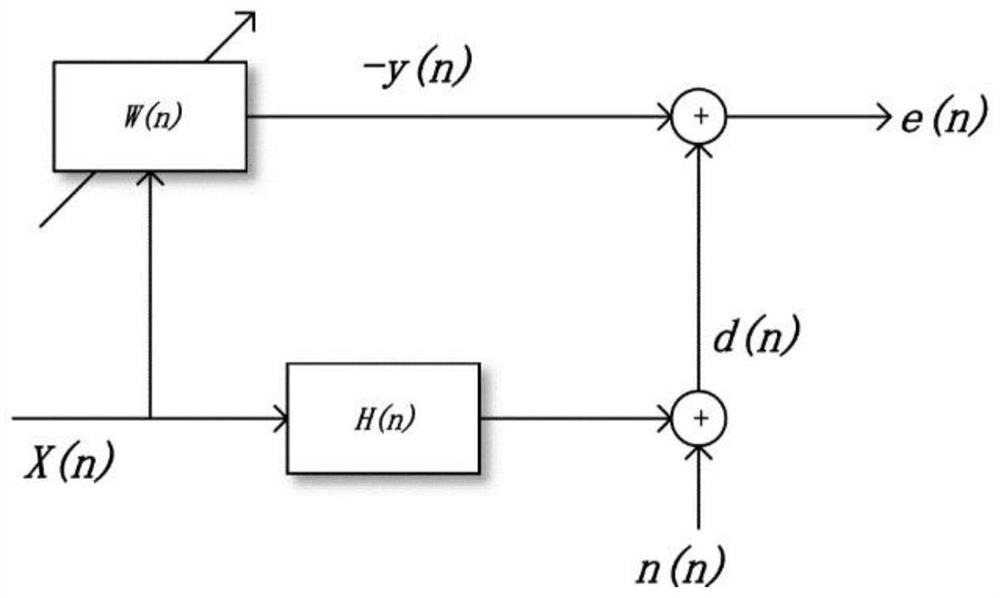
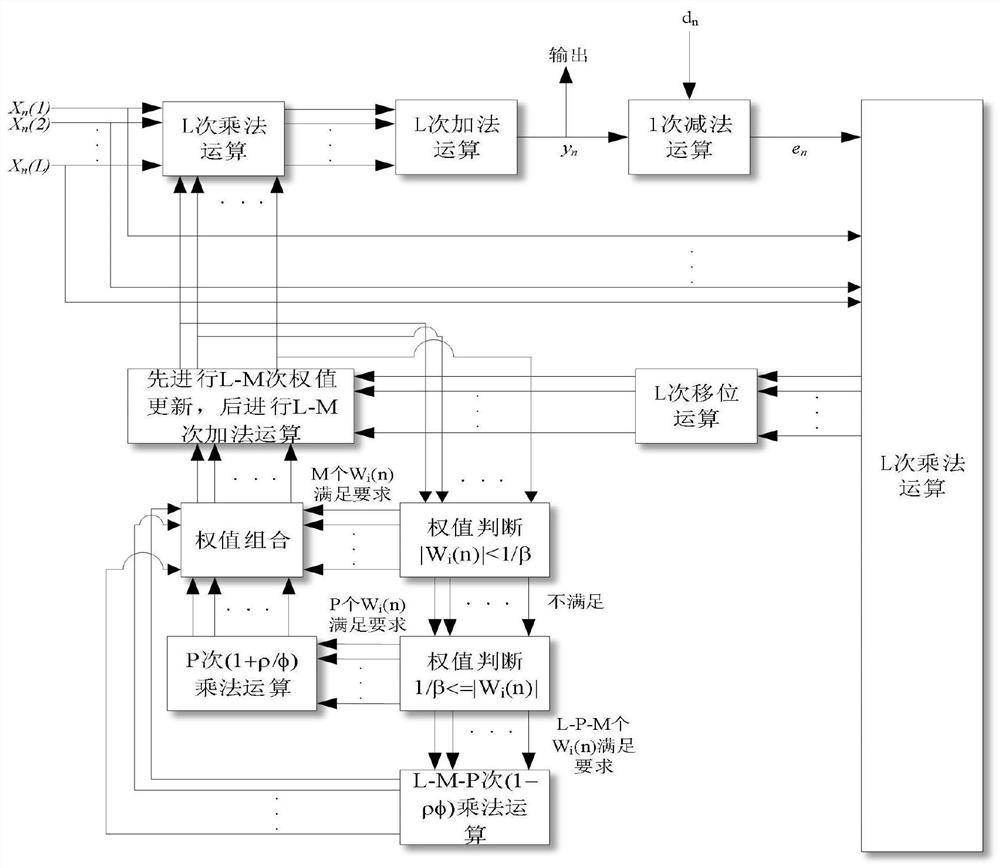
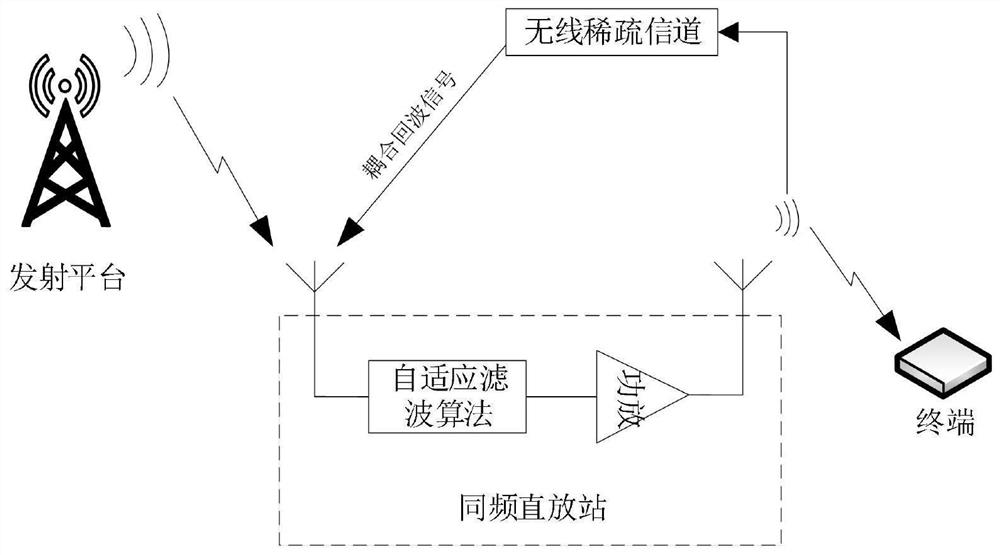
Sparse LMS method for combination of zero attraction penalty and attraction compensation
A zero-attraction and sparse technology, applied in the field of signal processing, can solve problems such as difficult hardware implementation, low mean square steady-state difference, and not excellent, and achieve the effect of accelerating the convergence speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] Embodiments of the present invention are described below through specific examples, and those skilled in the art can easily understand other advantages and effects of the present invention from the content disclosed in this specification. The present invention can also be implemented or applied through other different specific implementation modes, and various modifications or changes can be made to the details in this specification based on different viewpoints and applications without departing from the spirit of the present invention. It should be noted that the diagrams provided in the following embodiments are only schematically illustrating the basic concept of the present invention, and the following embodiments and the features in the embodiments can be combined with each other in the case of no conflict.
[0040] Wherein, the accompanying drawings are for illustrative purposes only, and represent only schematic diagrams, rather than physical drawings, and should...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com