Wound dressing
A technology for wound dressings and polymer materials, applied in dressings, adhesive dressings, non-adhesive dressings, etc., which can solve problems such as easy adhesion to the injured surface, easy drift away from the wound, and large difference in the amount of wound exudate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
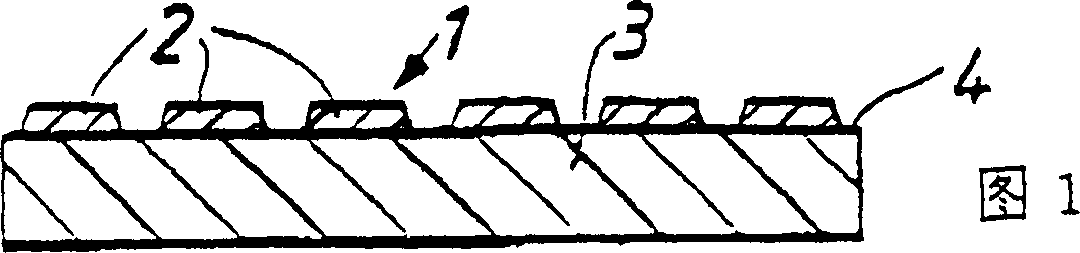
[0070] A solution containing 20% by weight of polyether polyurethane (ESTANE 5714F (trademark)) in a 60 / 40 (weight ratio) tetrahydrofuran / acetone mixture was cast into the groove of a 15 cm wide silicone sheet, where the The shape is a truncated square pyramid. The grooves are poured to a sufficient depth to provide individual truncated pyramids each about 60 μm thick and sink to the bottom of each groove after being dried by a hot air oven to remove the solvent.
[0071] The process of casting hydrophilic foam on the truncated polyurethane pyramid is as follows: Using a two-group dispensing device (Vario-mix provided by Prodef Engineering), the ratio of Hypol FHP 2002 and Brij 72 (2%) is 1:2.25. (Aqueous solution) mixed to make a foamed mixture. The foaming mixture is fed into the coating head through the output nozzle in the form of a 15cm fishtail template, and then coated with a roller coating head and a scraper above. The cast foam was passed through an air circulating oven...
example 2
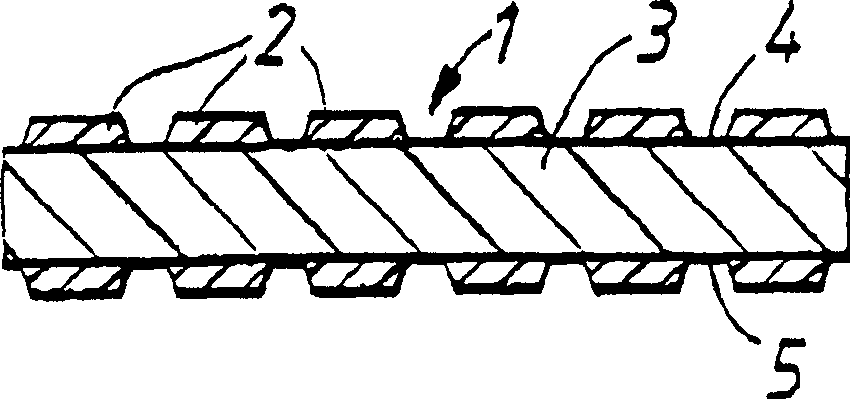
[0074] Two similar dressings were prepared according to the method described in Example 1. The difference is that before the foam has solidified, the two dressings are pressed on one side of the other, and a slight pressure is applied so that the two surfaces adhere to each other and become a dressing. , This dressing has bumps on both sides.
