Conventional direct-current valve area fault positioning method
A fault location, conventional DC technology, applied in the field of power systems, can solve problems such as economic loss, trouble spot troubleshooting that takes a lot of time, analysis and rigidity, and achieve the effect of reducing misjudgment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] In order to make the above objects, features and advantages of the present invention more comprehensible, the technical solutions of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. It should be pointed out that the described embodiments are only a part of the embodiments of the present invention, rather than all embodiments. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all those skilled in the art can obtain without creative work. Other embodiments all belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
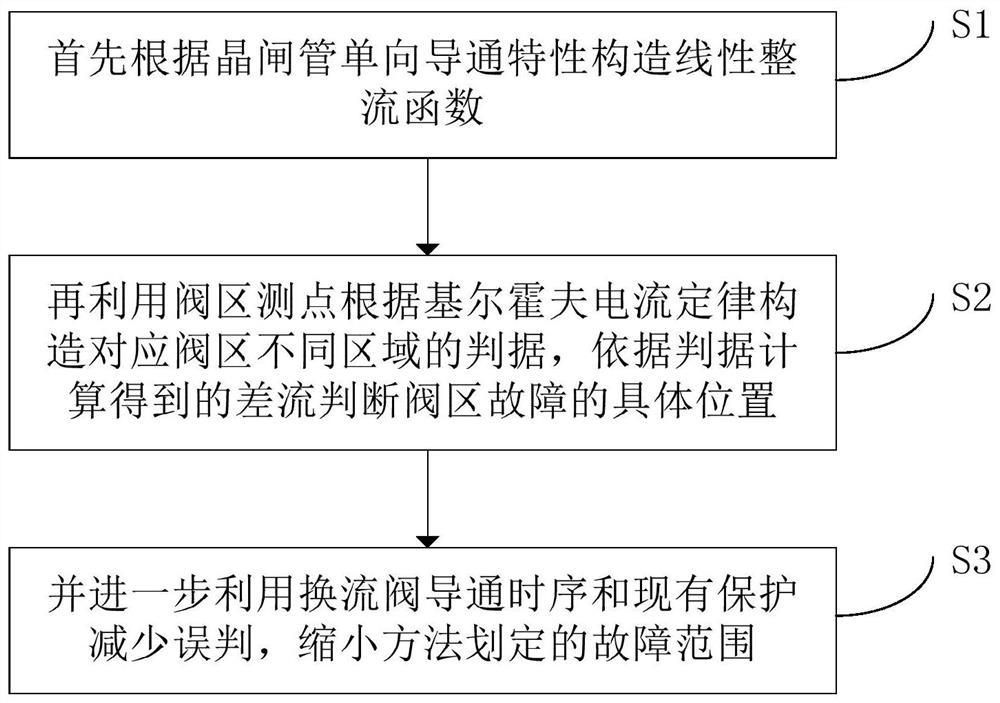
[0047] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a method for locating faults in conventional DC valve areas, including the following steps:
[0048] S1. Modeling of conduction characteristics of thyristor converter valve
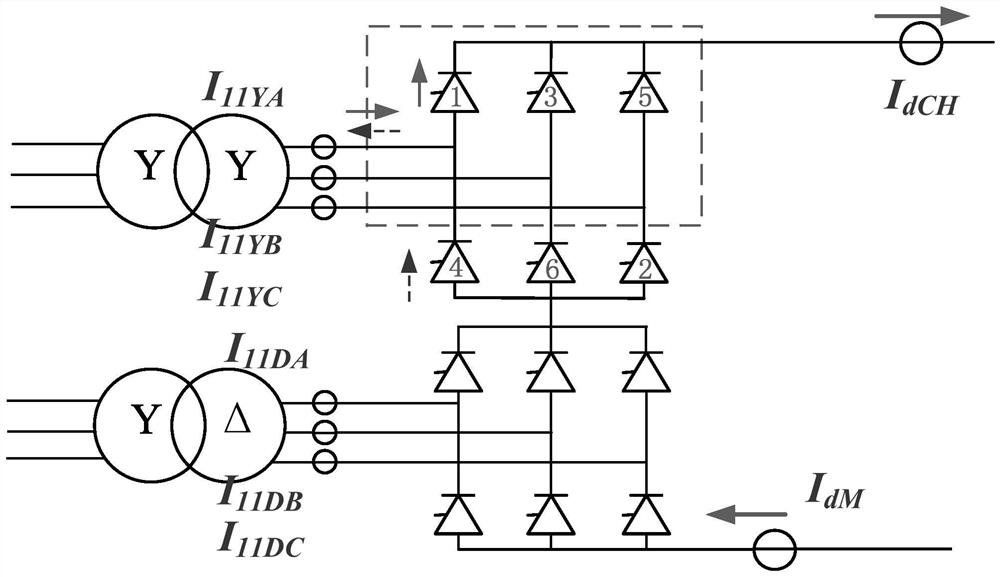
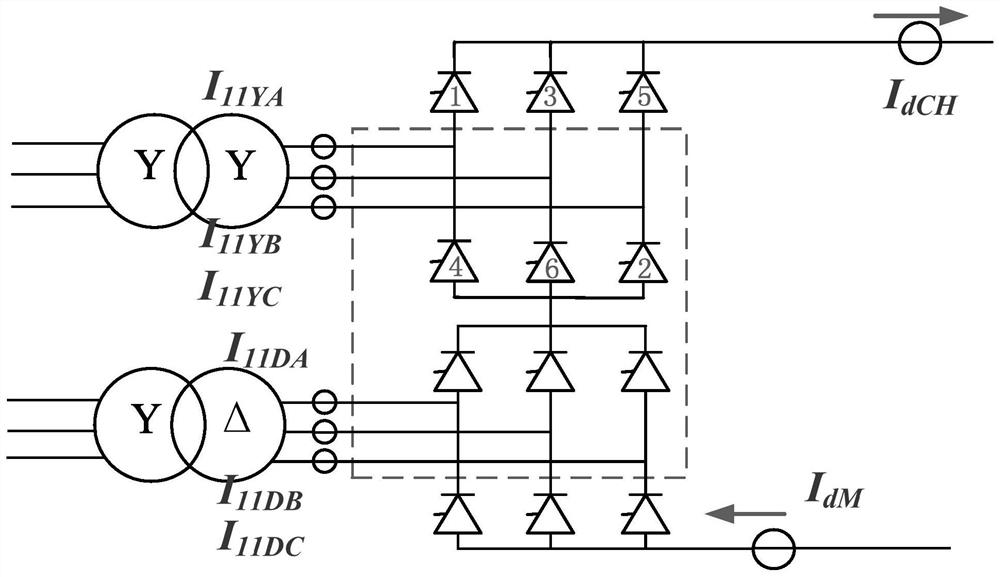
[0049] The schematic diagram of the common UHV DC high-valve twelve-pulse converter and its converter transformer is as follows: figure 2 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com