Aging and capacity grading method for lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery and battery technology, applied in the field of lithium-ion battery technology, can solve the problems of wasteful capacity dividing equipment, poor production efficiency, poor stability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
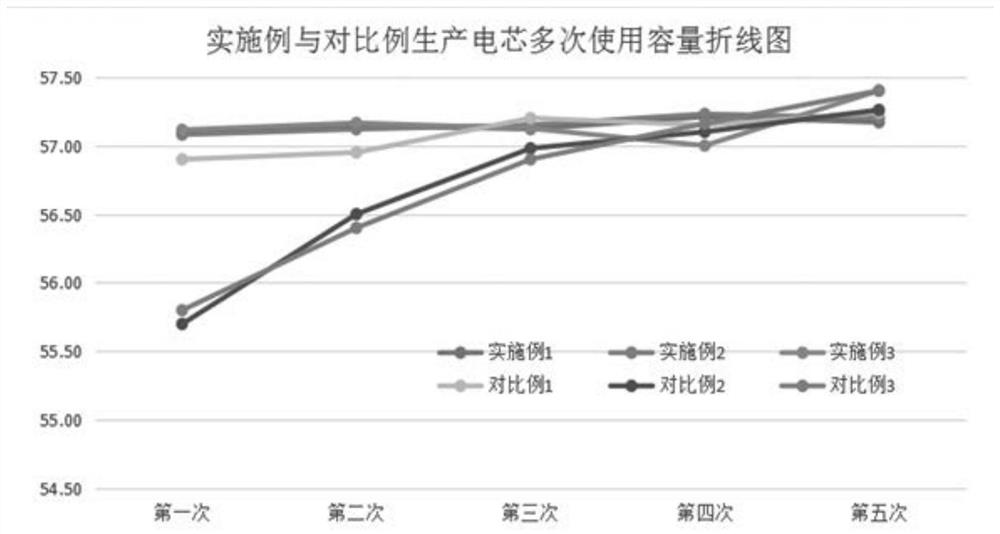
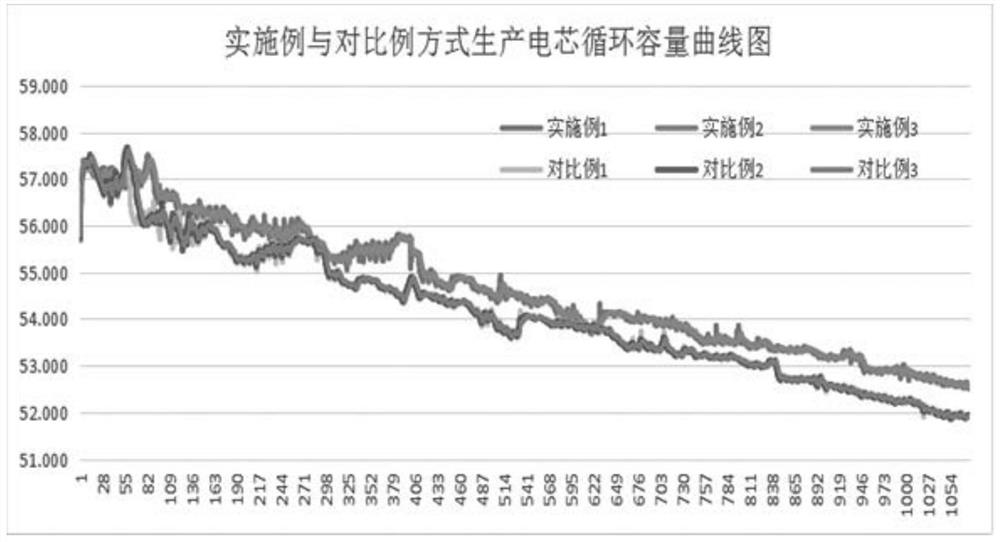
Examples
Embodiment 1
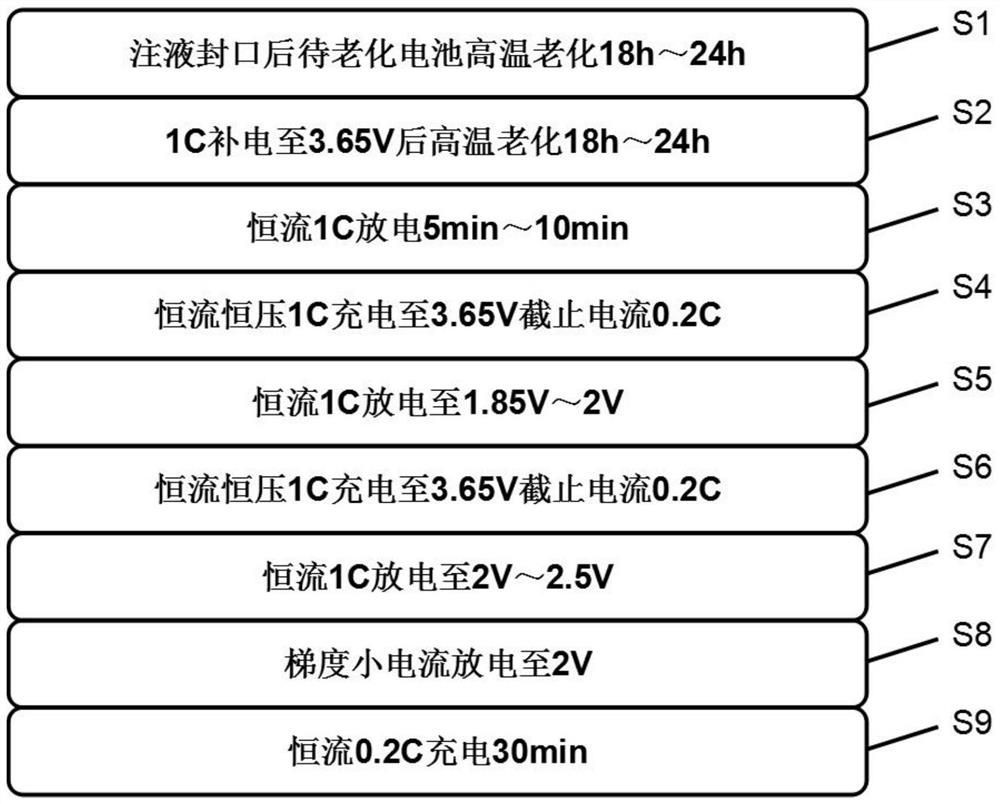
[0029] The lithium-ion battery aging capacity classification method comprises the following steps:
[0030] S1. Aging at 40°C for 18h after battery injection and sealing;
[0031] S2, constant current and constant voltage 1C charge to 3.65V cut-off current 0.2C, then aging at 45°C for 18h;
[0032] S3, constant current 1C discharge for 10min;
[0033] S4, constant current constant voltage 1C charging to 3.65V cut-off current 0.2C;
[0034] S5, constant current 1C discharge to 1.85V;
[0035] S6, constant current constant voltage 1C charging to 3.65V cut-off current 0.2C;
[0036] S7, constant current 1C discharge to 2.5V;
[0037] S8, constant current 0.3C discharge to 2V, constant current 0.02C discharge to 2V;
[0038] S9, constant current 0.2C charging for 30min. That is, a lithium-ion battery with capacity separation is obtained.
Embodiment 2
[0040] The lithium-ion battery aging capacity classification method comprises the following steps:
[0041] S1. Aging at 50°C for 18 hours after battery injection and sealing;
