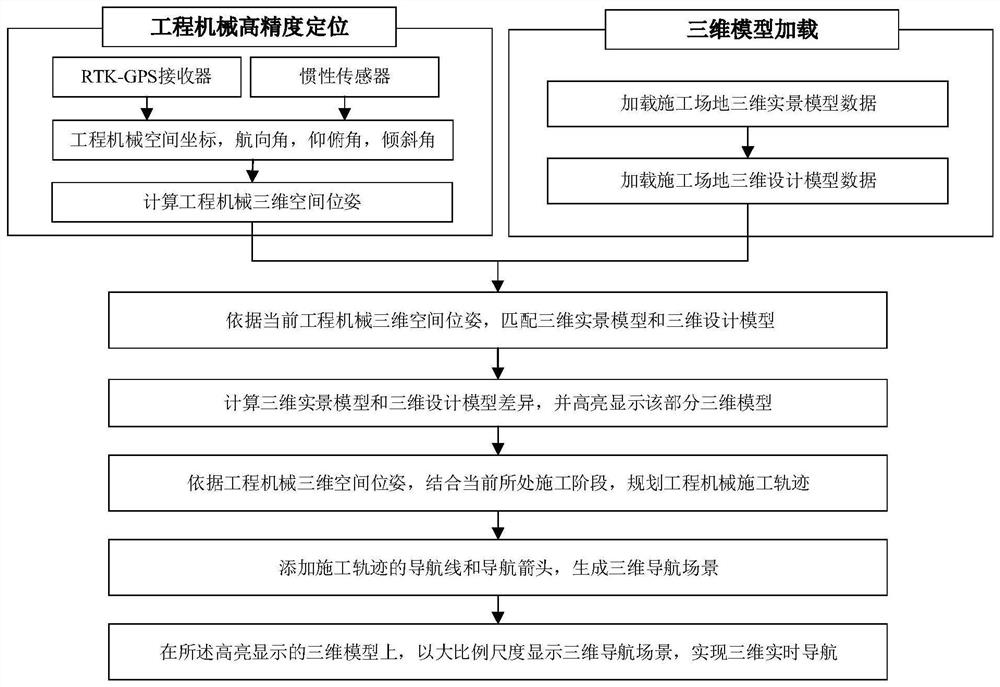
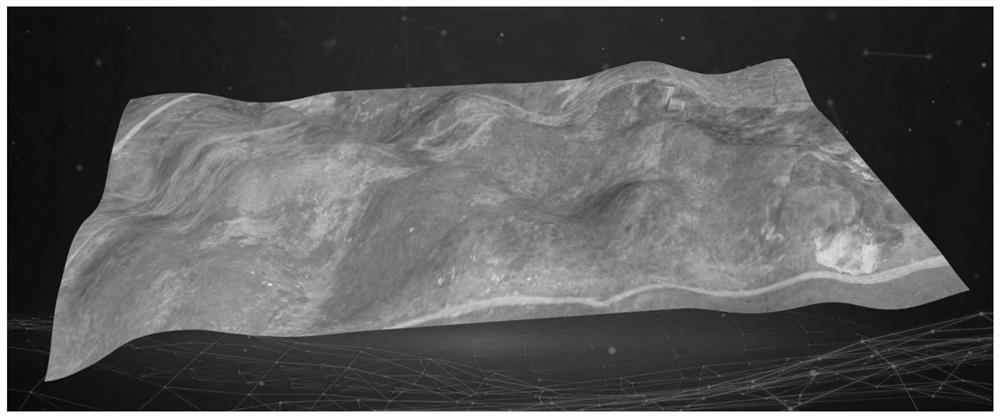
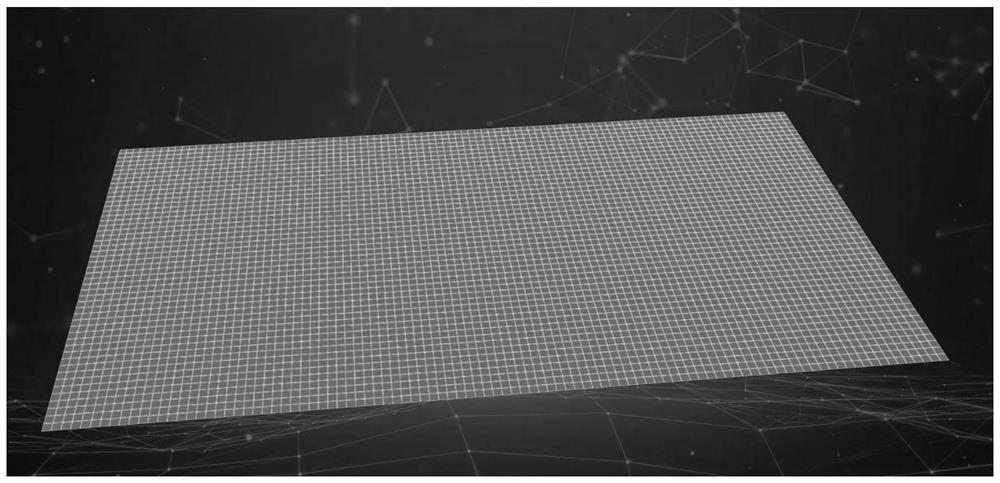
Three-dimensional real-time navigation method and system for earthwork construction
A navigation method and three-dimensional technology, applied in the direction of instruments, data processing applications, image data processing, etc., to achieve the effect of improving visualization, improving construction efficiency, and improving the degree of digital management
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0091] [Example 1] Path navigation planning of a manned bulldozer
[0092] For the straight-line operation of manned bulldozers, the goal is to find a straight-line operation direction and make full-arrangement straight-line operations in this direction to obtain the least number of fully-covered straight-line operation paths. The optimal straight-line operation direction is determined by the minimum number of operations, in order to flatten the land without repetition. Usually, the method of bulldozing along a certain corner or a certain side of the plot is divided into several vertical sections. Therefore, the operation of the straight-line operation method The number of times is equal to the width of the working area along the vertical working direction divided by the effective bulldozing width of the bulldozer.
[0093] Scenario assumptions:
[0094] 1) One coordinate point every five meters, that is, the distance between adjacent coordinate points is five meters, which i...
Embodiment 2
[0121] [Example 2] Unmanned bulldozer construction path navigation planning and blade working surface data generation
[0122] 1.1 Overview of the problem
