A read-write method and system for metadata information of a distributed file system
A technology of distributed files and metadata information, applied in the field of distributed file systems, can solve problems such as increasing startup time, data loss, and affecting user experience, and achieve the effects of shortening time, improving user experience, and improving system efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
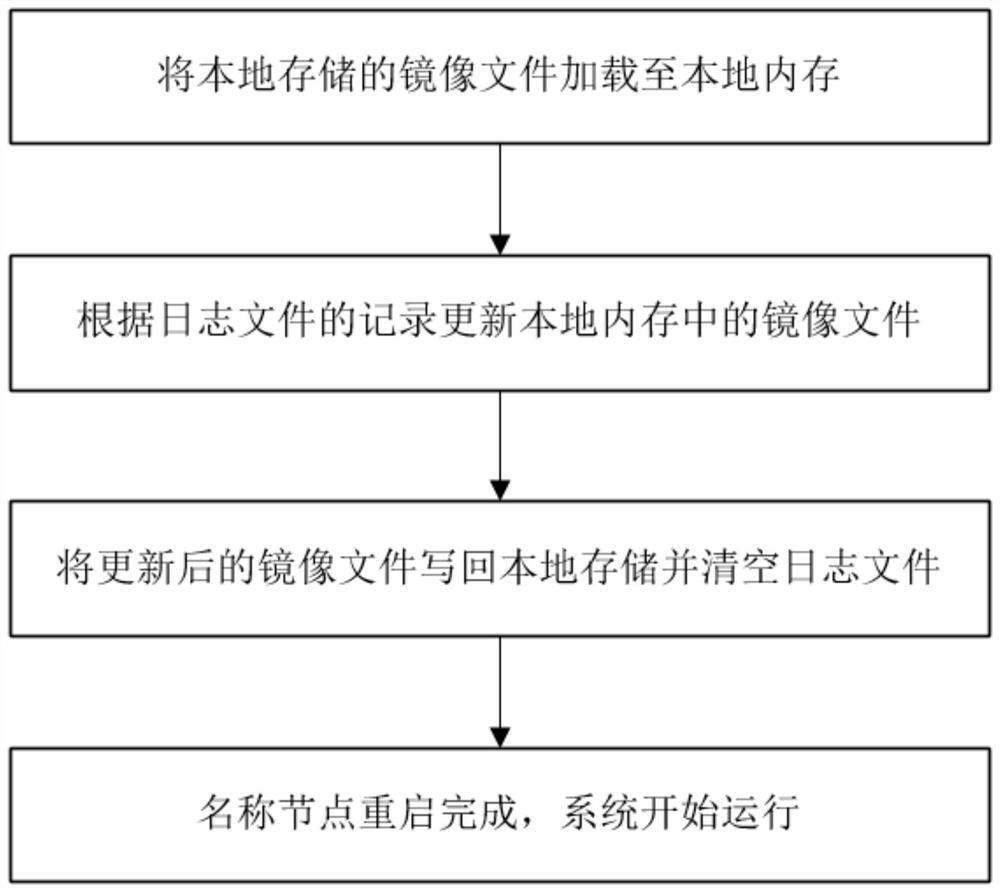
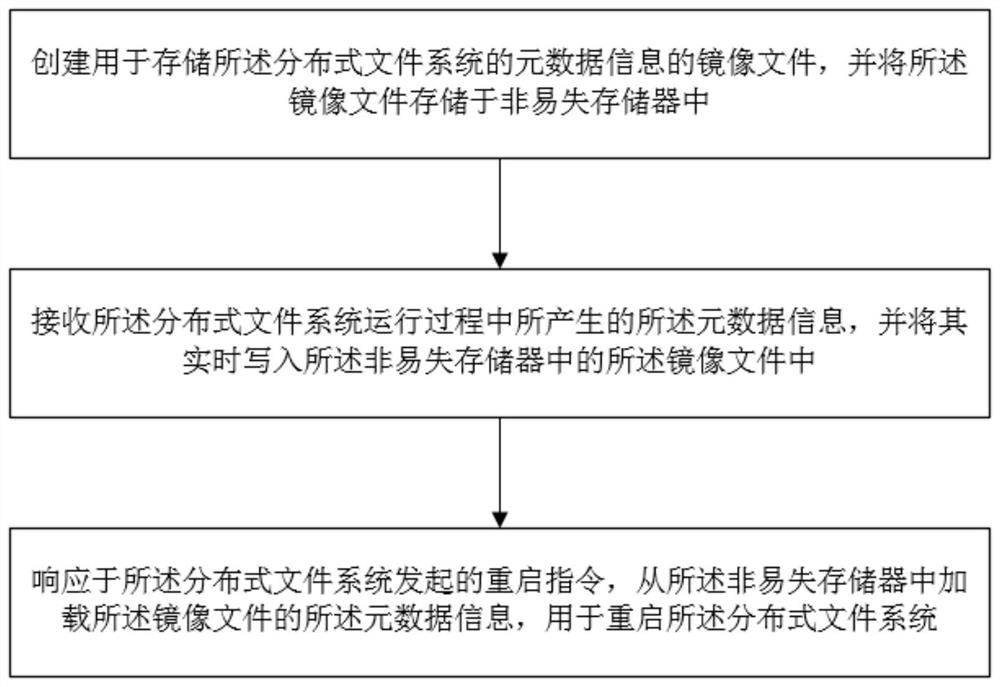
[0048] This embodiment provides a method for reading and writing metadata information of a distributed file system, wherein the distributed file system adopts a master-slave structure and includes multiple data nodes and at least one name node. The distributed file system stores data in the form of data blocks, that is, distributed files are divided into different data blocks and stored in different data nodes, and all data nodes are managed through name nodes. The name node maintains all metadata of the file system tree and the folders and files contained in the file tree through the image file, and the existing name node loads the image file into the local memory at runtime, while this The name node in the embodiment loads the image file into the non-volatile memory during operation, and when the name node needs to be restarted after a failure such as downtime or power failure occurs, the image file in the non-volatile memory saves the fault occurrence For the latest namespa...
Embodiment 2
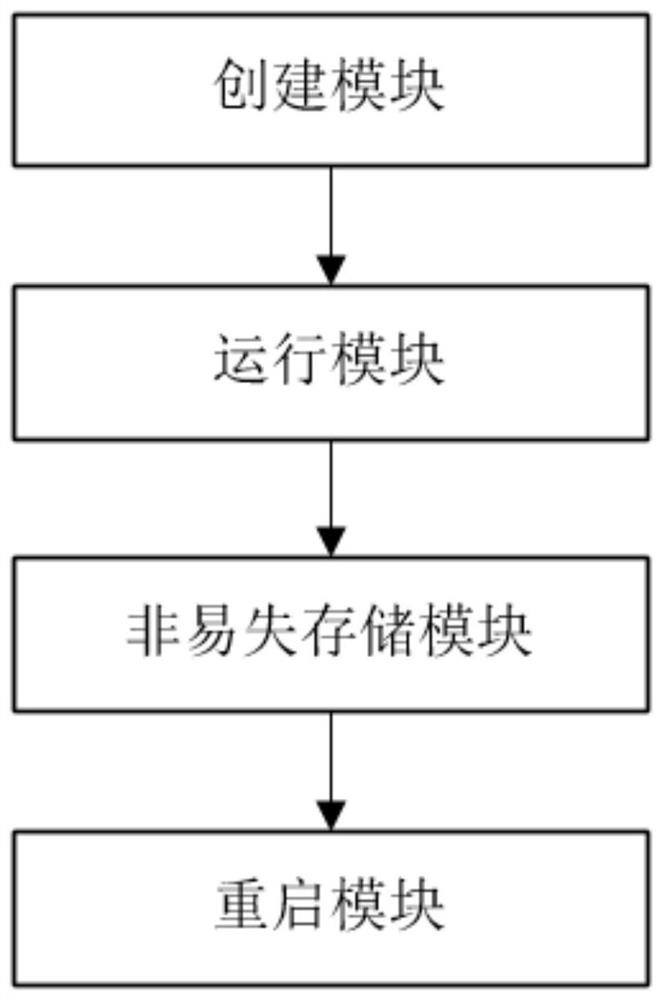
[0067] This embodiment provides a distributed file system, which executes the method for reading and writing metadata information of the distributed file system described in Embodiment 1, wherein, as image 3 As shown, the system specifically includes the following modules:
[0068] Create a module for creating an image file, where the image file is used to store the metadata of the distributed file system at runtime;
[0069] An operation module, configured to obtain metadata information when the distributed file system is running, and store it in the image file in real time;
[0070] A non-volatile storage module for storing the image file;
[0071] A restart module, configured to load metadata information of the image file from the non-volatile storage module, and perform a restart operation of the distributed file system.
[0072] The distributed file system of this embodiment saves the image file in the non-volatile storage module in real time during operation, and the ...
Embodiment 3
[0074] This embodiment provides an electronic device, including a program, a memory for storing the program, and a processor for loading the program to execute the method for reading and writing metadata information of a distributed file system as described above. In addition, this embodiment also provides a storage medium, which stores a program, and when the program is executed by a processor, implements the method for reading and writing metadata information of the distributed file system as described above.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com