[0075] By sprinkling colored water on the surface of the dressing with bumps prepared in Example 1, the effectiveness of the dressing's expansion and contraction was investigated. I saw the water was quickly sucked into the hydrophilic foam, while the bumps moved away from each other, moving 100% of the original distance. After allowing the water to evaporate from the dressing, the bump returns to its original position.
example 3
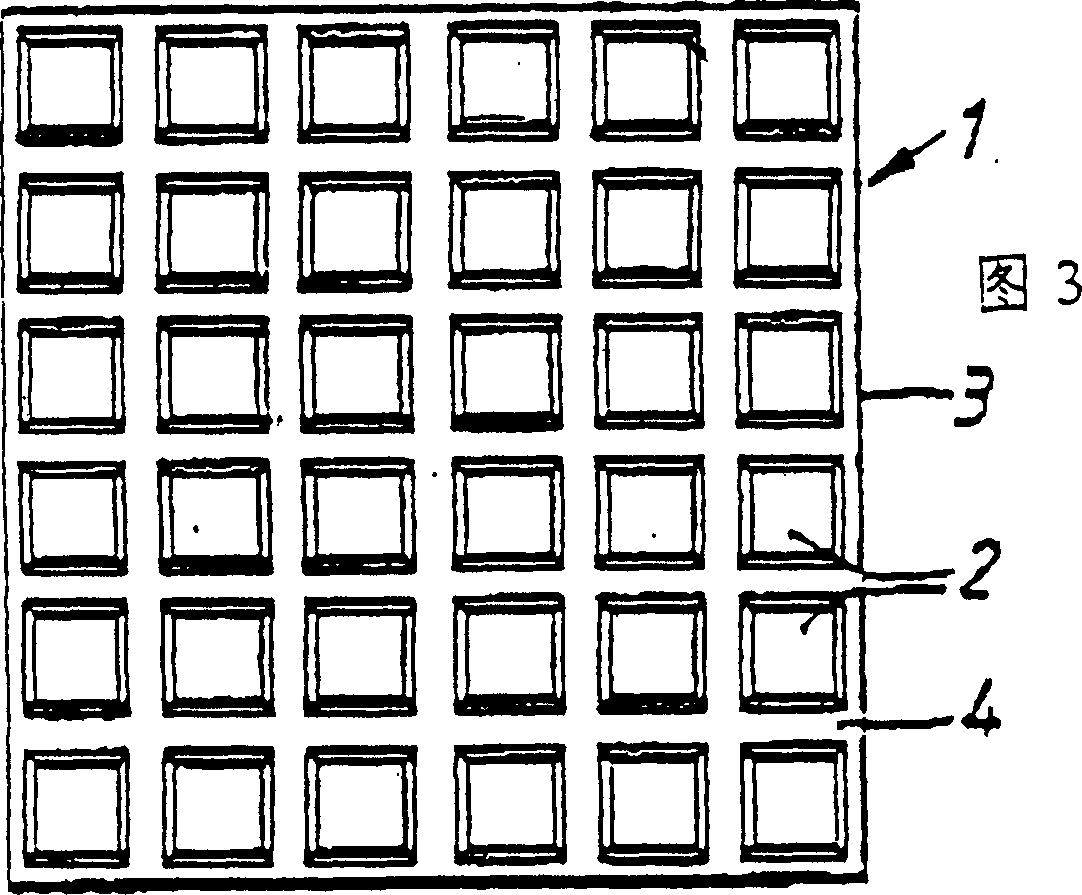
[0077] A layer of base film (175μm thick polypropylene) was coated with polyurethane (ESTANE5702) solution (35% dissolved in methyl ethyl ketone), and the square area of protrusions (3mm×3mm) on the film was divided by the recessed area of 1mm thickness. The coating layer is transferred to the surface of the foam in a water-absorbing (swelling) state. Let the foam dry at room temperature. The prepared dressing includes a layer of foam about 2 mm thick, with discontinuous square blocks of about 10 μm thick polyurethane film on the first surface.
[0078] When the dressing is placed on a wet surface, the dressing absorbs water and swells, allowing it to absorb more water and spread along the foam layer. When the wet surface dries to a certain point where there is only a small amount of residual moisture content, the foam dries and the bumps move closer to each other, and the surface can maintain a certain moisture content.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com