Infrared phase-locked thermal imaging defect identification method for honeycomb sandwich structure
An infrared phase locking, honeycomb interlayer technology, applied in the direction of material defect testing, can solve the problem of difficult to effectively determine the detection process of products with different structures, thicknesses and sizes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0173] The application will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain related inventions, rather than to limit the invention. It should also be noted that, for the convenience of description, only the parts related to the related invention are shown in the drawings.
[0174] It should be noted that, in the case of no conflict, the embodiments in the present application and the features in the embodiments can be combined with each other. The present application will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
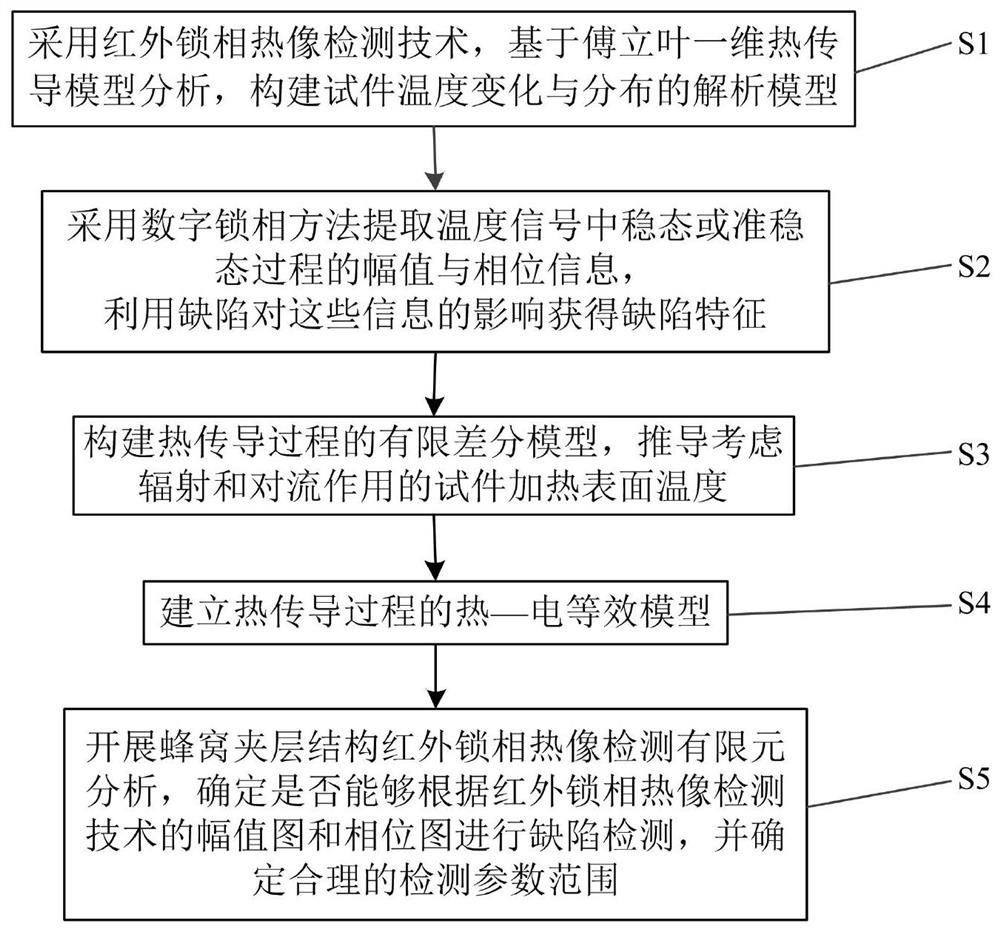
[0175] figure 1 The infrared lock-in thermal imaging defect identification method for honeycomb sandwich structure of the present invention is shown, the method includes the following steps:
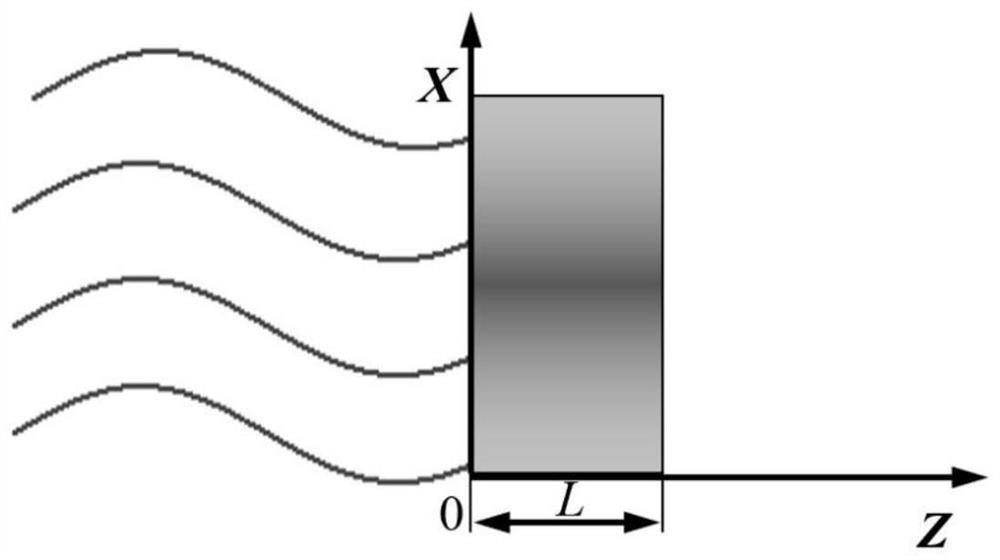
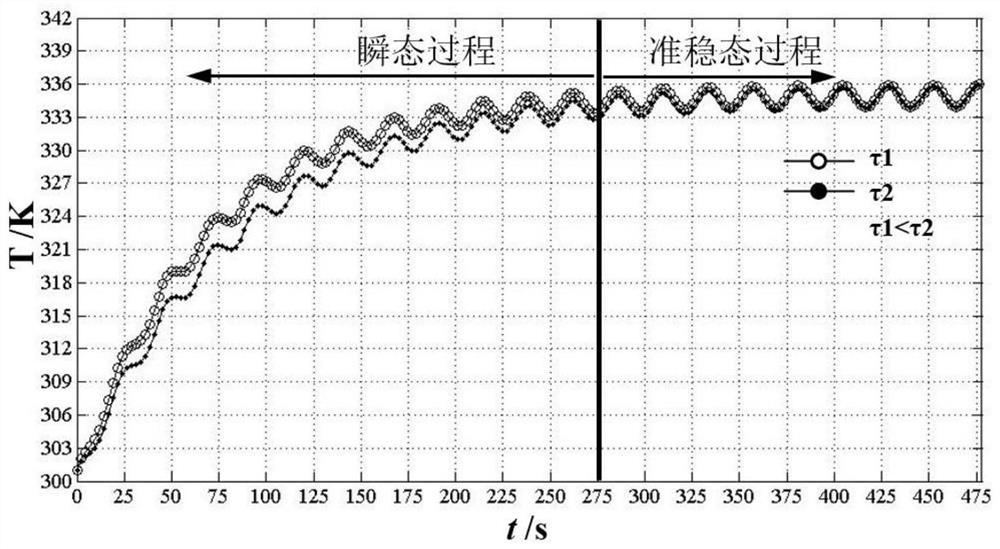
[0176] S1. Using infrared lock-in thermal imaging detection technology, based on ...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap