Coroutine processing and management method based on interrupt reentry mechanism
A processing method and coroutine technology, applied in the computer field, can solve problems such as large thread resource consumption, complex programming model, and no support for high-availability features of programs, and achieve the effect of low thread resource consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
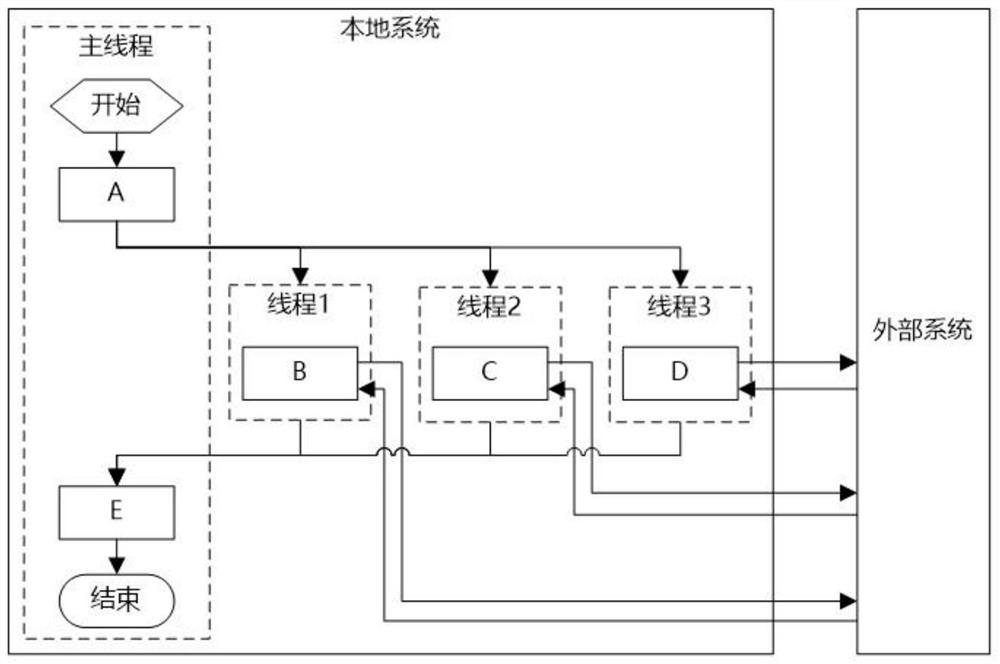
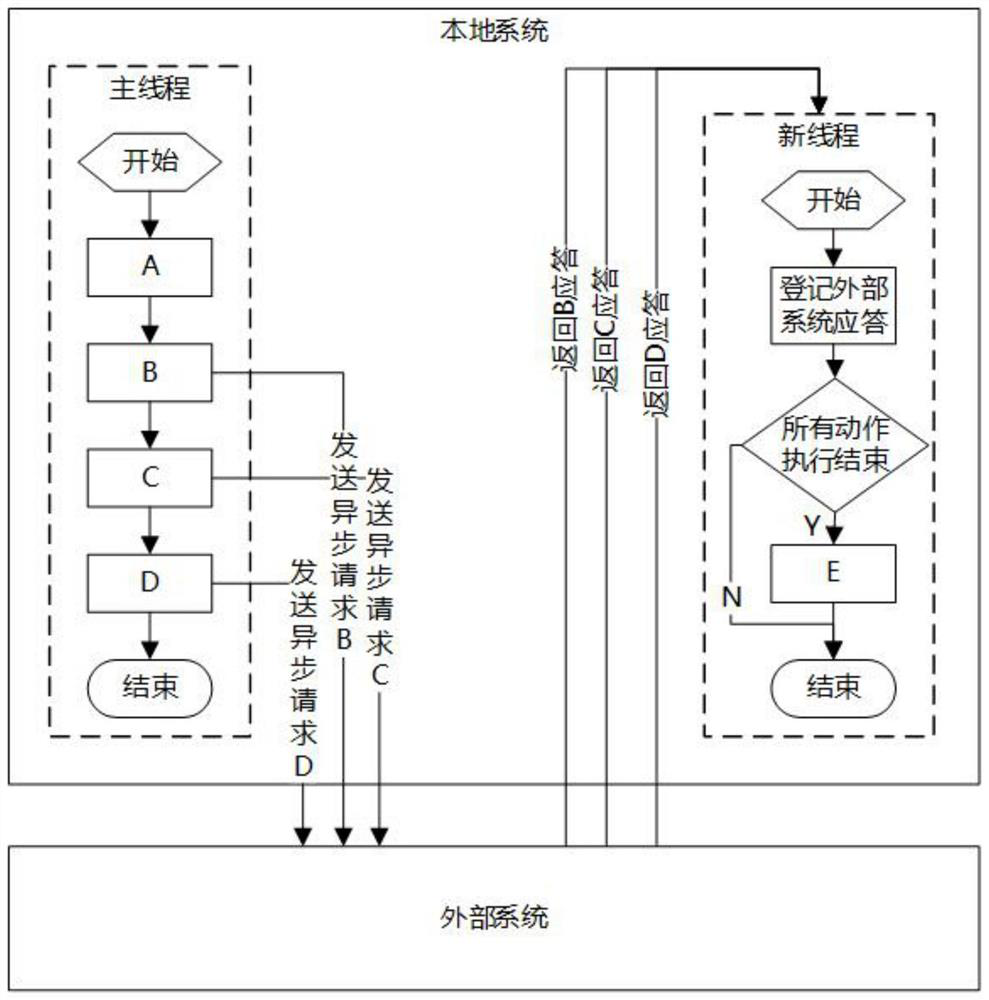
[0060] A coroutine processing method based on an interrupt reentry mechanism. The coroutine includes a main coroutine and a sub-coroutine. The interrupt reentry steps include:
[0061] S1: The main coroutine throws an interrupt request, and the underlying framework of the main coroutine responds to the interrupt request and sends the task request asynchronously;
[0062] S2: Switch to the external system processing logic, and the main coroutine releases thread resources;
[0063] S3: The task request response executes the reentrant sub-coroutine through the callback interface, and restores the context state at the time of interruption;
[0064] S4: The sub-coroutine continues to process subsequent logic until the execution ends and the thread resources are released; or the sub-coroutine throws an interrupt request as the new main coroutine, and repeats the above steps S1 to S4.