[0042] S2, constant current and constant voltage 1C charge to 3.65V cut-off current 0.2C, then aging at 50°C for 18h;
[0043] S3, constant current 1C discharge for 10min;
[0044] S4, constant current constant voltage 1C charging to 3.65V cut-off current 0.2C;
[0045] S5, constant current 1C discharge to 1.9V;
[0046] S6, constant current constant voltage 1C charging to 3.65V cut-off current 0.2C;
[0047] S7, constant current 1C discharge to 2.5V;
[0048] S8, constant current 0.3C discharge to 2V, constant current 0.02C discharge to 2V;
[0049] S9. Charging at a constant current of 0.2C for 30 minutes; that is, a lithium-ion battery with capacity division is obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0051] The lithium-ion battery aging capacity classification method comprises the following steps:
[0052] S1. Aging at 50°C for 18 hours after battery injection and sealing;
[0053] S2, constant current and constant voltage 1C charge to 3.65V cut-off current 0.2C, then aging at 50°C for 18h;
[0054] S3, constant current 1C discharge for 5min;
[0055] S4, constant current constant voltage 1C charging to 3.65V cut-off current 0.2C;
[0056] S5, constant current 1C discharge to 2.5V;
[0057] S6, constant current constant voltage 1C charging to 3.65V cut-off current 0.2C;
[0058] S7, constant current 1C discharge to 2.5V;
[0059] S8, constant current 0.3C discharge to 2V, constant current 0.02C discharge to 2V;
[0060] S9, constant current 0.2C charging for 30min. That is, a lithium-ion battery with capacity separation is obtained.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com