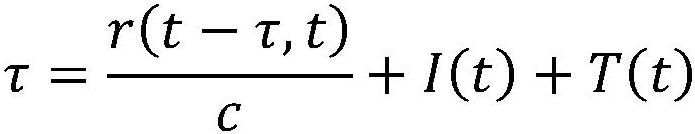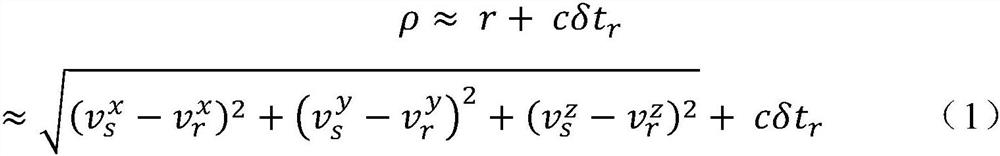How to Determine Bit Ambiguity
A technology for determining method and ambiguity, applied in the field of navigation, can solve problems such as incorrect counting, reduced number of pseudo-range observations, and inability to locate, and achieve the effects of simplifying the estimation process, facilitating estimation, and ensuring positioning capabilities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
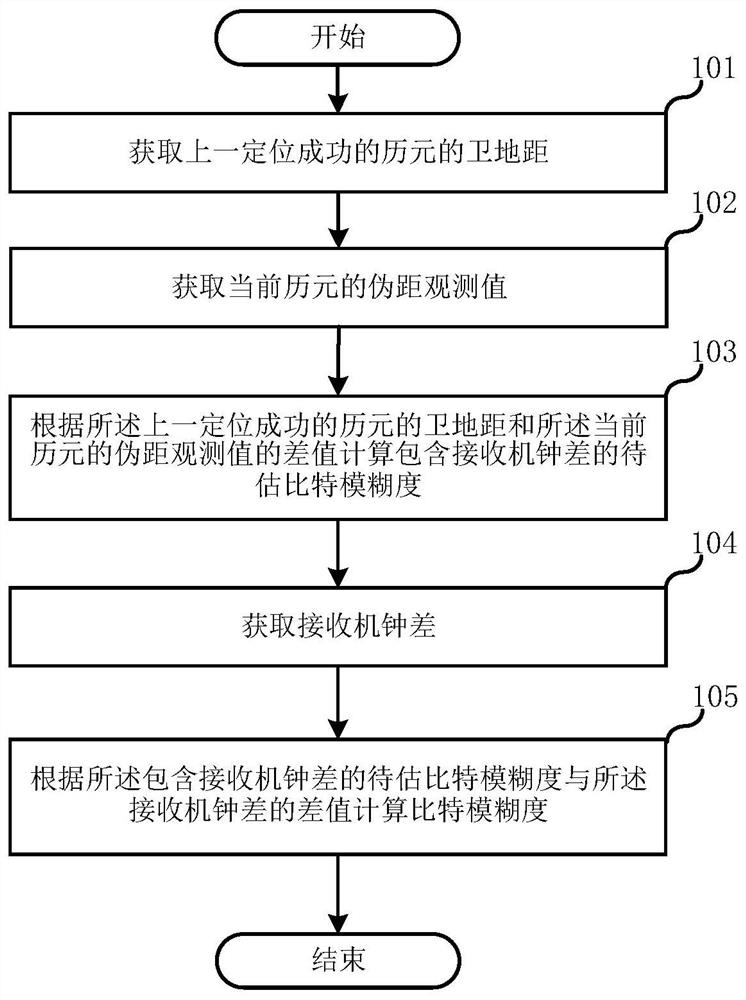
[0104] 1. Assume that in a certain epoch in a bad scenario, the receiver has 9 tracking channels that output pseudorange observations, that is, m=9.
[0105] 2. Obtain the satellite position and receiver position saved in the last successful positioning, and calculate the estimated value of the satellite-ground distance in the current epoch.
[0106] 3. Calculate l i Dataset L = (0.02-0.028), (0.04-0.048), (0.06-0.068), (0.08-0.088), (0-0.008), [-0.02-(-0.012)], [-0.04-(- 0.032)], [-0.06-(-0.052)], [-0.08-(-0.072)]=-0.008,-0.008,-0.008,-0.008,-0.008,-0.008,-0.008,-0.008,-0.008 . The -0.008 in the above data set is the difference in the remainder obtained by taking the remainder of 0.02.
[0107] 4. Obtain the estimated value of the receiver clock error according to the data set L
[0108] 5. The priori value of the clock error is about -0.008s, which can be obtained from the calibration formula i.e. round(q i )=0, the estimated value of the clock error No adjustment...
example 2
[0117] 1. Assume that in a certain epoch in a bad scenario, the receiver has 7 tracking channels that output pseudorange observations, that is, m=7.
[0118] 2. Obtain the satellite position and receiver position saved in the last successful positioning, and calculate the estimated value of the satellite-ground distance in the current epoch.
[0119] 3. Calculate l i Dataset L = (0-0.007), (0.02-0.027), (0.04-0.047), [-0.02-(-0.013)], [-0.04-(-0.033)], [-0.06-(-0.053) ], [-0.08-(-0.073)]=-0.007,-0.007,-0.007,-0.007,-0.007,-0.007,-0.007. The -0.007 in the above data set is the remainder difference obtained by taking the remainder of 0.02.
[0120] 4. Obtain an estimate of the clock error based on a univariate data set
[0121] 5. The prior information of the clock error is about 0.013s, which can be obtained from the verification formula i.e. round(q i )=1, the difference between the estimated value of the clock error and the prior information is not 0 but is close to a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com