Path fusion planning method for passage area, robot and chip
A traffic area and path technology, applied in the direction of instruments, two-dimensional position/channel control, vehicle position/route/altitude control, etc., can solve errors, sensor cumulative error visual map optimization, and obstacle grids that cannot be bypassed, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of increasing the success rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
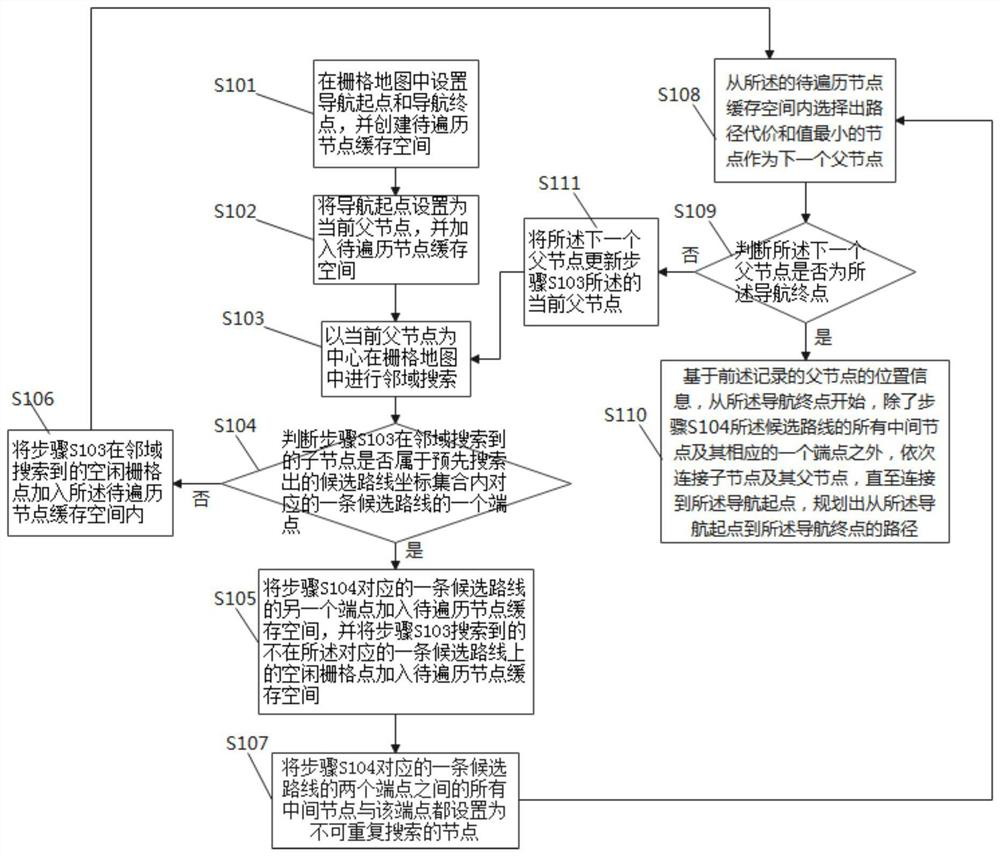
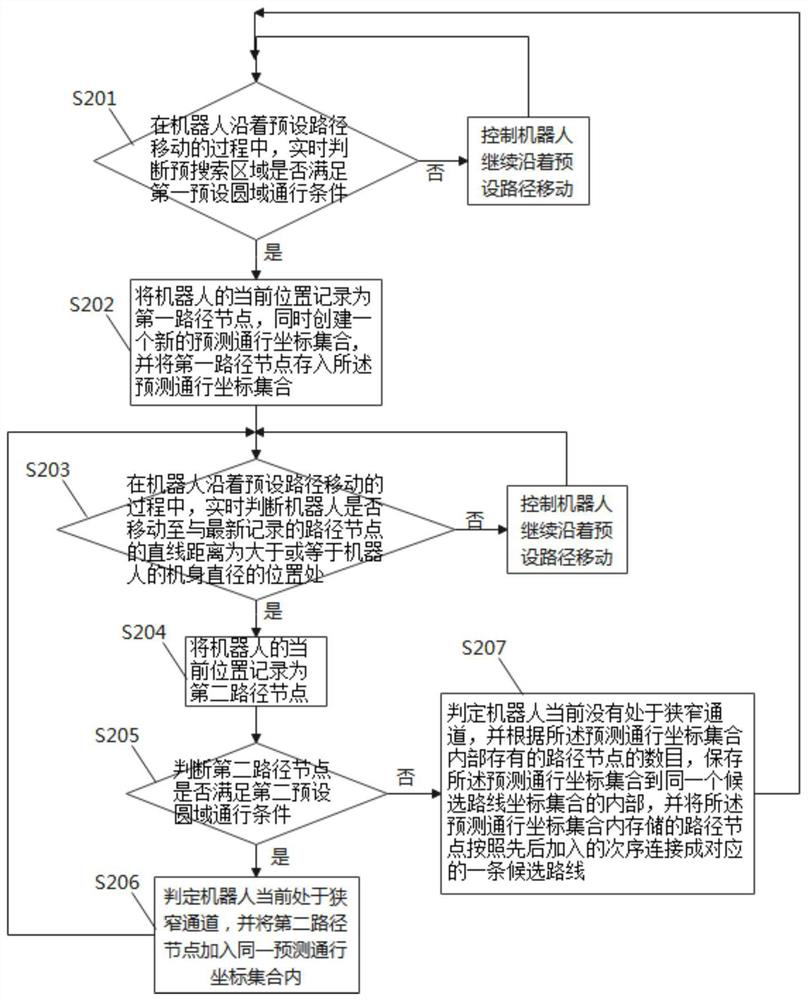
[0027] The specific embodiments of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0028] It should be noted that those skilled in the art can understand that the environment information around the current position of the robot is marked in the grid map, and the grids in the map area constructed by the robot include those marked as free, occupied and Unknown (unknown) three states; These grids are represented by grid points in this embodiment, that is, the center point of the grid; the grid points in the idle state refer to the grids that are not occupied by obstacles, which are accessible to the robot. The grid position points of , are free grid points, which can form an unoccupied area; the occupied grid points refer to the grids occupied by obstacles, which are obstacle grid points, and can form an occupied area; unknown grid points A point refers to a grid area where the specific situation is not clear in the process o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com