Virus exposure profile for detecting early hepatocellular carcinoma
A hepatocellular carcinoma, virus technology, applied in the field of identifying subjects with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma, can solve problems such as non-existence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0077] Example 1: Method
[0078] This example describes the materials and experimental procedures used for the studies described in Example 2.
[0079] Participants and VirScan Analysis
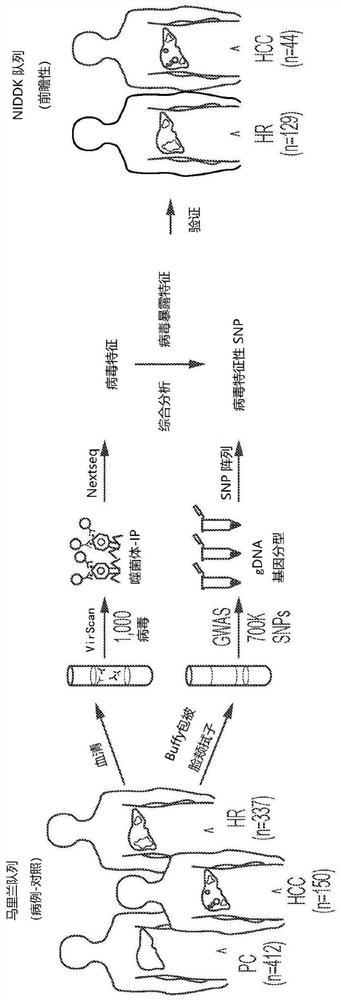
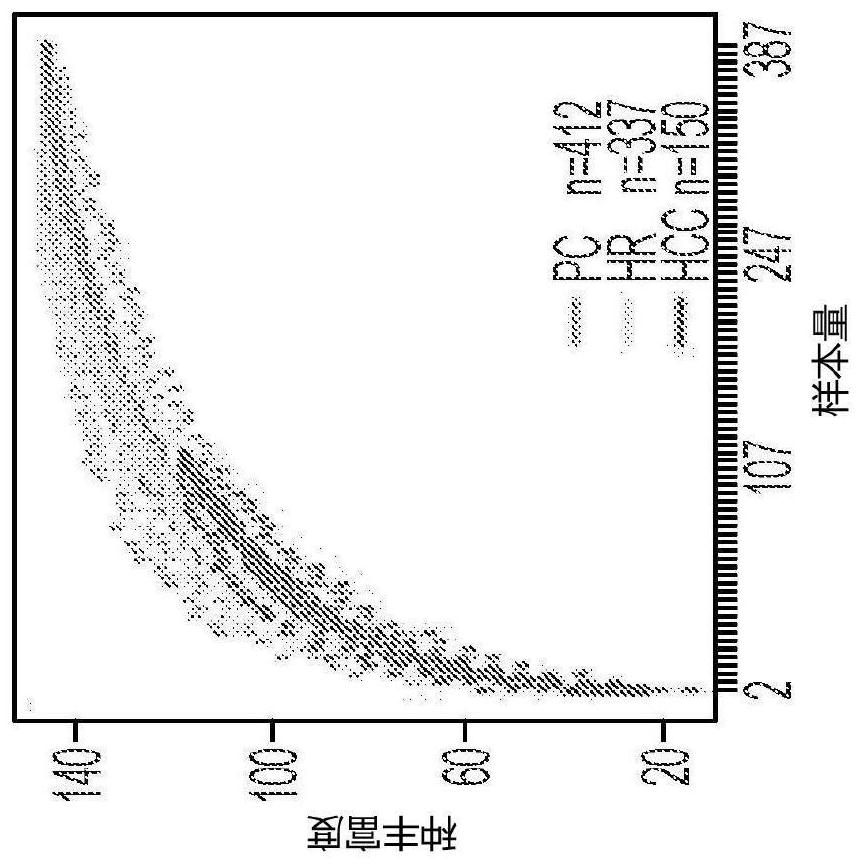
[0080] The patient cohort consisted of 899 sequentially enrolled participants (clinicaltrials.gov number: NCT0091375), including 150 HCC cases, 337 CLD as at-risk individuals (HR or AR, used interchangeably), and 412 healthy volunteers as an age- and sex-matched population control (PC) ( Figure 1A ).
