Conductive substrate and electrochromic device
A technology of electrochromic devices and conductive substrates, applied in instruments, nonlinear optics, optics, etc., can solve problems such as uneven discoloration of electrochromic devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
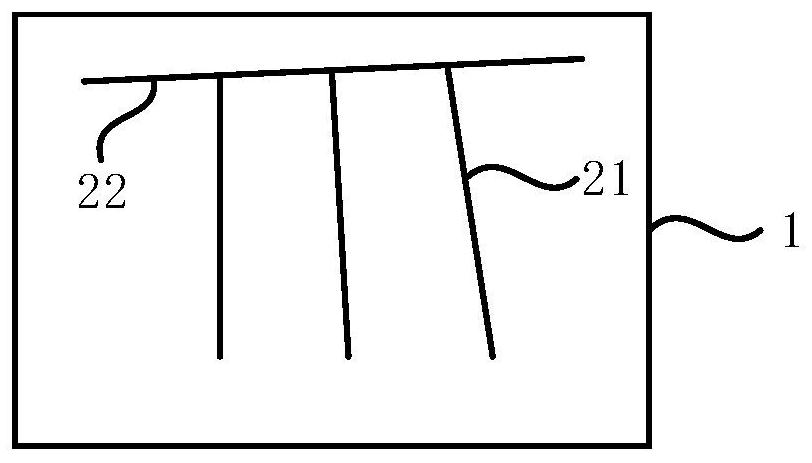
[0051] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a conductive substrate, the conductive substrate includes: a base layer, a conductive layer, and a wiring layer; wherein, the conductive layer is disposed on the base layer; the wiring layer is disposed on the conductive layer, and the wiring layer includes The first conductive circuit arranged in the first direction and the second conductive circuit arranged in the second direction, such as figure 1 As shown, the first conductive circuit 21 extends inward from the edge of the conductive layer 1 , the second conductive circuit 22 is disposed on the edge of the conductive layer 1 , and the first conductive circuit 21 and the second conductive circuit 22 are electrically connected.
[0052] Wherein, the base layer may be a transparent base, and is an optical grade transparent material, specifically, a flexible base material, including polyester film (Polyester Film, PET), cycloolefin copolymer, or cellulose triacetate. The cond...
Embodiment 2
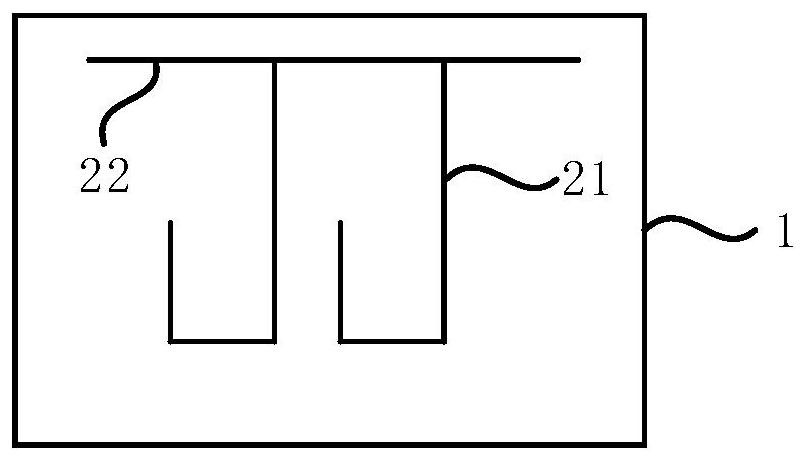
[0062] Embodiment 2 of the present invention provides a conductive substrate. The technical solution of this embodiment is further refined on the basis of the technical solution of the above embodiment, optionally, such as Image 6 As shown, the wiring layer further includes: an extraction structure 23 electrically connected to the second conductive circuit 22 . Specifically, the material of the lead-out structure 23 can be the same as that of the second conductive circuit 22, and the shape can be L-shaped, I-shaped, T-shaped, etc., connected to the second conductive circuit 22, or a structural extension of the second conductive circuit 22, When applied to an electrochromic device, it can be used to replace the second conductive line 22 to connect with the lead-out electrode, thereby avoiding damage to the second conductive line 22 and reducing the difficulty of welding. Optionally, there is only one lead-out structure 23 , which can be connected to one end or the center of t...
Embodiment 3
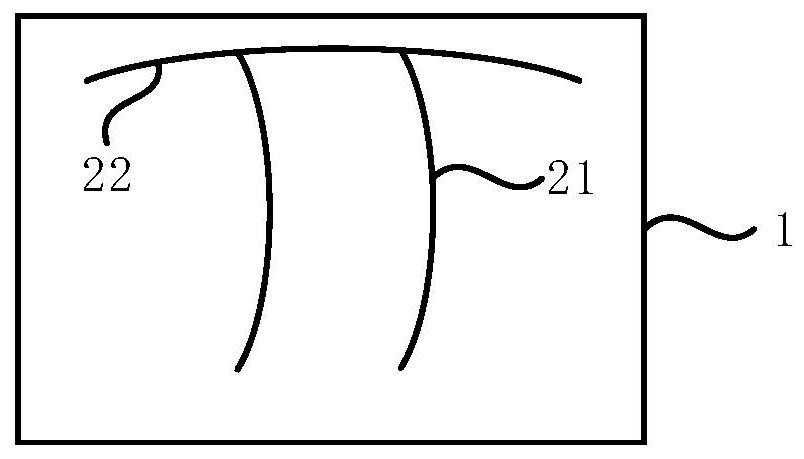
[0066] Embodiment 3 of the present invention provides a conductive substrate. The technical solution of this embodiment is further refined on the basis of the technical solution of the above embodiment, optionally, such as Figure 9 As shown, the end of the first conductive circuit 21 includes bifurcated structures 211 arranged symmetrically. Specifically, since when applied to an electrochromic device, the end of the first conductive line 21 usually does not diffuse the discolored area outwards in a rectangle, but diffuses in a circular arc shape, even if it has been completed in other aspects Optimizing, there will always be a region where the discoloration is always slow in the non-overlapping part of the rectangle and the arc shape. Therefore, by setting the end of the first conductive line 21 as a symmetrical bifurcated structure 211, the slow discoloration can be effectively reduced. area, thereby further improving the uniformity of the overall discoloration. preferred...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com