[0123] In subgrade engineering, the straight-line operation of unmanned bulldozers is generally similar to the goal of manned bulldozers. It is also to find a straight-line operation direction, and make full-arrangement straight-line operations in this direction, and obtain the least number of full-coverage straight-line operations path. The optimal straight-line operation direction is determined by the shortest number of operations, in order to bulldoze all the land without repetition. Usually, the method of bulldozing along the corners of the plot is divided into several verticals. Therefore, the number of vertical bulldozing in the straight-line operation method It is equal to the width of the working area along the direction of the vertical bulldozing path divided by the effective bulldozing width of the bulldozer. I...
Embodiment 3
[0157] [Example 3] Construction path algorithm for grader
[0158] 1.1 Overview of the problem
[0159] The goal of the grader operation path planning is to find a straight-line operation direction, and make a full-arrangement straight-line operation in this direction, and obtain a fully-covered straight-line operation path with the least number of times. The optimal straight-line operation direction is determined by the shortest number of operations, in order to expect the land to be completely leveled without repetition. Usually, it is divided into several vertical flats along a certain corner or a certain side of the plot. Therefore, the repeated vertical The number is equal to the width of the working area along the vertical working direction divided by the effective leveling width of the grader.
[0160] Question assumptions:
[0161] 1) One coordinate point every five meters, that is, the distance between adjacent coordinate points is five meters;
[0162] 2) The path...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com