A laser method for measuring the Fe isotope composition of Cr-rich geological samples
A geological sample and laser measurement technology, applied in the field of chemical analysis, to achieve the effect of avoiding the pretreatment process, wide application prospects, and improving application potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Example 1 Preparation of Cr-rich glass standard
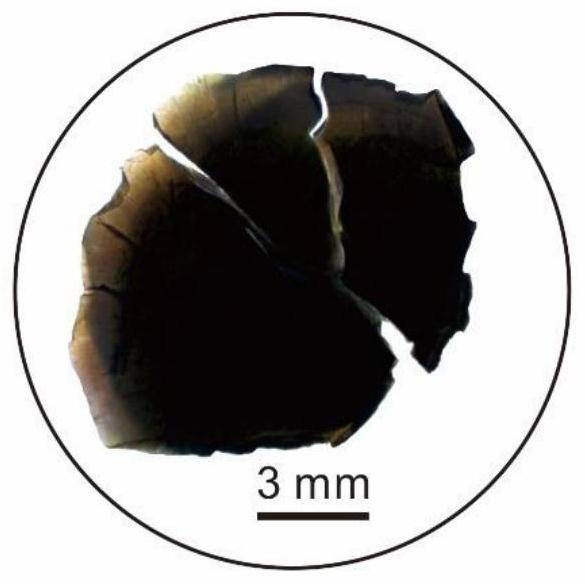
[0066] The oxide powders of Si, Ti, Al, Na, Mg and Ca and the international standard material NIST SRM 979 (chromium nitrate nonahydrate, Cr (NO 3 ) 3 ·9H 2 O) After the powder is fully ground and uniform, put it into a platinum crucible, burn it in a high temperature furnace (KSL-1700X-A4) at 1500°C for 12 hours under normal pressure, and take it out. After it cools and solidifies into glass, the solidified The resulting glass is divided into ~1cm glass fragments, which are fixed on double-sided tape and injected with epoxy resin to make a 0.5-inch epoxy resin target, which is polished to expose the surface of the sample, polished and cleaned before waiting for testing.
[0067] Principal component analysis was performed on the synthesized Cr-rich glass (Cr-979S) standard sample using electron probe technique (EPMA). The photos under the microscope are as follows figure 1 The analysis results are shown in Table 1:
...
Embodiment 2
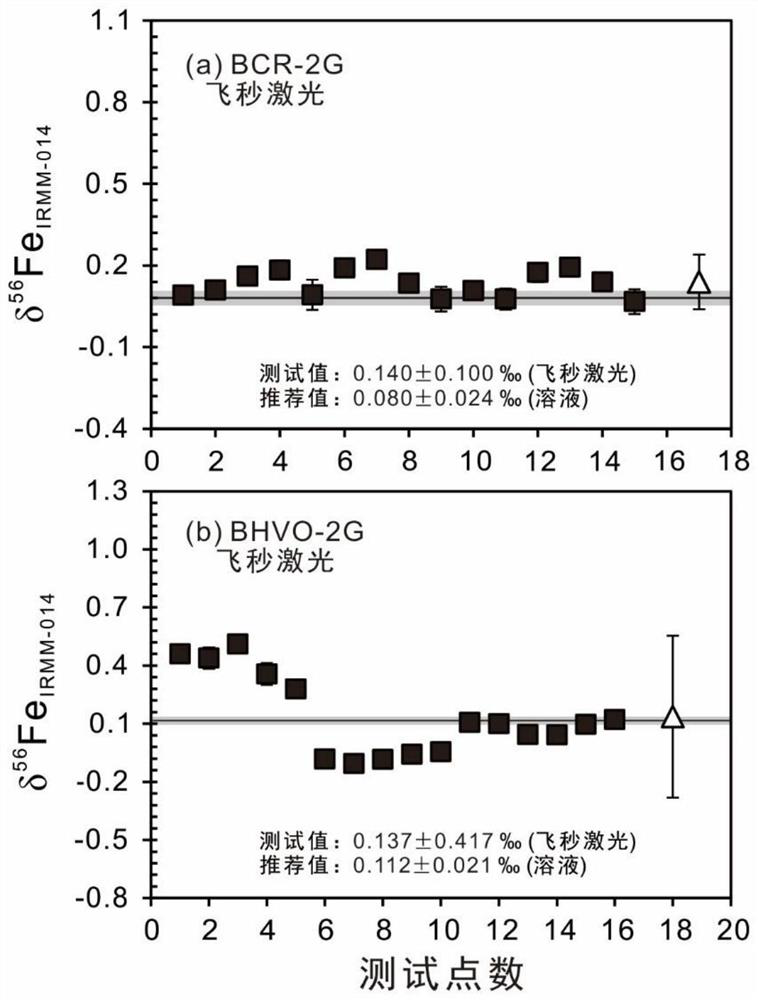
[0071] Example 2 Determination of Fe isotopic fractionation composition of geological samples using femtosecond laser for non-matrix matching correction
[0072] In this example, the IRMM-014 pure iron sample is used as the standard sample, the BCR-2G and BHVO-2G basaltic glass samples are used as the samples to be tested, and the femtosecond laser is used for laser ablation, and the ablated aerosol particles are introduced into the mass spectrometer. carry out testing. The influence of the femtosecond laser ablation process on the Fe isotopic composition of glass samples with different Cr contents was investigated, and the test results of the isotopic fractionation induced by the femtosecond laser were calculated and compared with the data reported by the solution method.
