Industrial two-layer fabric
A double-layer fabric, industrial technology, applied in the direction of fabrics, multi-strand fabrics, textiles, etc., can solve the problems of fiber, filler shedding, excessive surface space, penetration, etc., to meet rigidity, reduce water retention, and improve dehydration. sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
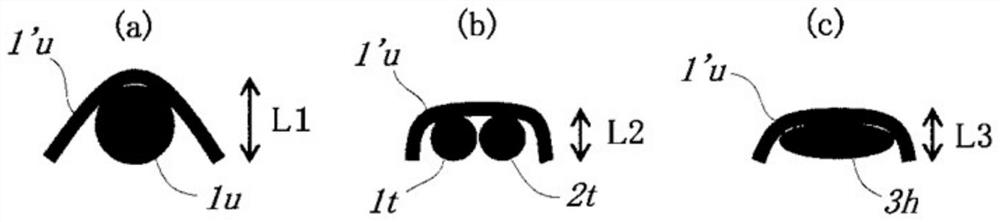
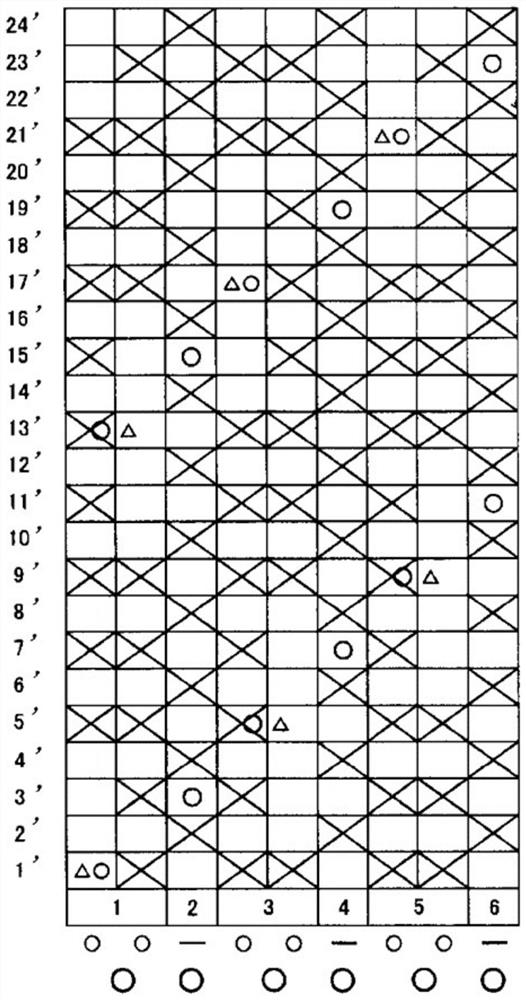
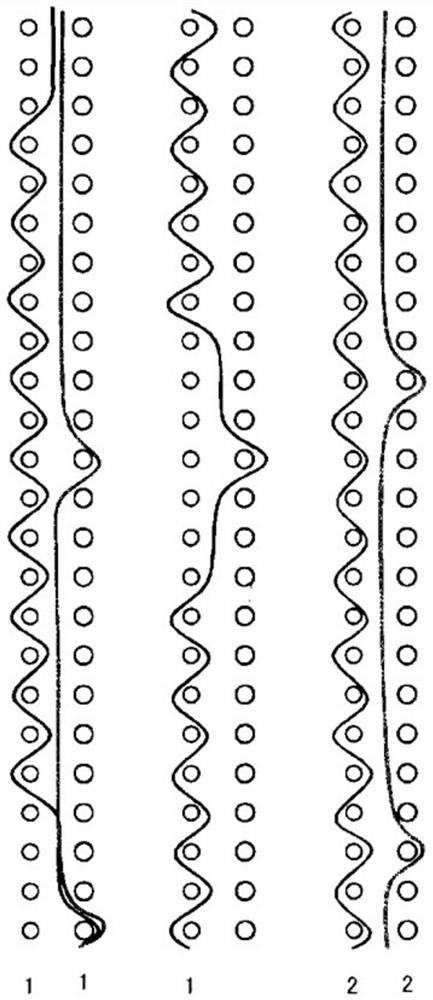
[0059] figure 2 It is a design drawing of Embodiment 1 of the industrial two-layer fabric of this invention. image 3 It is a partial side view arrangement diagram of Embodiment 1 of the industrial two-layer fabric of this invention. The first weave in Embodiment 1 is constituted by a set of two upper warp yarns and one lower warp yarn. The upper warp yarns in the first weave are formed of warp binding yarns having a function of binding the upper fabric and the lower fabric. In addition, a set of two upper warp yarns forming the first weave is arranged adjacent to each other to form a partial double flat weave on the surface of the upper weave. In addition, the second weave is constituted by one upper warp yarn and one lower warp yarn. The upper side warp yarns in the second weave are formed of flat warp yarns. Additionally, if figure 2As shown, the first tissue 1, 3, 5 and the second tissue 2, 4, 6 are arranged adjacently and alternately. Furthermore, the diameter of ...
Embodiment approach 2
[0065] Figure 4 It is a design drawing of Embodiment 1 of the industrial two-layer fabric of this invention. Figure 5 It is a partial side view arrangement diagram of Embodiment 2 of the two-layer fabric for industrial use of the present invention. The first weave in Embodiment 2 is constituted by a set of two upper warp yarns and one lower warp yarn. The upper warp yarns in the first weave are formed of warp binding yarns having a function of binding the upper fabric and the lower fabric. In addition, a set of two upper warp yarns forming the first weave is arranged adjacent to each other to form a partial double flat weave on the surface of the upper weave. In addition, the second weave is constituted by one upper warp yarn and one lower warp yarn. The upper side warp yarns in the second weave are formed of flat warp yarns. Additionally, if Figure 4 As shown, the first tissue 1, 3, 5 and the second tissue 2, 4, 6 are arranged adjacently and alternately. Furthermore,...
Embodiment approach 3
[0072] Image 6 It is a design drawing of Embodiment 3 of the industrial two-layer fabric of this invention. Figure 7 It is a partial side view arrangement diagram of Embodiment 3 of the two-layer fabric for industrial use of the present invention. The first weave in Embodiment 3 is constituted by a set of two upper warp yarns and one lower warp yarn. The upper warp yarns in the first weave are formed of warp binding yarns having a function of binding the upper fabric and the lower fabric. In addition, a set of two upper warp yarns forming the first weave is arranged adjacent to each other to form a partial double flat weave on the surface of the upper weave. In addition, the second weave is constituted by one upper warp yarn and one lower warp yarn. The upper side warp yarns in the second weave are formed of flat warp yarns. Additionally, if Image 6 As shown, the first tissue 1, 3, 5 and the second tissue 2, 4, 6 are arranged adjacently and alternately. Furthermore, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com