Hybrid quantum computing architecture for solving quadratic unconstrained binary optimization problem
A technology for quantum computing and optimization problems, applied in the field of quantum computing, which can solve problems such as the number of controllable quantum mechanical systems and the number of continuously executed control actions, and the instability of superposition/entanglement states of quantum mechanical systems.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0066] The features and numerous advantages of the method and hybrid quantum computing system according to the invention will be best understood from the detailed description of preferred embodiments with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which:
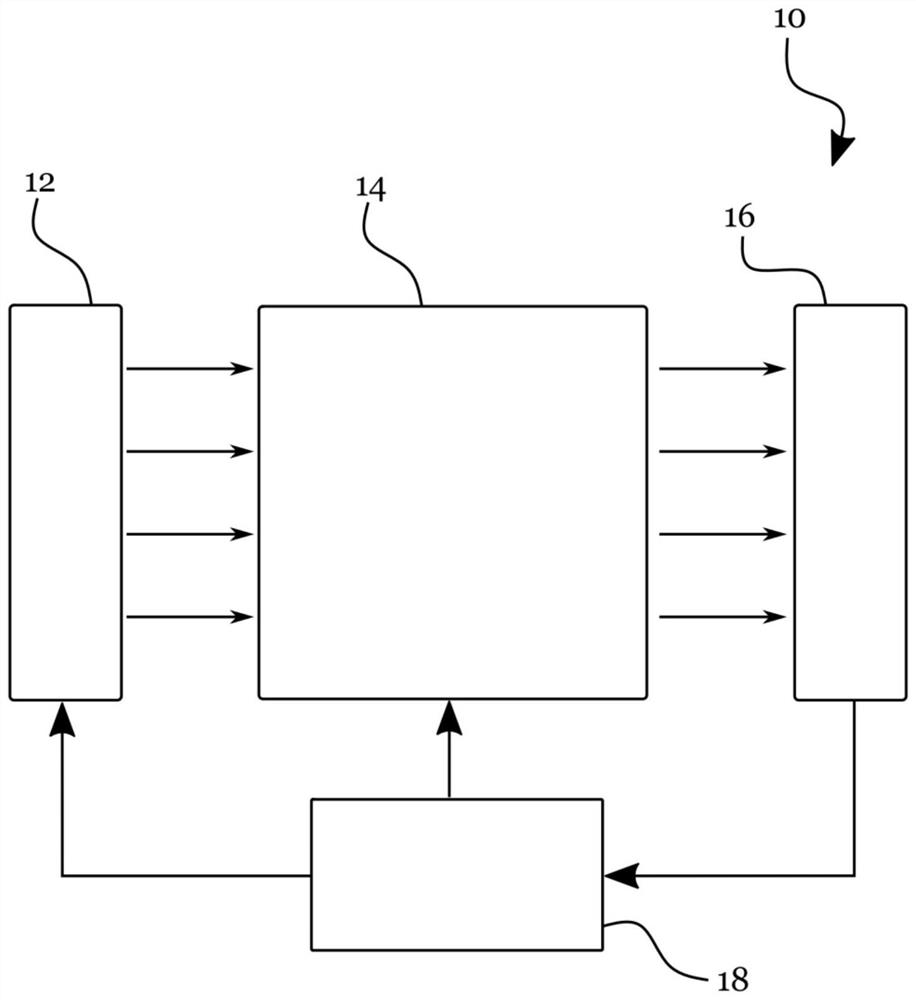
