Robot path exploration method based on double-agent competitive reinforcement learning
A reinforcement learning and intelligent body technology, applied in instruments, computer parts, biological neural network models, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in designing an ideal reward function, easy to be affected by random noise, etc., to solve the problem of sparse reward, strong The effect of robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
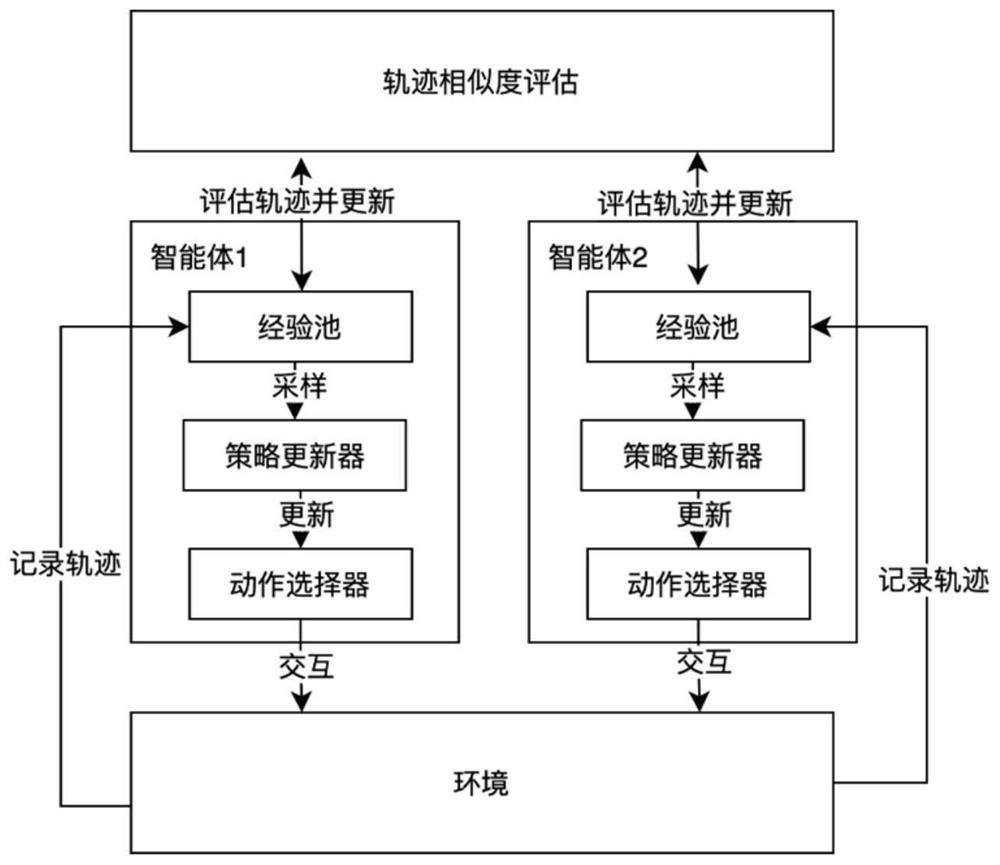
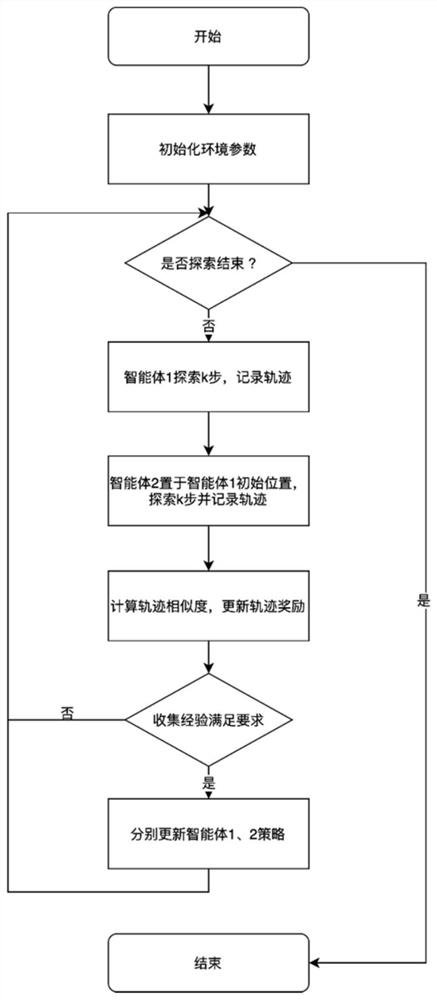
[0040] A kind of method of the present invention, the present invention is a kind of robot path exploration method based on dual-agent competitive reinforcement learning, utilizes two intelligent bodies (in this example, be two identical robots or a robot in repeatable experimental environment) The similarity of the exploration state is used to generate intrinsic rewards, thereby enhancing the agent's exploration, without the need for complex reward function design, avoiding the introduction of domain knowledge, and using the certainty of the agent's explored trajectories to eliminate the influence of random noise.
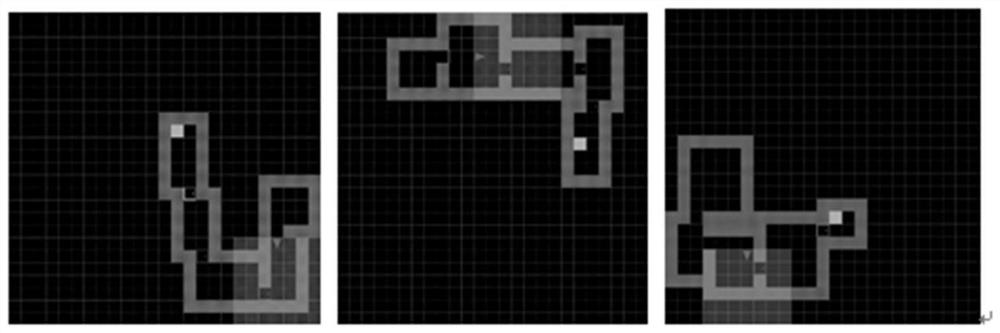
[0041] The framework diagram of this method is shown in the figure 1 As shown, the verification environment adopts the reinforcement learning test environment MultiRooms trajectory exploration environment, that is, a series of exploration environments with 4 to 6 rooms are randomly generated in the two-dimensional grid plane, as shown in figure 2 As shown, the tr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com