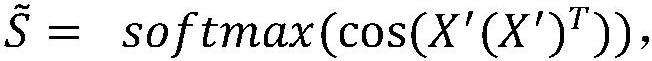Unsupervised graph representation learning method and device on large-scale attribute graph based on sub-graph sampling
A large-scale attribute and learning method technology, applied in the information field, can solve the problems of limited scalability, lack of node attribute information and utilization of high-level structure information on the graph, so as to improve scalability, enhance scalability, Node vectors representing valid effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0037]In order to make the above objects, features and advantages of the present invention more comprehensible, the present invention will be further described in detail below through specific embodiments and accompanying drawings.
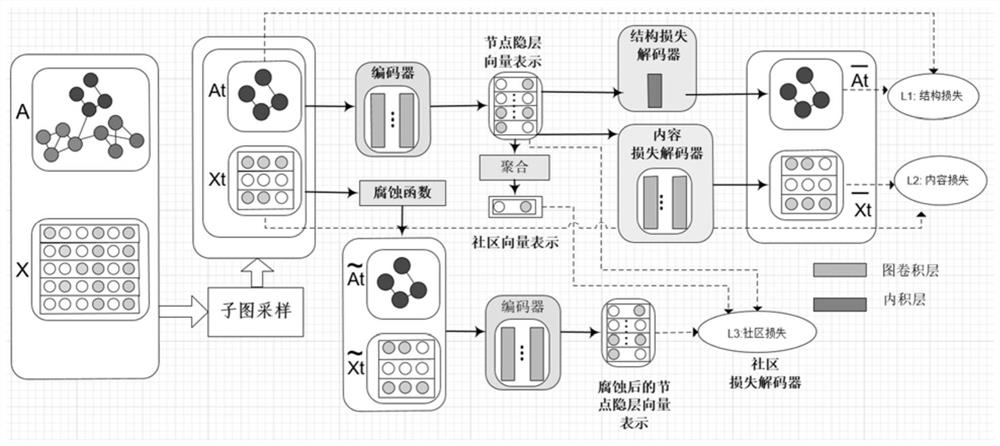
[0038] This patent uses a graph neural network to learn a low-dimensional vector representation of nodes in an attribute graph under an unsupervised setting. In order to improve the scalability of the algorithm, for large graphs, this patent uses the method of subgraph sampling to reduce the scale of training data. The subgraph sampling method comprehensively considers the structural information and node attribute information of the graph, making the sampled subgraph more efficient. Reasonable. In order for the network to comprehensively utilize the structural information of the graph, the node attribute information, and the community information on the graph during the learning process, a loss function related to the above three information is de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com