Treatment of immune diseases by administration of antigen-specific formulations
An antigen, disease technology, applied in the fields of medicine and immunology, which can solve problems such as low compliance and adherence rates, difficulty in defining exact antigen doses, long treatment regimens, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
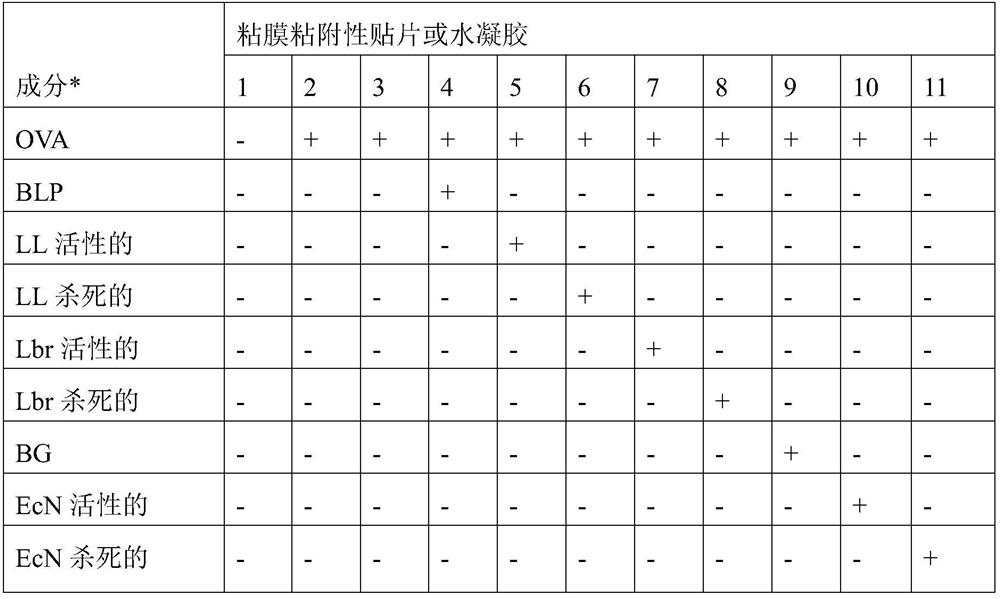
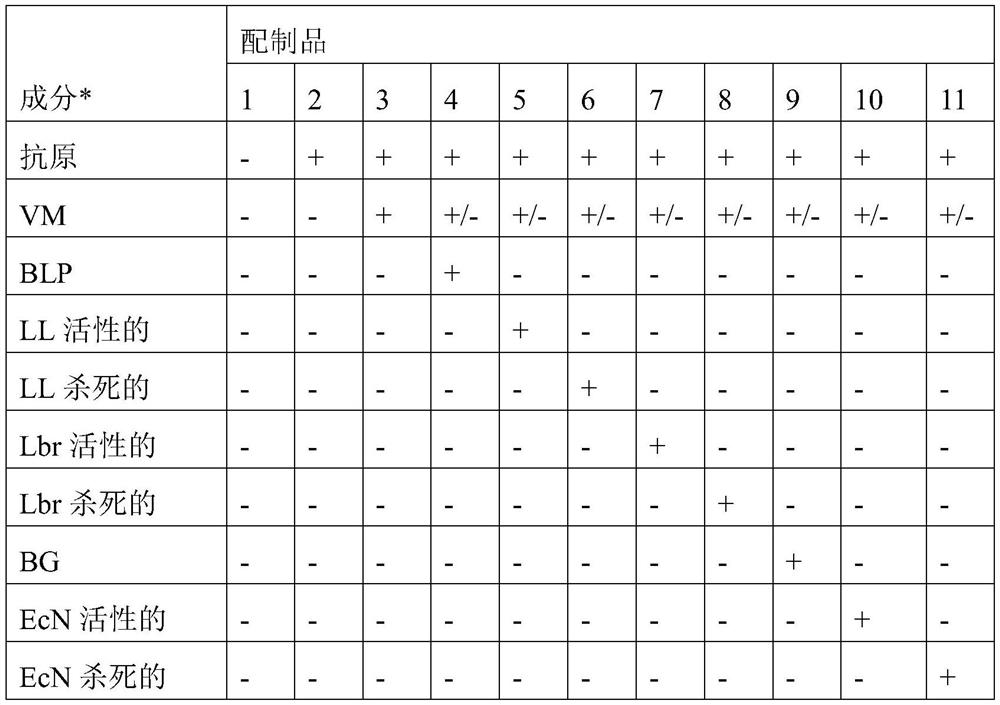
[0075] 1. A mucoadhesive carrier comprising non-living bacterial particles for administration in the oral mucosa to treat immune response-related diseases in a patient, wherein said non-living bacterial particles are associated with at least one of said immune response-causing Combination of antigens, and wherein said immune response-related disease is selected from the group consisting of celiac disease, allergic asthma, allergic rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis, atopic dermatitis, multiple sclerosis, type I diabetes, autoimmune uveal autoimmune thyroiditis, autoimmune myasthenia gravis, rheumatoid arthritis, pemphigus vulgaris, or food allergy.
