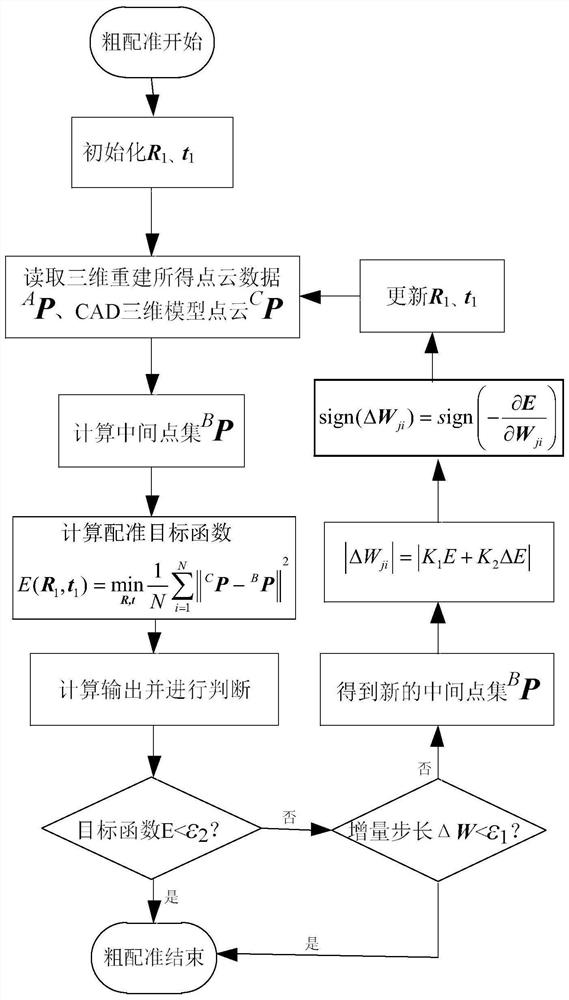
[0086] Embodiment 2: refer to figure 2 , a PD-like algorithm combined with an ICP algorithm for accurate parts alignment method, including the following steps;
[0087] The steps of the PD-like algorithm for rough registration also include the following:
[0088] Step 1), initialize the rotation matrix R 1 with the position vector t 1 .
[0089] Step 2), read the point cloud data obtained from 3D reconstruction A Point cloud data of P and computer CAD 3D model C P, calculate the registration objective function E(R 1 ,t 1 ).
[0090] Step 3), constructing the registration objective function Calculate the function output and expected error and get a new set of intermediate point cloud data sets B p.
[0091] Step 4), judging whether the objective function E is less than ε 1 , ε 2 , if less than ε 1 , ε 2 When the algorithm ends, the calculation result is output; otherwise, iterative learning is performed.
[0092] where ε 1 Indicates the expected error value, ε...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com