[0081] study cohort
[0082] UMD queue. To measure virus-host interactions, 899 participants were recruited. Participants were grouped into (1) a population control group (PC, n=412) if they were relatively healthy without any liver disease diagnosis; (2) if diagnosed with chronic liver disease (hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), hepatitis D virus (HDV), aflatoxins from fungal contamination, alcohol, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and nonalcoholic steatohepatit...
Embodiment 2
[0107] Example 2: Viral Exposure Signature (VES) for Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
[0108] This example describes the development of two viral exposure signatures - the first VES based on detection of 61 virus strains and the second VES based on detection of 31 virus strains - to identify subjects at risk for HCC.
[0109] OVERVIEW OF VIRUS EXPOSURE CHARACTERISTICS
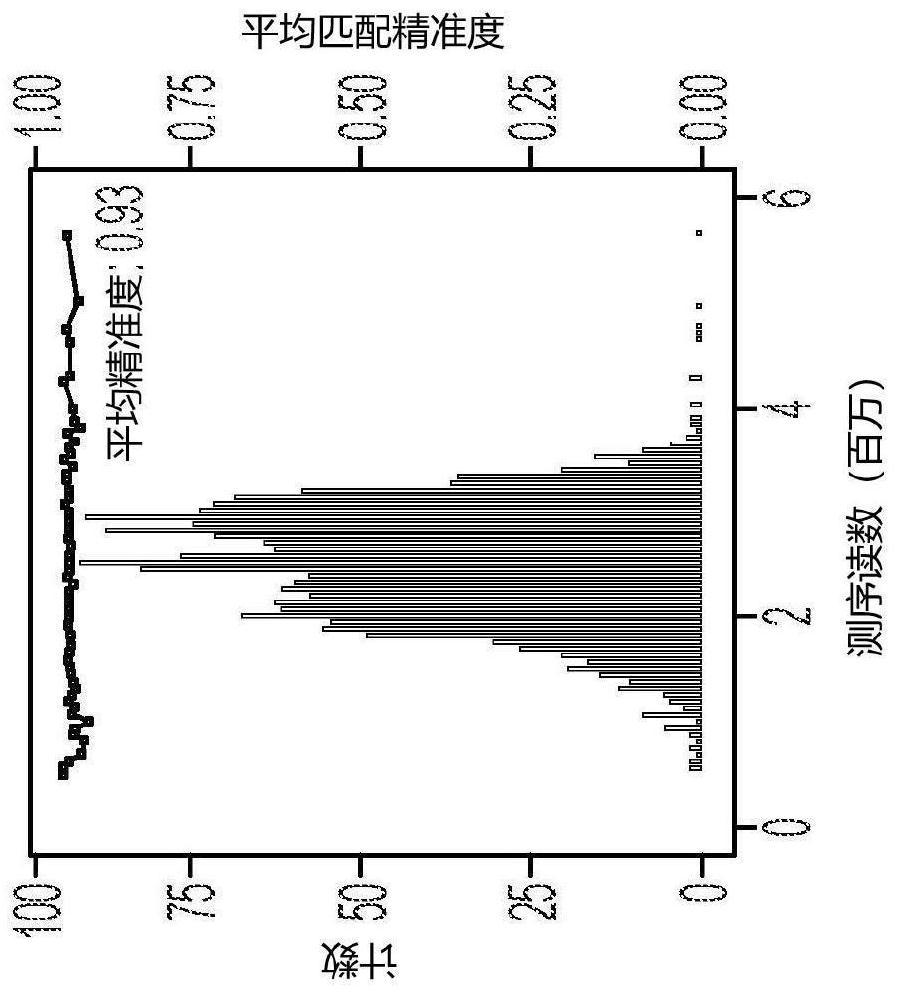
[0110] VirScan applied a phage display library covering 93,904 viral epitopes, representing 206 human virus species and over 1000 virus strains, to screen for prior exposure history (Xu et al., Science 2015;348:aaa0698). Phage particles with epitopes recognized by participant antibodies were immunoprecipitated (Phage-IP), followed by sequencing of the encoded DNA barcodes ( Figure 1A ). A case-control design of the Maryland (NCI-UMD) cohort was used to characterize virus exposure. Enrollment and enrolment of study subjects at Figure 5E As outlined in CONSORT guidelines (Schulz et al., BMJ340:c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com