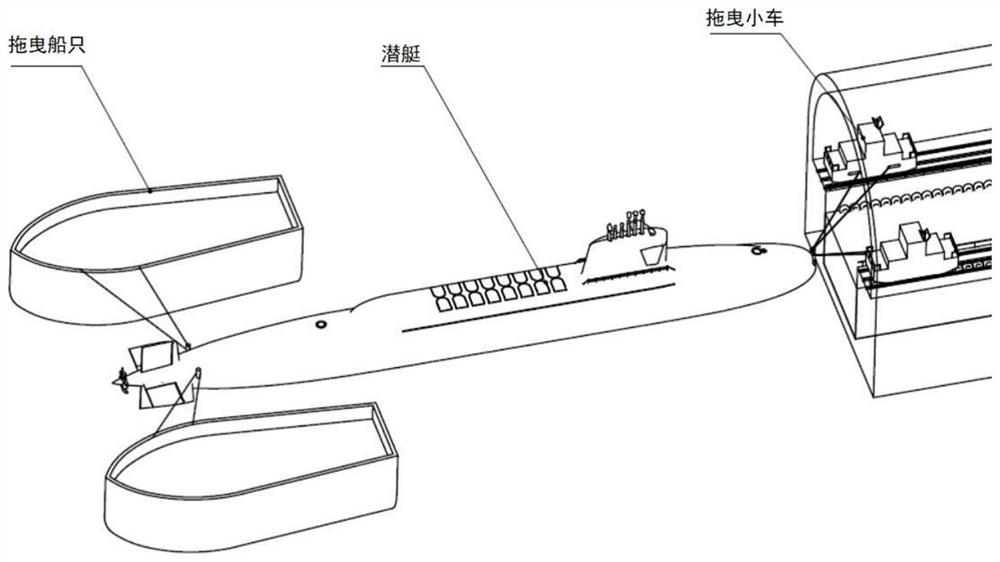
An automatic traction method and system for a submersible entering and exiting a tunnel
A technology for submersibles and tunnels, applied in control/regulation systems, instruments, non-electric variable control, etc., can solve problems such as poor positioning effect, difficult control, and difficulty in accessing specific narrow spaces to maintain ports, tunnels, and canals, etc. Achieve the effect of reducing labor costs, simplifying automatic calibration, improving positioning accuracy and traction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
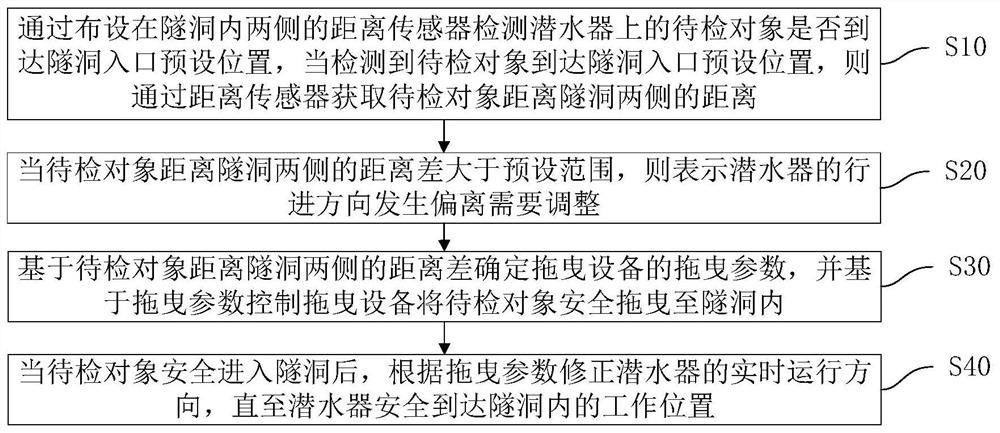
[0046] like figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides an automatic towing method for a submersible entering and exiting a tunnel, including:
[0047]S10: Detect whether the object to be inspected on the submersible reaches the preset position of the tunnel entrance through the distance sensors arranged on both sides of the tunnel, and when it is detected that the object to be inspected reaches the preset position of the tunnel entrance, obtain the distance of the object to be inspected through the distance sensor The distance on both sides of the tunnel.
[0048] The objects to be inspected on the submersible include the head and tail of the submersible. When the submersible drives into the tunnel, the object to be inspected is the head of the submersible; when the submersible leaves the tunnel, the object to be inspected is the tail of the submersible.
[0049] S20: When the distance difference between the object to be inspected and the two sides of the tunnel is greater ...
Embodiment 2
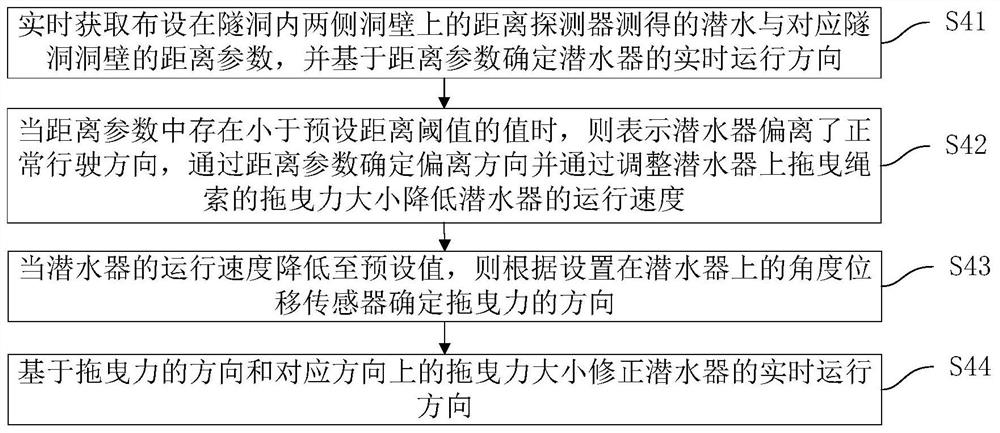
[0079] like Figure 5 As shown, this embodiment provides an automated towing system for submersibles entering and exiting tunnels that corresponds to the automated traction method for submersibles entering and exiting tunnels in Embodiment 1, including:
[0080] The parameter acquisition module 10 of the object to be inspected is used to detect whether the object to be inspected on the submersible has reached the preset position of the tunnel entrance through the distance sensors arranged on both sides of the tunnel. When it is detected that the object to be inspected has reached the preset position of the tunnel entrance, then Obtain the distance of the object to be inspected from both sides of the tunnel through the distance sensor.
[0081] The submersible traveling direction deviation determination module 20 is used for when the distance difference between the object to be inspected and the two sides of the tunnel is greater than the preset range, it means that the traveli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com