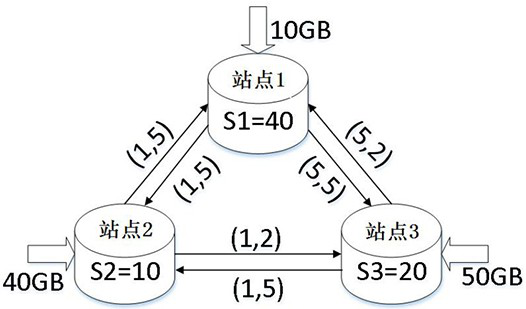
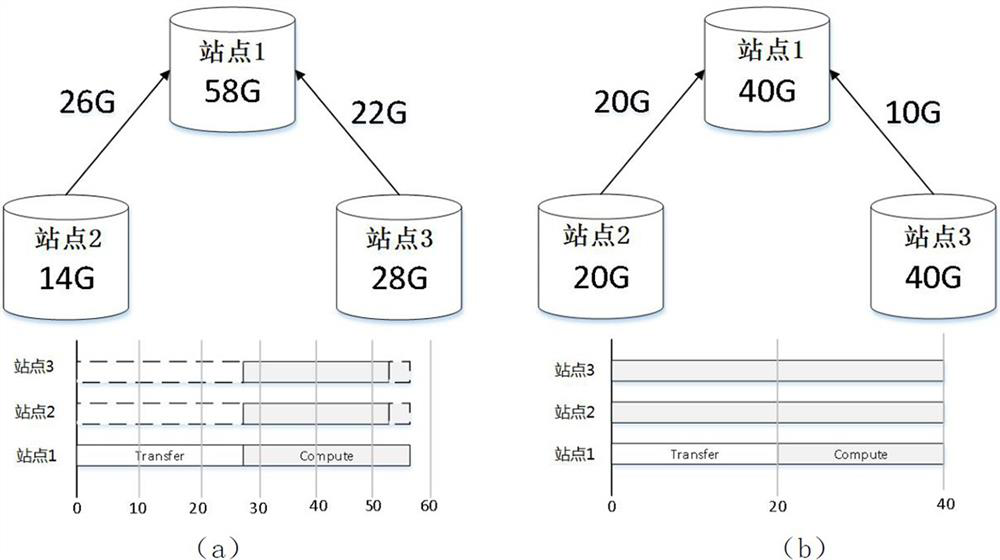
A method and system for accelerating data distributed processing across multiple data centers
A distributed processing, multi-data technology, applied in the field of data analysis, can solve problems such as insufficient consideration of site heterogeneity, and achieve the effect of reducing job processing time, accurate time estimation, and job response time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0205] This example evaluates the performance of SDTP by comparing SDTP with several classical task placement methods in terms of average response time and average slowdown, mainly by reducing average response time and average slowdown compared to various methods to draw conclusions. Among them, slowdown is defined as the response time reduction rate of a single job compared to other methods. For example, the response time for job A using In-Place is , the response time of job A using SDTP is ; so the slowdown for job A compared to using the In-Place response time is . Average slowdown is the sum of all slowdowns for each job divided by the number of jobs.
[0206] Figure 9 (a) shows the SDTP improvement in average job response time with different number of sites. Clearly, SDTP significantly outperforms other benchmark methods. In particular, when the number of sites is 10, the method of the present invention reduces the average job response time of all job types by...
Embodiment 2
[0214] This example will quantify the impact of various parameters on SDTP, including and count the number of instances, is the ratio of the amount of intermediate data to the input data import stage.
[0215] Figure 12 (a) depicts Impact. The figure indicates the different The response time of the value is the same as ratio, where Yes response time. It can be seen that the job response time increases with increases with the increase. This is because the larger More intermediate data will be generated. Both transmitting this intermediate data during the shuffle phase and processing it during the reduce phase may increase the overall response time.
[0216] Figure 12 (b) illustrates the difference compared to In-Place, Iridium and Tetrium The reduction in the average response time of the value. It can be observed that as q increases, the decrease in mean response time increases compared to Tetrium, while the decrease in mean response time is relatively...
Embodiment 3
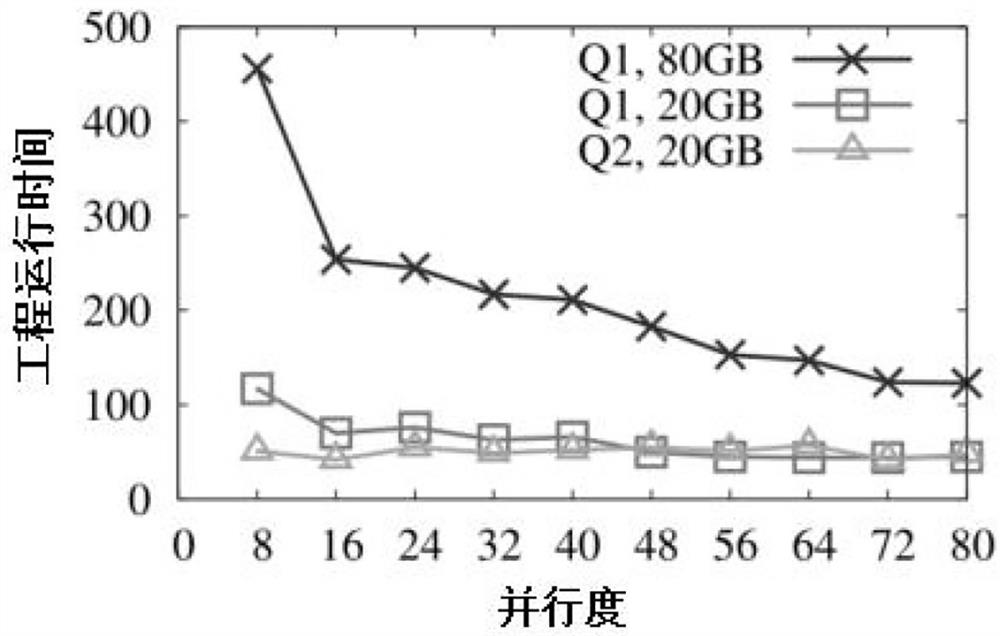
[0220] This embodiment considers the influence of parallelism in parallel computing. The effect of the forecasting method on the response time of different stages is first evaluated. Thereafter, the impact of computational properties on different methods in parallel computing and the improvement of the average response time of the methods are evaluated under consideration of the degree of parallelism.
[0221] This example uses BigDataBench to measure the time of multiple queries running on Spark with varying amounts of data and degrees of parallelism. According to the results, the present embodiment uses the multiple linear regression algorithm to construct a prediction model of the computation time of each stage. The results show that the R2 statistics are all greater than 0.9, where R is the correlation coefficient. The value of the F statistic is greater than the value according to the F distribution table. The probabilities p corresponding to the F statistic are all le...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com