A Navigation Path Modeling and Shortest Path Solving Method Based on Convex Hull Features
A shortest path and navigation path technology, applied in the field of intelligent transportation, it can solve the problems of reduced path solving speed, reduced computing efficiency, and increased number of nodes and edges.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
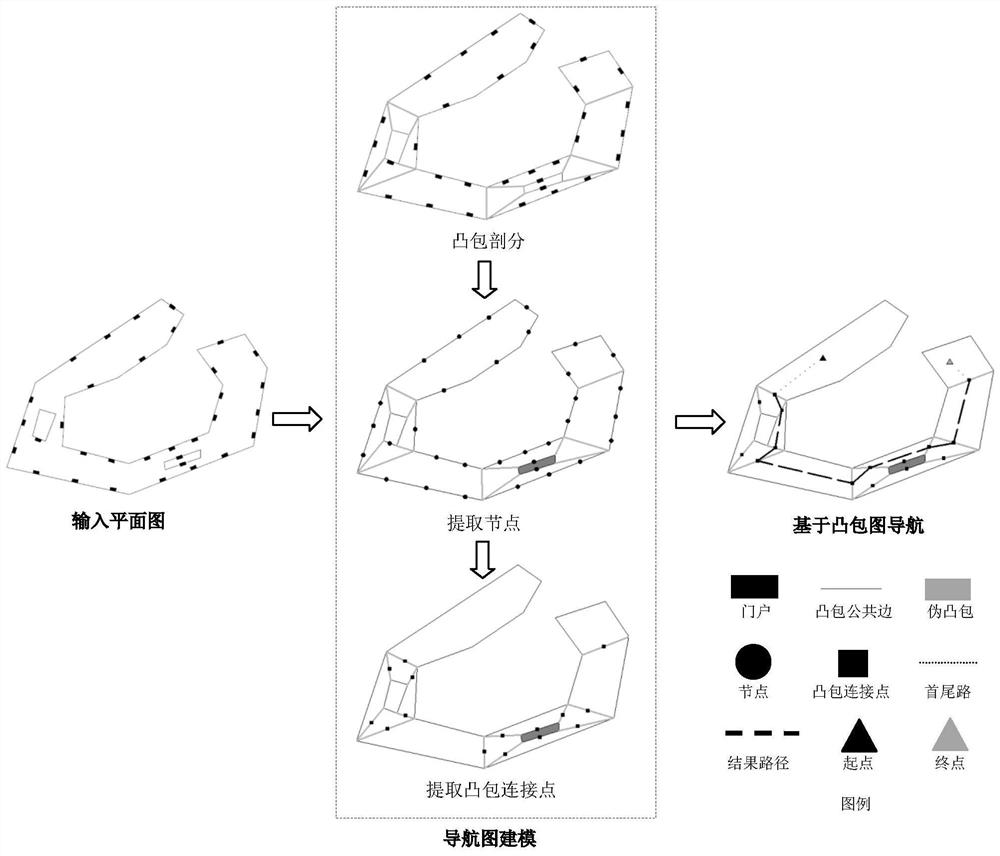
[0026] like figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a navigation path modeling and shortest path solution method based on convex hull features, which mainly includes the following steps:
[0027] 1) Space division based on holes
[0028] Compared with the input floor plan, the polygonal areas such as local rooms and counters are regarded as holes, and the convex polygon space with holes is divided into the entire free space to form a convex hull set, which is expressed as:
[0029] C={c i |i∈n}
[0030] c i is a convex polygon; n is the number of convex polygons.
[0031] If a hole in space contains several portals and the portals belong to different convex hulls, the hole is recorded as a pseudo-convex hull.
[0032] 2) Node extraction
[0033] Using the convex polygon space partition map constructed in step 1), for each convex polygon, each portal is recorded as a node, which is expressed as:
[0034] V={v i |i∈n}
[0035] where, v i is a node, expressed ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com