Regeneration control method and device for particle catcher and engine management system
A particle trap and engine management technology, which is applied in the field of particle traps, can solve problems such as damage, particle trap torque limitation, failure to meet the conditions for triggering active regeneration, etc., and achieve the effect of avoiding torque limitation or even damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
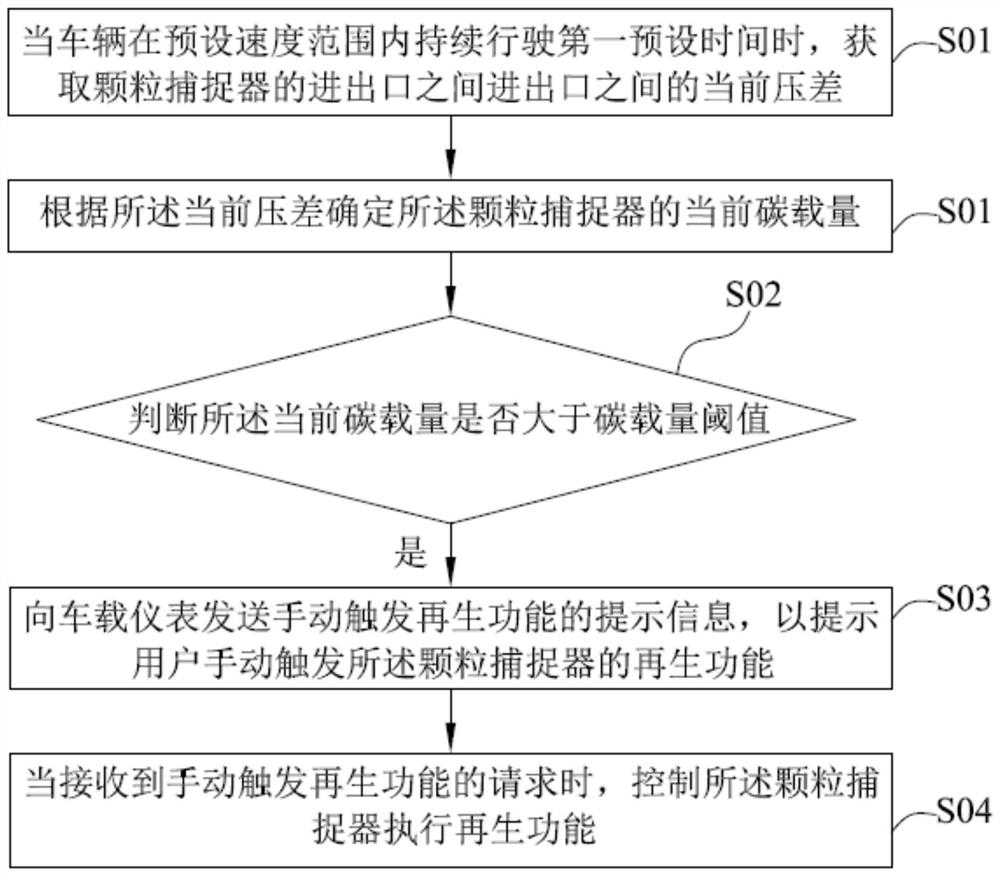
[0054] see figure 2 , shows the regeneration control method of the particle trap in the first embodiment of the present invention, which can be applied in the engine management system (ESC), and the method specifically includes steps S01-step S05.
[0055] Step S01 , when the vehicle continues to run within a preset speed range for a first preset time, the current pressure difference between the inlet and outlet of the particle trap is acquired.
[0056]Wherein, the preset speed range is a low speed range, such as 10-30km / h, and the first preset time may be specifically 10-30 minutes, which means that the vehicle is in a low-speed driving state for a long time.
[0057] In addition, during specific implementation, pressure sensors can be installed at the inlet and outlet of the particle trap to respectively collect the pressure at the inlet and outlet of the particle trap, so as to obtain the current pressure between the inlet and outlet of the particle trap. differential pr...
