A kind of enzymolysis-resistant α-helical antimicrobial peptide bound by full carbon and hydrogen side chains, its preparation method and application
An antimicrobial peptide and anti-enzymolysis technology, applied in the direction of peptide preparation methods, antibacterial drugs, chemical instruments and methods, etc., to achieve high application potential, stable secondary structure, and low degree of degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Design of Antimicrobial Peptides
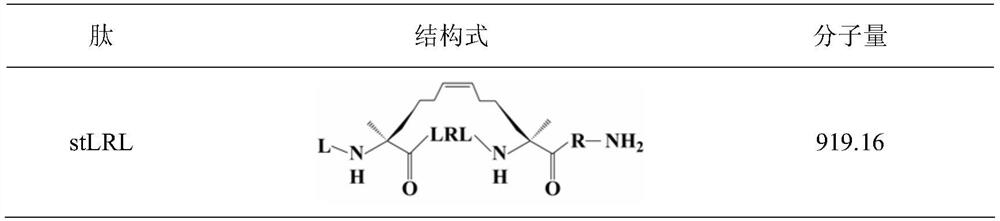
[0015] The amino acid sequence of the antimicrobial peptide stLRL is from N-terminal to C-terminal:
[0016] Leu Xaa Leu Arg Leu Xaa Arg - NH 2
1 5 7
[0018] Wherein, Xaa is (S)-2-(4-pentenyl)alanine;
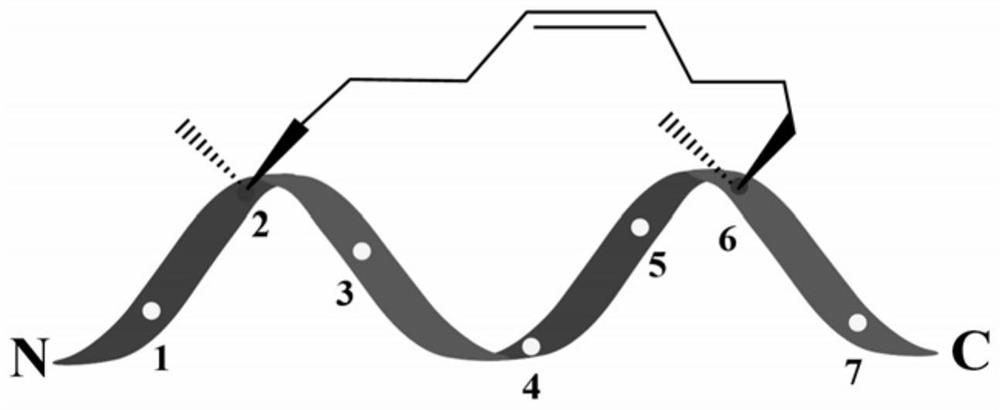
[0019] Referring to the properties of amino acids and the structural properties of "stitching", in order to avoid the enzymatic cleavage sites of trypsin and chymotrypsin, firstly, Arg was selected as a cationic amino acid to provide a positive charge, and secondly, the hydrophobic amino acid Leu was selected to enhance the hydrophobic depth. Leu is placed in the position (a position) to eliminate the cleavage of the chymotrypsin site, Arg and Leu are placed in the "staple" structure to improve antibacterial activity, and Arg is placed in the seventh position (g position) to provide positive charges, which can hinder pancreatic Cleavage by proteases, carboxy-terminal amidation for increased stability. The structural formula of th...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2
[0023] Synthesis of Antimicrobial Peptide stLRL by Solid Phase Chemical Synthesis
[0024] 1. The preparation of antimicrobial peptides is carried out one by one from the C-terminal to the N-terminal, and is completed by a peptide synthesizer. First, Fmoc-X (X is the first amino acid at the C-terminal of each antimicrobial peptide) is inserted into Wang resin, and the Fmoc group is removed to obtain X-Wang resin; then Fmoc-Y-Trt-OH (9-fluorene Methoxycarboxy-trimethyl-Y, Y is the second amino acid at the C-terminus of each antimicrobial peptide); as above, it is synthesized from the C-terminus to the N-terminus, until the synthesis is completed, and the resin obtained by removing the side chain protection of the Fmoc group ;
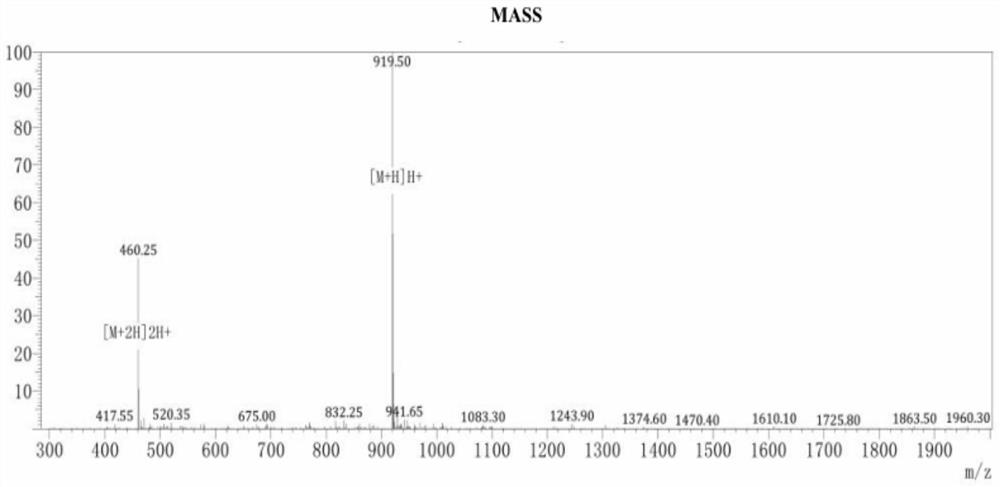
[0025] 2. Add a cleavage reagent to the peptide resin obtained above, react at 20°C for 2 hours in the dark, filter; precipitate with TFA (trifluoroacetic acid) and wash, mix the washing liquid with the above filtrate, concentrate wi...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3
[0030] Detection of antimicrobial peptide antibacterial activity and hemolytic activity in vitro:
[0031] 1. Determination of antibacterial activity: the minimum inhibitory concentration of antimicrobial peptides was determined by microdilution method. Add different concentrations of peptides to 0.2% BSA dilution (containing 0.01% acetic acid) in a 96-well plate, and then add an equal volume of the final concentration of 1 × 10 5 CFUmL -1 of bacterial suspensions in 96-well plates with final peptide concentrations ranging from 0.25 to 128 μM. Incubate at 37° C. for 18-22 hours, measure the light absorption value at 492 nm (OD=492 nm) with a microplate reader, and determine the minimum inhibitory concentration. The test results are shown in Table 2.
[0032] 2. Determination of hemolytic activity: collect 1mL of human fresh blood into a sodium heparin anticoagulant tube, centrifuge at 1000g for 5min to collect red blood cells, wash with PBS for 3 times a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com