Lifting device for large-range lodging of traffic guardrail
A large-scale guardrail technology, applied to road safety devices, roads, roads, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming and labor-intensive human manual lifting of guardrails, obstructing traffic, etc., to reduce workload, avoid obstacles, and ensure stability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. Wherein the same components are denoted by the same reference numerals. It should be noted that the words "front", "rear", "left", "right", "upper" and "lower" used in the following description refer to the directions in the drawings, and the words "bottom" and "top ”, “inner” and “outer” refer to directions toward or away from the geometric center of a particular part, respectively.
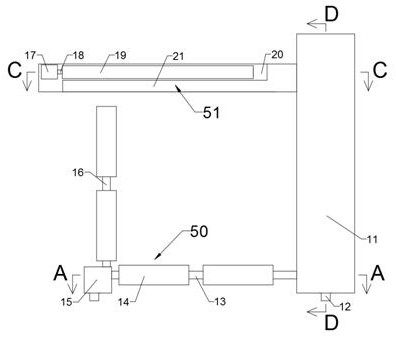
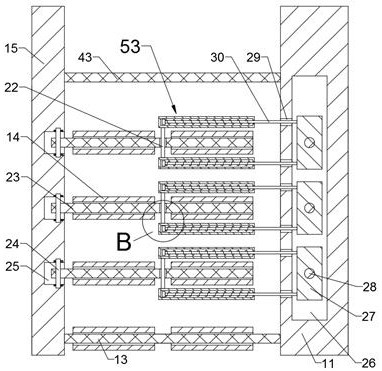
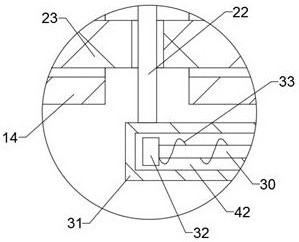
[0022] Such as Figures 1 to 6 As shown, the lifting device for the large-scale lodging of the traffic guardrail includes a transmission box 11, and the side of the transmission box 11 near the traffic guardrail is provided with a support device 50 for supporting the lodging guardrail. The bottom rod 13 on the end face of the transmission box 11 close to the side of the traffic guardrail, the end surface of the bottom rod 13 away from the transmission box 11 is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com