Embodiment 2
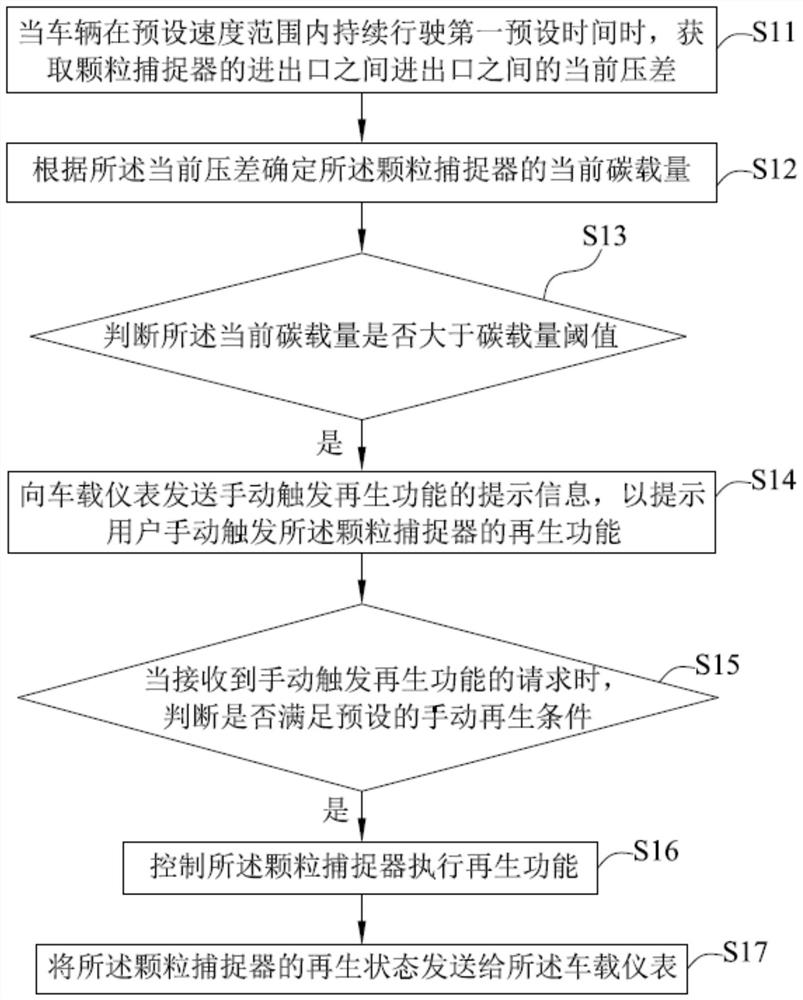
[0067] see image 3 , shows the regeneration control method of the particle trap in the second embodiment of the present invention, which can be applied to an engine management system (ESC), and the method specifically includes steps S11 to S17.
[0068] Step S11 , when the vehicle continues to run within the preset speed range for a first preset time, the current pressure difference between the inlet and outlet of the particle trap is acquired.
[0069] Step S12, determining the current carbon load of the particle trap according to the current pressure difference.
[0070] Step S13, judging whether the current carbon load is greater than a carbon load threshold.
[0071] Among them, when it is judged that the current carbon load is greater than the carbon load threshold, which means that the DPF is clogged or about to be clogged, step S14-step S15 is performed; when it is judged that the current carbon load is not greater than the carbon load threshold, no action is taken an...
Embodiment 3
[0081] see Figure 4 , shows the regeneration control method of the particle trap in the third embodiment of the present invention, which can be applied in an engine management system (ESC), and the method specifically includes steps S21 to S27.
[0082] Step S21 , when the vehicle continues to run within the preset speed range for a first preset time, the current pressure difference between the inlet and outlet of the particle trap is acquired.
[0083] Step S22, determining the current carbon load of the particle trap according to the current pressure difference.
[0084] Step S23, judging whether the current carbon load is greater than a carbon load threshold.
[0085] Among them, when it is judged that the current carbon load is greater than the carbon load threshold, which means that the DPF is clogged or about to be clogged, step S24-step S25 is performed; when it is judged that the current carbon load is not greater than the carbon load threshold, no action is taken an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com