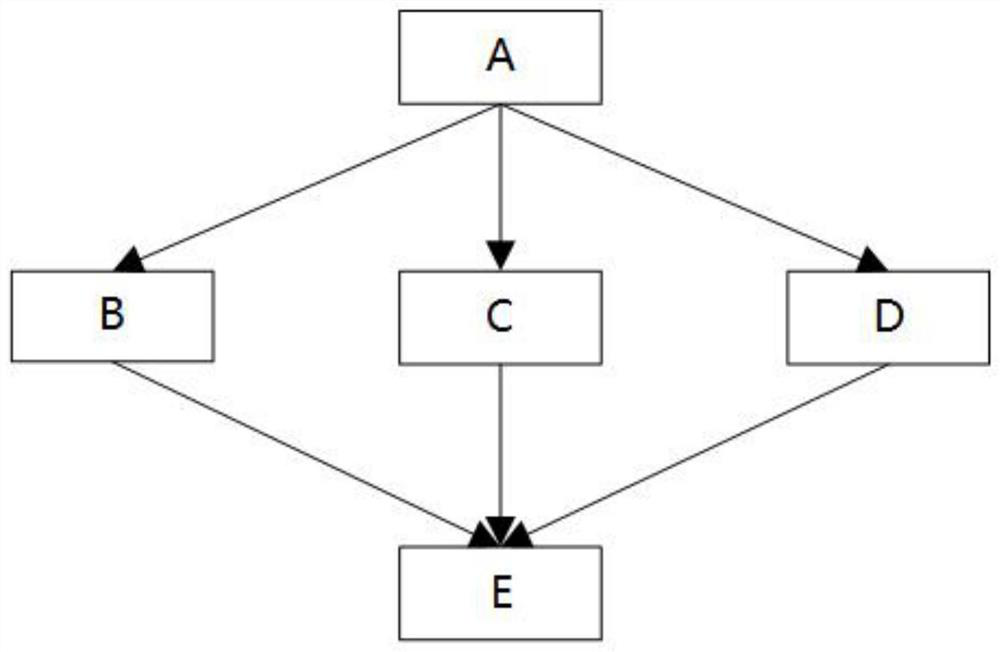
[0065] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the main coroutine executes the PartA action and throws an in...
Embodiment 3
[0092] Such as Figure 11 As shown, a coroutine management method based on the interrupt reentrant mechanism, the coroutine described in Embodiment 1 is combined into an application, the coroutine includes a coroutine identifier, an interrupt identifier isInterrupted and a memory, and the application operation includes a start processing interface Process() and multiple reentry processing interface Resume() calls, including application entry OnProcess(), start processing interface Process() and reentry processing interface Resume() are executed by calling application entry OnProcess() Logic, the application entry OnProcess() includes the CallBatch() interface described in Embodiment 1; before calling the application entry OnProcess(), the application entry OnProcess() is invoked by traversing the set of coroutines of the application.
[0093] Looping through the application's collection of coroutines involves the following steps:
[0094] 1. Execute the while loop to traverse t...
Embodiment 4
[0110] Apply the method for processing coroutines based on the interrupt reentry mechanism described in Embodiment 1 and the method for managing coroutines based on the mechanism of interrupt reentry described in Embodiment 3 to process the case of batch wage payment transactions during the day.
[0111] The transaction processing process includes 3 steps: file reading and warehousing —> wage payment —> result file generation. The data scale to be processed in the file may be relatively large (ranging from tens of thousands to millions). In order to improve transaction processing performance on the basis of efficient use of thread resources, these three steps are arranged in the batch salary payment scheduling application (executed based on the scheduling system). When step 2 is executed, we will The data is divided into blocks, and each block corresponds to a batch batch processing task (executed based on the batch processing system). In this way, all batch processing task re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com