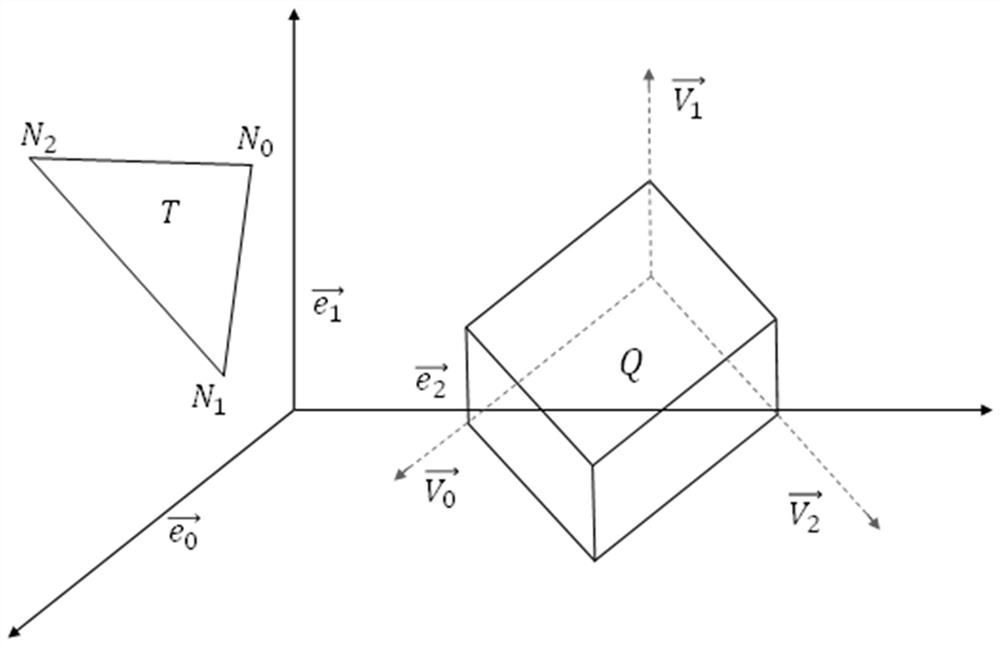
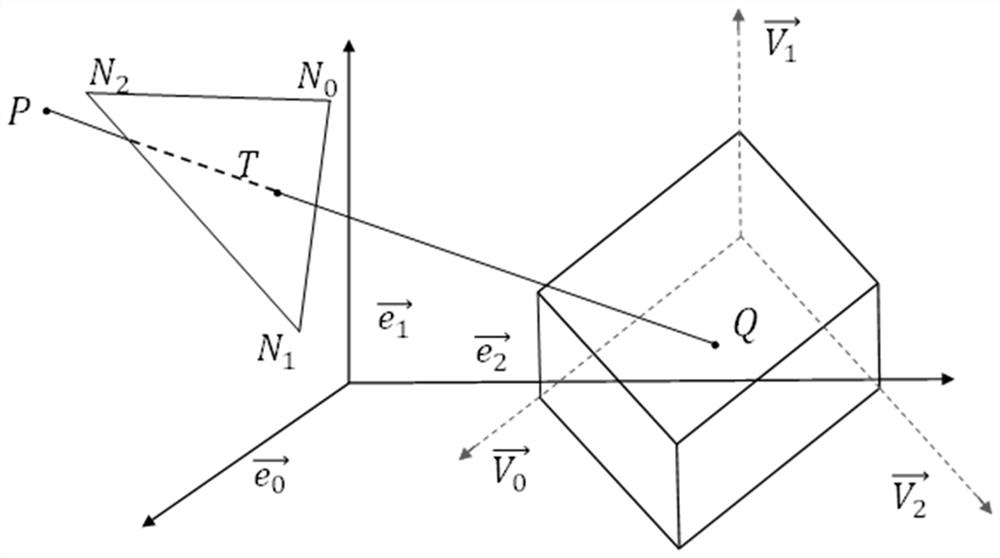
Self-adaptive Cartesian grid generation method for three-dimensional streaming problem of any shape
A Cartesian grid and self-adaptive technology, applied in special data processing applications, constraint-based CAD, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as sudden increase in storage capacity, occupation of computing resources, and limited accuracy of computer floating-point numbers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
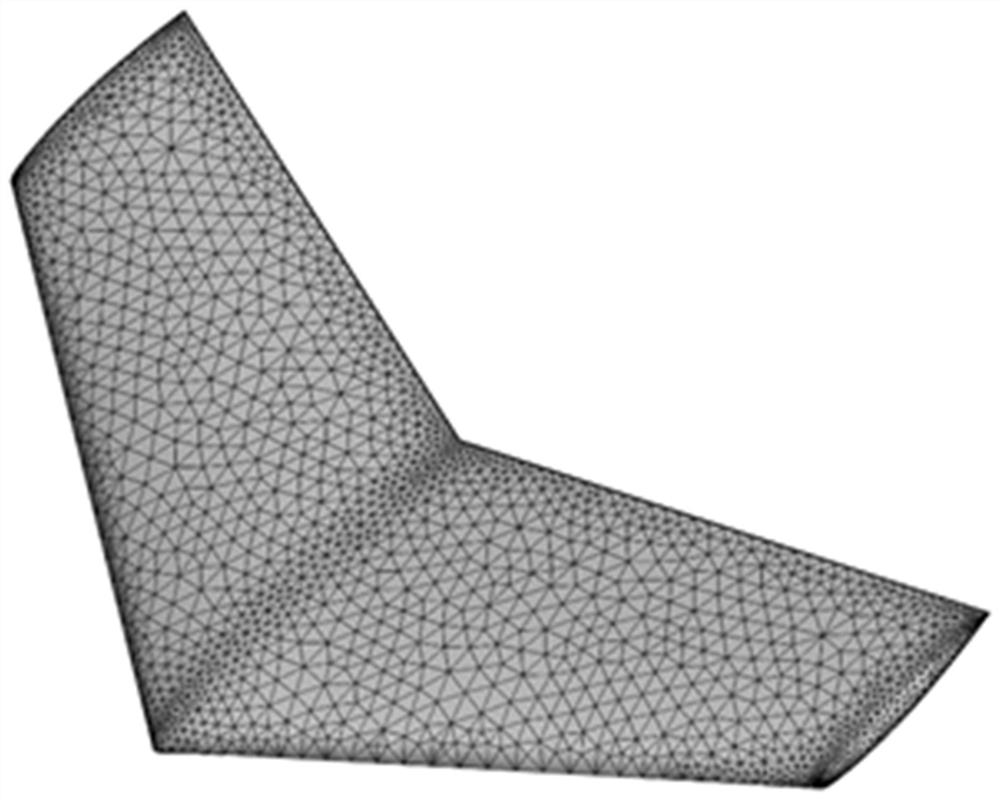
[0144] Embodiment 1, ONERA-M6 three-dimensional non-body-fit adaptive Cartesian grid generation. The ONERA-M6 airfoil is a classic example to test the stability of the computational fluid dynamics numerical method and the flow field solver. Its numerical simulation results and experimental results are very complete. At the same time, its model is relatively simple, which is very suitable as an initial method verification example. . The current ONERA-M6 model surface set is composed of 8132 triangles, and the triangles are densely distributed in the wingtips and other parts. A total of 7 mesh adaptive operations have been performed. The buffer factor α Take 3, the number of grids is 386044, and 32 cores are used in parallel, which takes 32s. like Figure 5 Shown is a multi-section schematic diagram of an adaptive Cartesian grid based on the shape of the ONERA-M6 wing.
Embodiment 2