[0073] The specific detection process is as follows:
[0074] 1) Place the IRMM-014 pure iron sample, BCR-2G and BHVO-2G basaltic glass samples in the ablation tank at close range;
[0075] 2) Femtosecon...
Embodiment 3
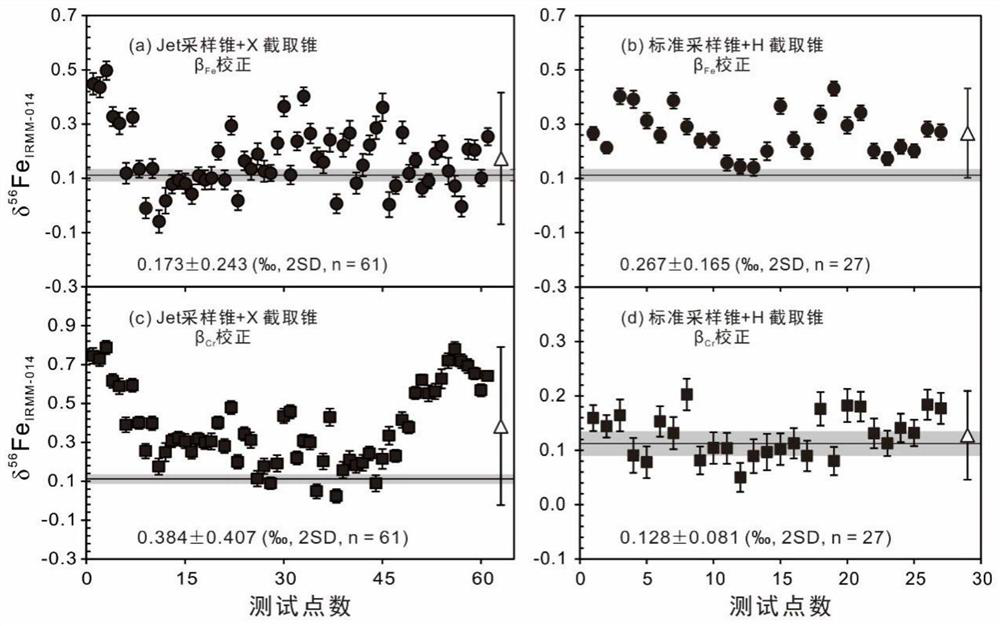
[0084] Example 3 Influence of different cone combinations on the determination of Fe isotopic composition of basaltic glass samples
[0085] In this example, the femtosecond laser in-situ detection method as provided in Example 2 is used to measure the Fe isotopic composition of the basalt glass sample, which is divided into two groups according to the cone combination used, the first group is Jet skimmer + X sampling cone , the second group is the standard intercept cone + H sampling cone, the specific method is:
[0086] 1. Place the Cr-rich glass samples, BCR-2G and BHVO-2G basaltic glass samples in the ablation tank at close range;
[0087] 2. Use femtosecond laser (257nm 300fs) to ablate the Cr-rich glass sample, and introduce the ablated aerosol particles into a mass spectrometer equipped with a cone combination for testing;
[0088] 3. Use femtosecond laser (257nm 300fs) to ablate BCR-2G basaltic glass, and introduce the ablated aerosol particles into a mass spectromet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com