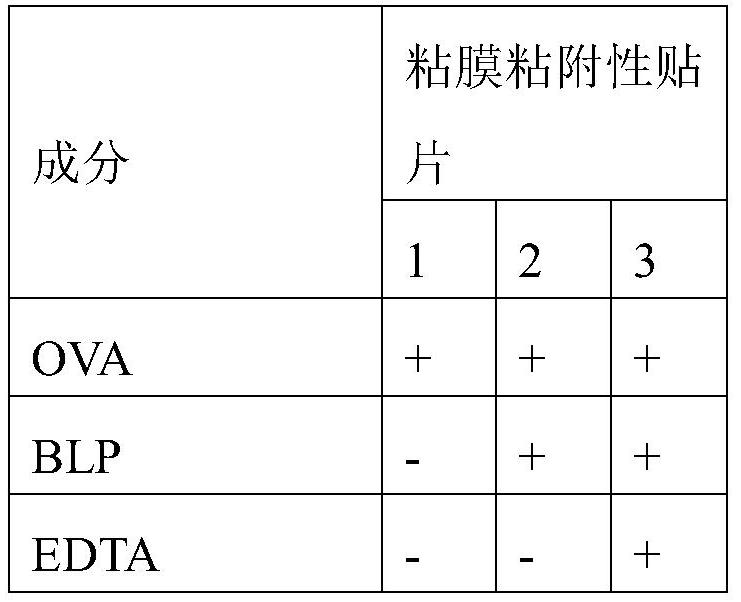
[0076] 2. A mucoadhesive carrier according to embodiment 1, wherein the carrier is a mucoadhesive patch, a biofilm or a hydrogel.
[0077] 3. A mucoadhesive patch according to embodiment 2, wherein said patch comprises electrospun fibers.
[0078] 4. A mucoadhesive carrier according to any one of embodiments 1 to 3, wherein the an...
Embodiment A1
[0092] Example A1: Determination of Loading in and In Vitro Release from Nanoreservoirs of Bacterial Particles
[0093] introduction
[0094] The ability to load BLP into prefabricated nanoreservoir layers made of different types of polymer fibers and to release BLP in vitro from these nanoreservoirs into buffers after drying was tested.
[0095] Materials and Methods
[0096] Bacterial particles: BLPs of Lactococcus lactis MG1363 were prepared essentially according to WO 02 / 101026.
[0097] Nanoreservoir layer: Using polycaprolactone (PCL, Mw 80,000 g / mol, Sigma Aldrich) or a mixture (1:1) of polycaprolactone and silk fibroin (PSF) polymers, by electrospinning Preparation of the nanoreservoir layer. Procedure as described by Masek et al. (2017, J Control Rel, 249:183-195). In this way, PCL and PSF nanoreservoir layers were obtained, in which the average pore size was about 5 μm.
[0098] Experimental setup: By placing a droplet on the surface of the reservoir layer, a 1 ...
Embodiment A2
[0103] Reservoir layers of PCL and PSF nanofibers can be used to load and release BLP, and the PSF nanoreservoir layer has the highest efficiency. Example A2: Determination of ex vivo release and penetration into oral mucosal tissues from mucoadhesive patches or hydrogels of bacterial particles combined with antigens
[0104] introduction
[0105] Tested in realistic conditions (mucosal tissue surface wetted with limited amount of water, typical mucus layer, etc.) In, the ability of mucoadhesive patches and hydrogels to target and release associated bacterial particles formulated with antigens. The release of bacterial particles formulated with antigen from mucoadhesive patches and hydrogels in a separate experiment was studied by confocal microscopy of fluorescent signals measured in cross-sections of adjacent tissues.
[0106] Materials and Methods
[0107] Bacterial particles: BLP of Lactococcus lactis MG1363 and BG of Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 were prepared essential...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com