Treatment of diabetic retinopathy with whole human post-translationally modified anti-VEGF Fab
A retinopathy, diabetic technology for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy with a fully human post-translationally modified anti-VEGF Fab
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
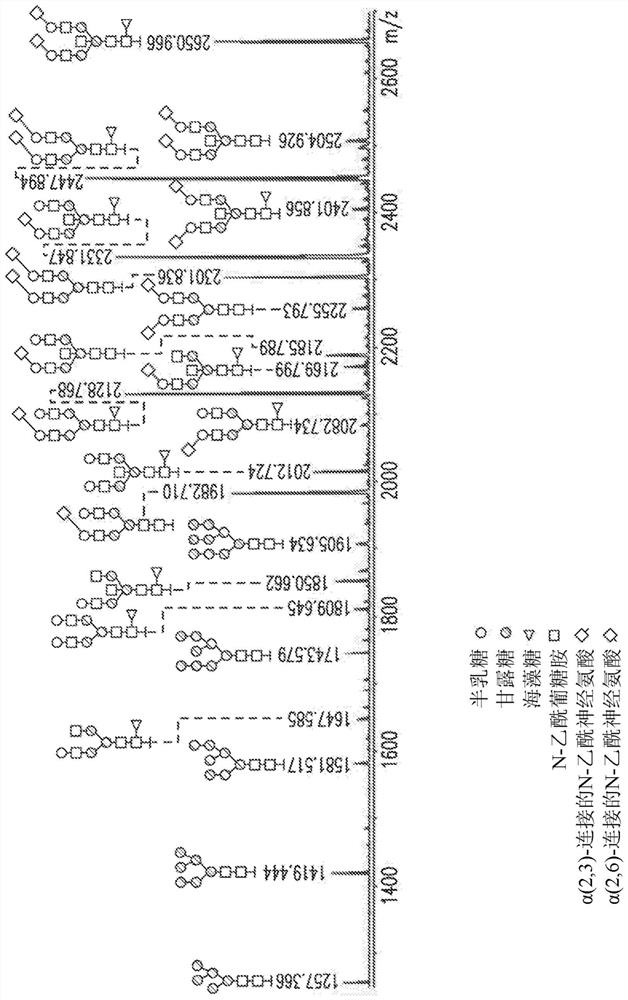
Image
Examples
example 2
[0416] 6.2 Example 2: Ranibizumab cDNA-based vector
[0417] A ranibizumab Fab cDNA-based vector comprising a transgene comprising the ranibizumab Fab light and heavy chain cDNAs (not encoding the portion of SEQ ID NO. 12 and 13 of the signal peptide, respectively) was constructed. Transgenes also include nucleic acids comprising a signal peptide selected from the group listed in Table 1. The nucleotide sequences encoding the light and heavy chains are separated by an IRES element or 2A cleavage site to generate a bicistronic vector. Optionally, the vector additionally includes a hypoxia-inducible promoter.
example 3
[0418] 6.3 Example 3: Vectors based on hyperglycosylated bevacizumab Fab cDNA
[0419] A hyperglycosylated bevacizumab Fab cDNA-based vector comprising a transgene comprising the bevacizumab Fab of the light and heavy chain cDNA sequences (SEQ ID NO. 10 and 11, respectively) was constructed. A portion having a mutation in the sequence encoding one or more of the following mutations: L118N (heavy chain), E195N (light chain) or Q160N or Q160S (light chain). Transgenes also include nucleic acids comprising a signal peptide selected from the group listed in Table 1. The nucleotide sequences encoding the light and heavy chains are separated by an IRES element or 2A cleavage site to generate a bicistronic vector. Optionally, the vector additionally includes a hypoxia-inducible promoter.
[0420] 6.4 Example 4: Hyperglycosylated ranibizumab cDNA based vector
[0421] A vector based on the hyperglycosylated ranibizumab Fab cDNA comprising the transgene comprising the ranibizumab li...
example 7
[0476] 6.7 Example 7: Open-label Phase 2a Dose Evaluation of Construct II Gene Therapy in Participants with Diabetic Retinopathy
[0477] This example is an updated version of Example 6 and provides an overview of the Phase 2a dose evaluation of Construct II gene therapy in participants with diabetic retinopathy (DR). Continued stable expression of the construct II transgene product following a single gene therapy treatment for DR could potentially reduce the treatment burden of currently available therapies while preserving vision, its favorable benefit:risk spectrum. The current proof-of-concept study was designed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Construct II gene therapy at 2 different dose levels in participants with DR.
[0478] 6.7.1 Purpose and Endpoints
[0479] Table 6: Primary Purposes and Endpoints and Secondary Purposes and Endpoints
[0480]
[0481]
[0482]
[0483] AAV8 = adeno-associated virus serotype 8; AE = adverse event; CI-DME = centrally...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com