Water supply pipe network pipeline roughness coefficient and joint water demand synchronous self-adaptive checking method
A technology of roughness coefficient and water supply pipe network, which is applied in pipeline systems, measuring devices, measuring fluid pressure, etc., can solve the problems of low convergence rate, unmeasurable monitoring value error, and less research on checking the two parameters.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
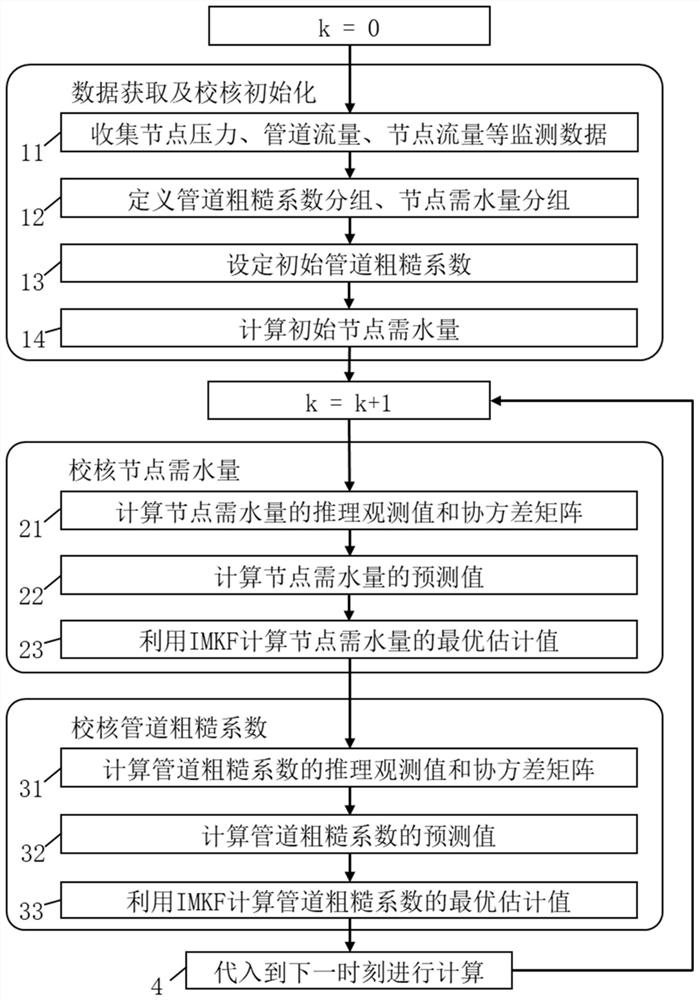
[0100] Such as figure 1 As shown, a water supply network pipeline roughness coefficient and node water demand synchronous self-adaptive calibration method, the method includes the following steps:
[0101] (1) Collect water supply network monitoring data and initialize the self-adaptive calibration process;
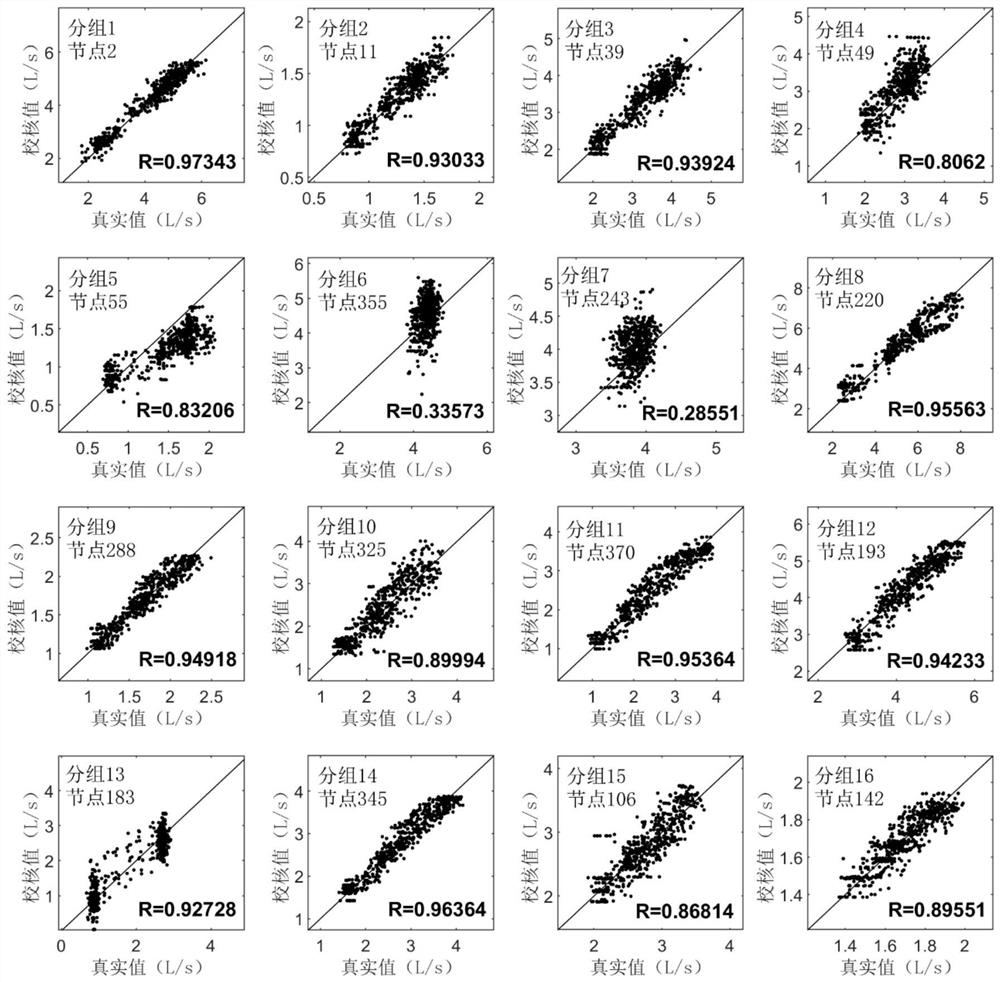
[0102] (2) Based on the monitoring data of the water supply network, calculate the inference observation value of the node water demand at the current moment, and substitute it into the inference observation Kalman filter (IMKF) to calculate the optimal estimated value of the node water demand at the current moment;
[0103] (3) Calculate the inference observation value of the pipeline roughness coefficient at the current moment based on the monitoring data of the water supply network, and substitute it into the inference observation Kalman filter (IMKF) to calculate the optimal estimate value of the pipeline roughness coefficient at the current moment;
[0104] (4) Subs...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com