[0145] Embodiment 2: The wing-body assembly model DLR-F6 with the engine nacelle and the pylon is generated with a three-dimensional non-body-fitting adaptive Cartesian grid. DLR-F6 is a twin-engine wide-body airliner. The DLR-F6 wing-body assembly model without the engine is the drag prediction model selected by AIAA DPW III, a series of drag prediction seminars organized by AIAA. This example is to verify the robustness of the algorithm , considering complex shapes such as hollow shells and concave surfaces, using the DLR-F6 model of the engine shell as the input object to generate an adaptive Cartesian grid. The surface of the current DLR-F6 model is composed of 35532 triangles, which are densely distributed at the leading edge of the fuselage, wingtips and other places with large geometric changes. A total of 9 geometric adaptive operations have been performed, and the buffer factor α Take 5, the number of grids is 17483250, and 96 cores are used in parallel, which takes 9...
Embodiment 3
[0146] Embodiment 3. Generation of three-dimensional non-body-fitted Cartesian grids of the COVID-19 virus model. In order to fully verify the robustness of the current invention, a 3D Cartesian grid is generated with the input shape of COVID-19. The COVID-19 virus model is different from the streamlined shape of the wing. The surface contains a total of 54 tentacles, which are composed of 188,280 discrete triangles. It includes multiple concave surfaces, convex tentacles and other special complex shape structures. A total of 6 geometric adaptive operations have been performed. buffer factor α Take 3, the number of grids is 2032927, and 96 cores are used in parallel, which takes 596s. like Figure 7 Shown is a multi-section diagram of an adaptive Cartesian grid constructed based on the shape of COVID-19.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com