Time sequence network immunization method based on random walk
A random walk and time series network technology, applied in the field of social network and control of disease spread, can solve the problem of imbalance between immune cost and immune effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
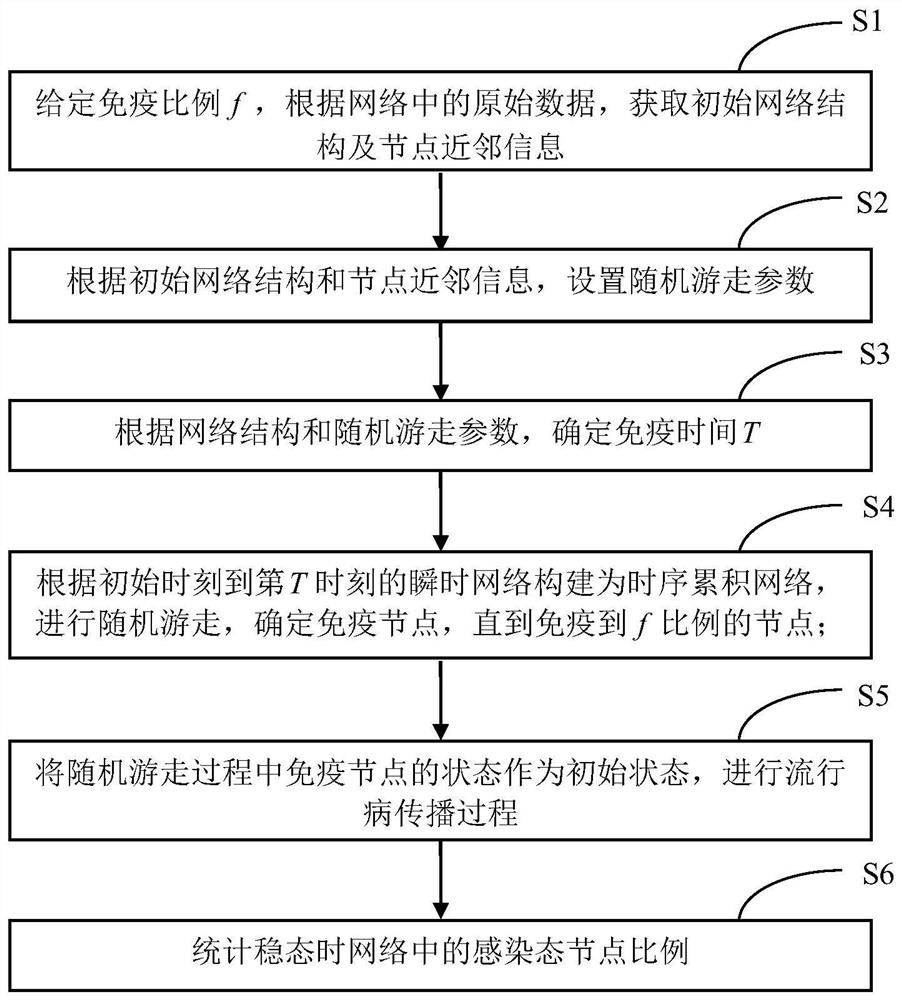
[0065] see figure 1 , a sequential network immune method based on random walk, applied to the sequential network, the operation steps are as follows:
[0066] Step S1: Given the immune ratio f, obtain the network structure and node neighbor information according to the original data in the network;
[0067] Step S2: Set random walk parameters according to the initial network structure and node neighbor information;
[0068] Step S3: Determine the immune time T according to the network structure and random walk parameters;
[0069] Step S4: According to the instantaneous network from the initial moment to the Tth moment, construct a time-series accumulation network, perform random walk, and determine the immune nodes until the immune nodes reach the proportion of f;
[0070] Step S5: Take the state of the immune node during the random walk as the initial state, and carry out the epidemic propagation process;
[0071] Step S6: Calculate the proportion of infected nodes in the...
Embodiment 2
[0074] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and the special features are as follows:
[0075] In the step S1, the method for obtaining network structure and node neighbor information includes:
[0076] Step S1.1: Assign an activity factor a∈(0,1) to all nodes in the network, and the activity follows a power-law distribution with a given power exponent γ: F(a)∝a -γ ;
[0077] Step S1.2: At each moment, all nodes in the instantaneous network are activated with their own activity factor a, which is called an active node; the activated node generates m edges to connect other nodes. Inactive nodes cannot actively send edges, but can receive connected edges; in the entire network construction, self-loops and repeated connections are not allowed;
[0078] Step S1.3: The duration of all connected edges in the network is Δt;
[0079] Step S1.4: After Δt time, delete all connected edges in the network;
[0080] In the step S2, the random walk parameters include: th...
Embodiment 3
[0106] This embodiment is basically the same as the above-mentioned embodiment, and the special features are as follows:
[0107] A sequential network immune method based on random walk, applied to the sequential network, the operation steps are as follows:
[0108] Step S1: This step is the same as the second embodiment;
[0109] Step S2: This step is the same as the second embodiment;
[0110] Step S3: This step is the same as the second embodiment;
[0111] Step S4: This step is the same as the second embodiment;
[0112] Step S5: Use the state of the immune node during the random walk as the initial state to simulate the epidemic spreading process, including:
[0113] Step S5.21: Select p 0 Proportional nodes are used as infected nodes;
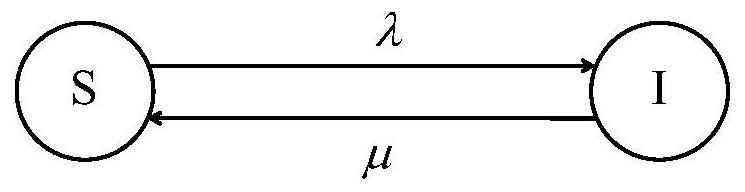
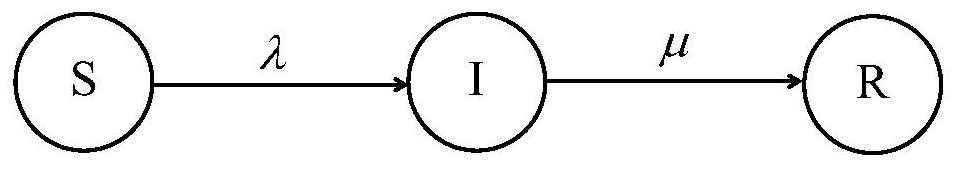
[0114] Step S5.22: using the "susceptibility-infection-recovery" (SIR) transmission model to simulate the virus transmission process;
[0115] Step S5.23: At each moment, the instantaneous network evolves according to the rules of s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com