[0067] figure 1 An example of a hybrid quantum computing system is schematically illustrated;
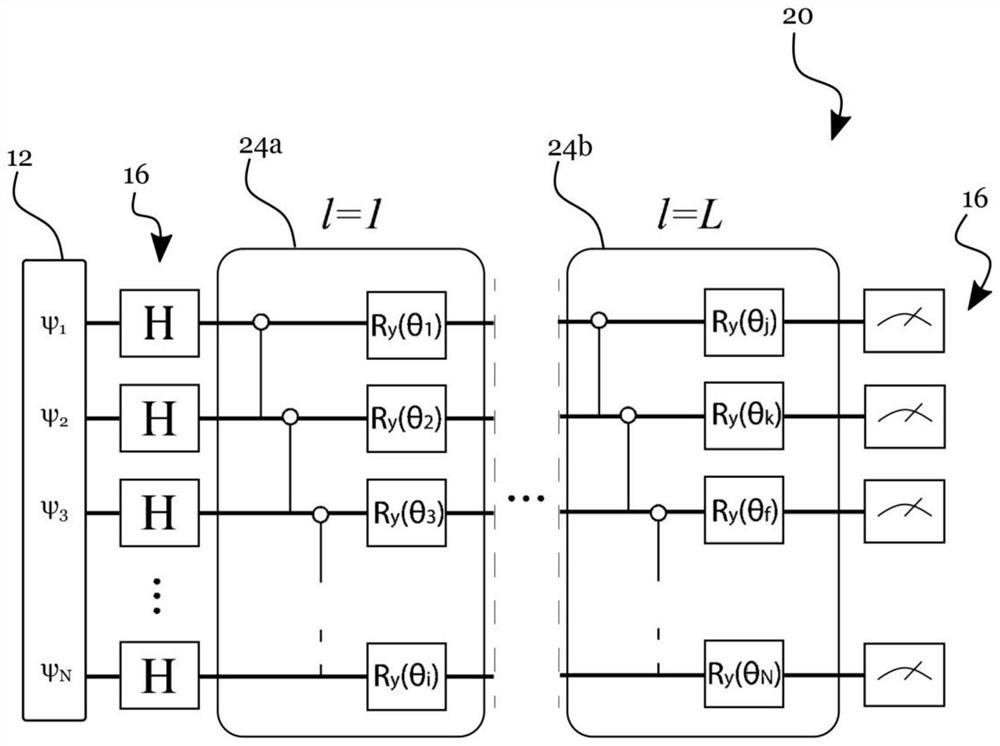
[0068] figure 2 An example of a quantum computing network 20 with a plurality of quantum gates is illustrated;
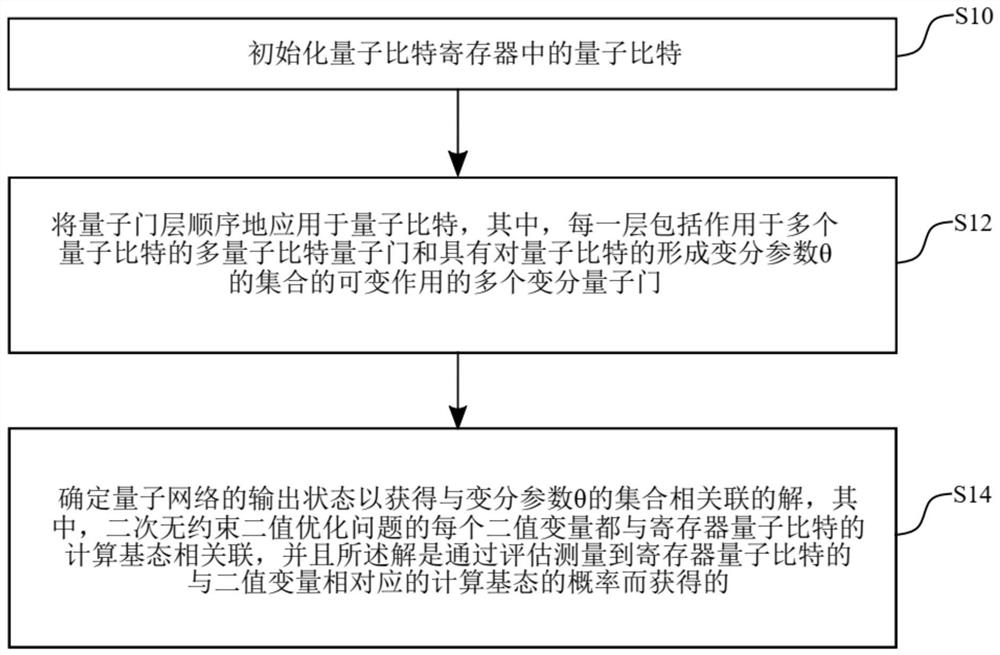
[0069] image 3 An example of a flowchart illustrating a method for obtaining a solution to a QUBO problem;
[0070] Figure 4 An example of a flowchart illustrating a method for iteratively improving a solution to a computational problem using a quantum computing network;
[0071] Figure 5 A flowchart illustrating an iterative method for improving the solution of a computational problem using a quantum computing network;
[0072] Figure 6A , Figure 6BTwo graphs illustrating the simulated performance of hyb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com