Repurposing beads in sample cleanup
A bead, magnetic bead technology, applied in the field of nucleic acid capture, which can solve the problems of inaccessibility of therapeutics, limited automation of RNA and DNA analysis, and increased cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0025] Example 1: Benchtop method.
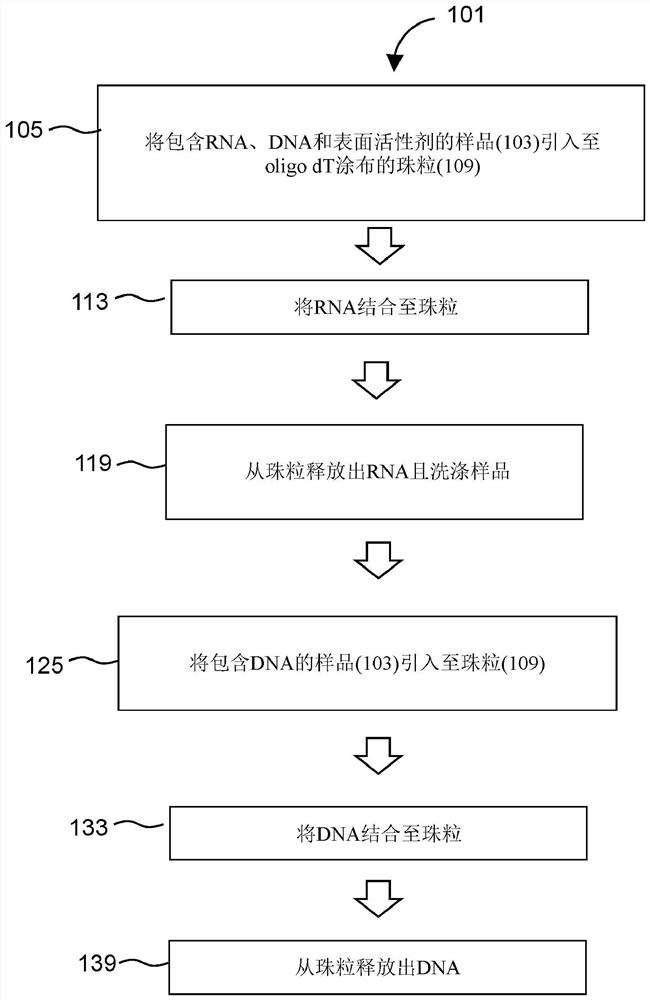
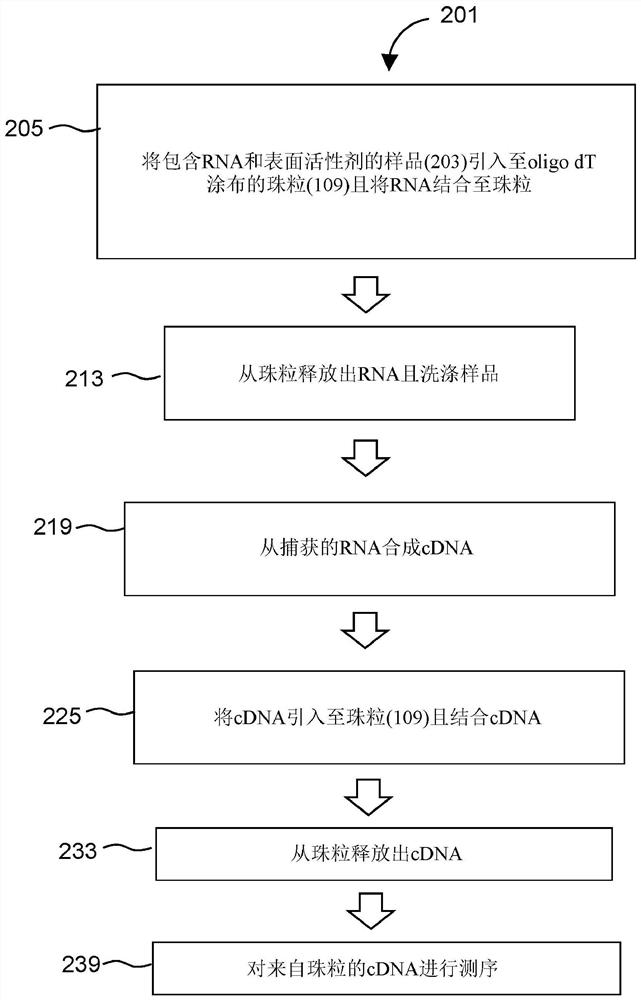
[0026] RNA-Seq libraries were generated in which all purification steps were performed using a single set of oligo dT magnetic beads (GE Health Care, Ser-Mag oligo dT beads). 100 ng of total RNA derived from the K562 cell line was mixed with 35 μl of Oligo dT beads following the supplier's recommendation. After annealing, the beads were pulled to the side of the tube and the solution containing any unbound RNA was discarded. Beads were resuspended and washed as recommended by the supplier. The beads were collected and the wash buffer was discarded. Bound RNA was eluted in 20 μl of RNA Fragmentation Buffer (Tecan Group Ltd., Universal RNA-Seq) and incubated at 94° C. for 7 minutes as recommended. The beads were collected, and the fragmented RNA was transferred to a new tube.
[0027] The oligo dT beads were resuspended in 40 μl of reconstitution solution (bead binding buffer) containing 21% PEG 4000, 2.5M NaCl, 50 mM Tris, 0.1 mM EDTA an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com