Overall design method of multilayer rod end spherical hinge
A design method and technology of ball joints, applied in the direction of mechanical equipment, shafts and bearings, non-rotational vibration suppression, etc., can solve the problems of easy wrinkling and fracture of the rubber layer, low service life of ball joints, and reduced service life of metal joints, so as to avoid The rubber folds are broken, the difficulty of processing technology is reduced, and the effect of reducing rubber stress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
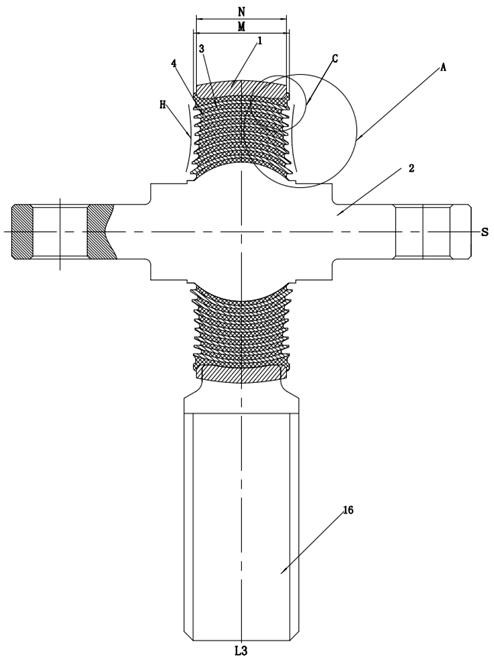
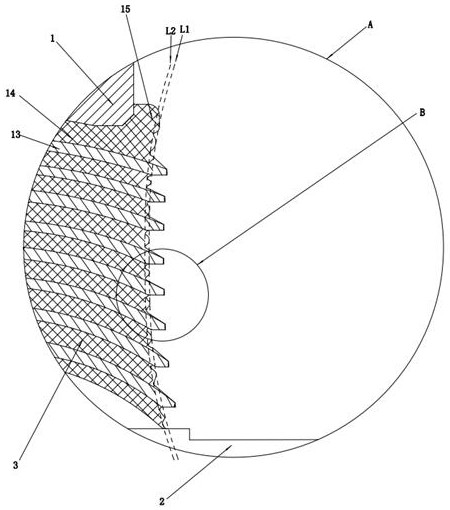
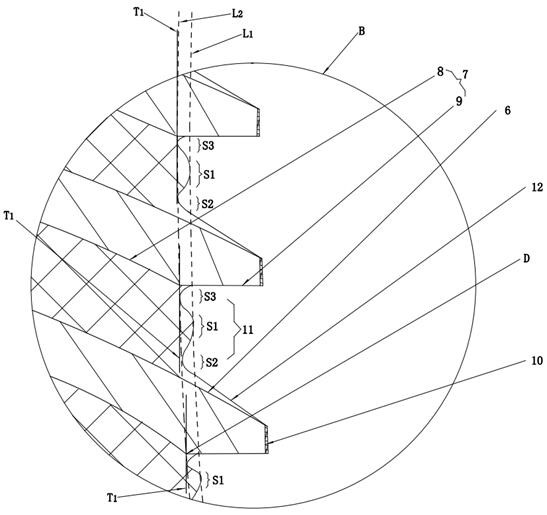
[0052] as attached Figure 1-9 As shown, an overall design method of a multi-layer rod-end ball joint, the above-mentioned rod-end ball joint includes an outer casing 1, a mandrel 2 and a rubber layer 3, and a plurality of spacers 4 are arranged in the rubber layer 3, and the adjacent spacers The rubber profile between 4 is combined with the spacer 4 to form a concave anti-stretch unit, such as image 3 As shown, the anti-stretch unit includes a concave bottom surface 11, a first outer surface 12 located on the lower side of the concave bottom surface 11 and facing the outside of the ball joint, and a second outer surface 9 located on the upper side of the concave bottom surface 11 and facing the outside of the ball hinge. The bottom surface 11 is set as a rubber profile structure composed of multi-arc sections to improve the tensile performance of the rubber layer 3 of the ball joint, prevent the rubber layer 3 from wrinkling and breaking when the ball joint is subjected to a...
Embodiment 2
[0081] This example is attached Figure 10 with Figure 11 As shown, the difference between Embodiment 2 and Embodiment 1 is that the end face 5 of the spacer is arranged obliquely from the outer end of the upper side 6 of the spacer toward the inner side of the ball joint, and the intersection of the upper side 6 of the spacer and the end face 5 of the spacer is formed. Tip E, using tip E to make point contact with the mold for axial positioning of the spacer during vulcanization. Setting the spacer sleeve end surface 5 from the outer end of the spacer sleeve upper side 6 towards the inner side of the ball joint can make the positioning of the spacer sleeve 4 more stable in the mould. , which further reduces the difficulty of processing the ball joint before vulcanization.
Embodiment 3
[0083] as attached Figure 12 As shown, the difference between the present embodiment and the second embodiment is that several narrow and long small grooves 33 are arranged at the groove bottom of the curved surface groove 25. The groove 33 further increases the bonding area between the outer layer spacer 13 and the outer layer 1 to prevent the outer rubber 13 from peeling off from the outer layer 1 and the outer layer spacer 13 when the ball joint is subjected to a large torsional load, thereby increasing the strength of the ball joint. service life.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com