Bit likelihood calculation method and demodulation device
A calculation method, a likelihood technique, applied in phase-modulated carrier systems, other decoding techniques, shaping networks in transmitters/receivers, etc., and can solve problems such as hindering bit likelihood
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment
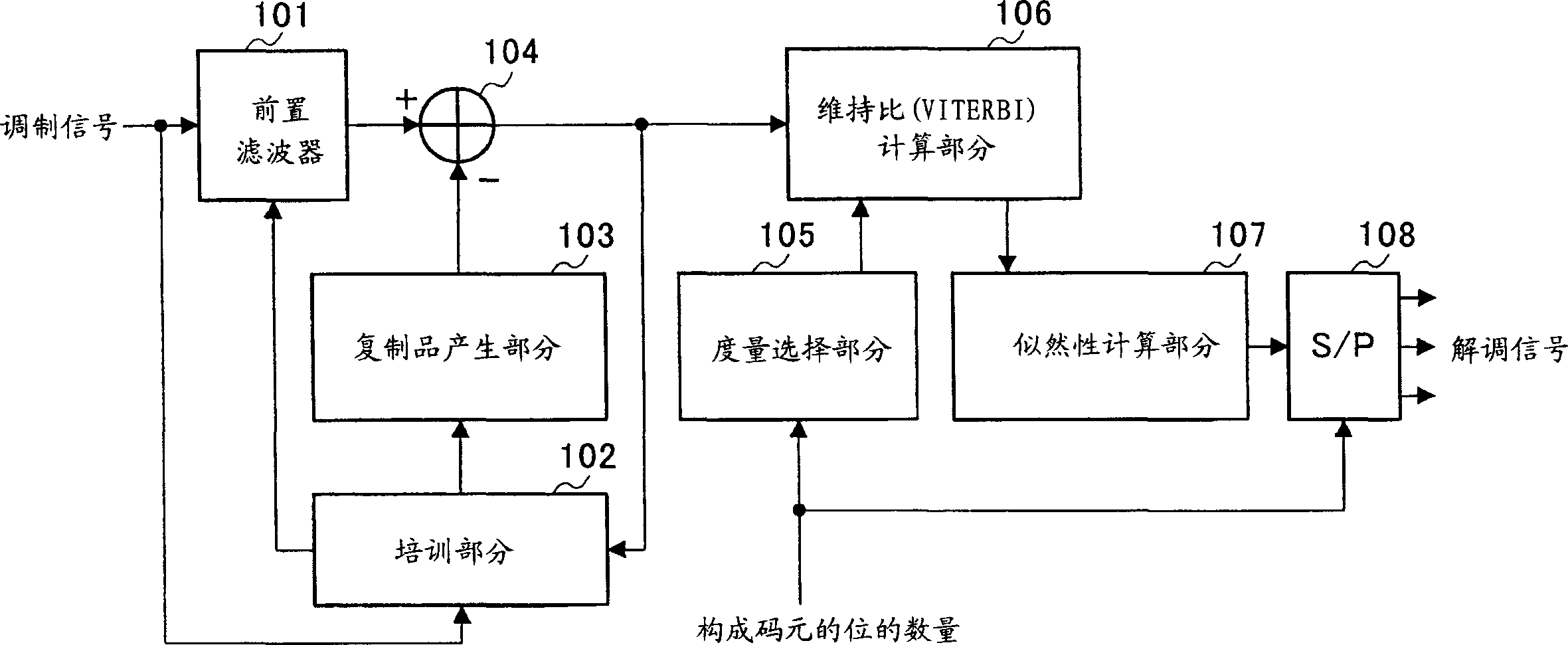
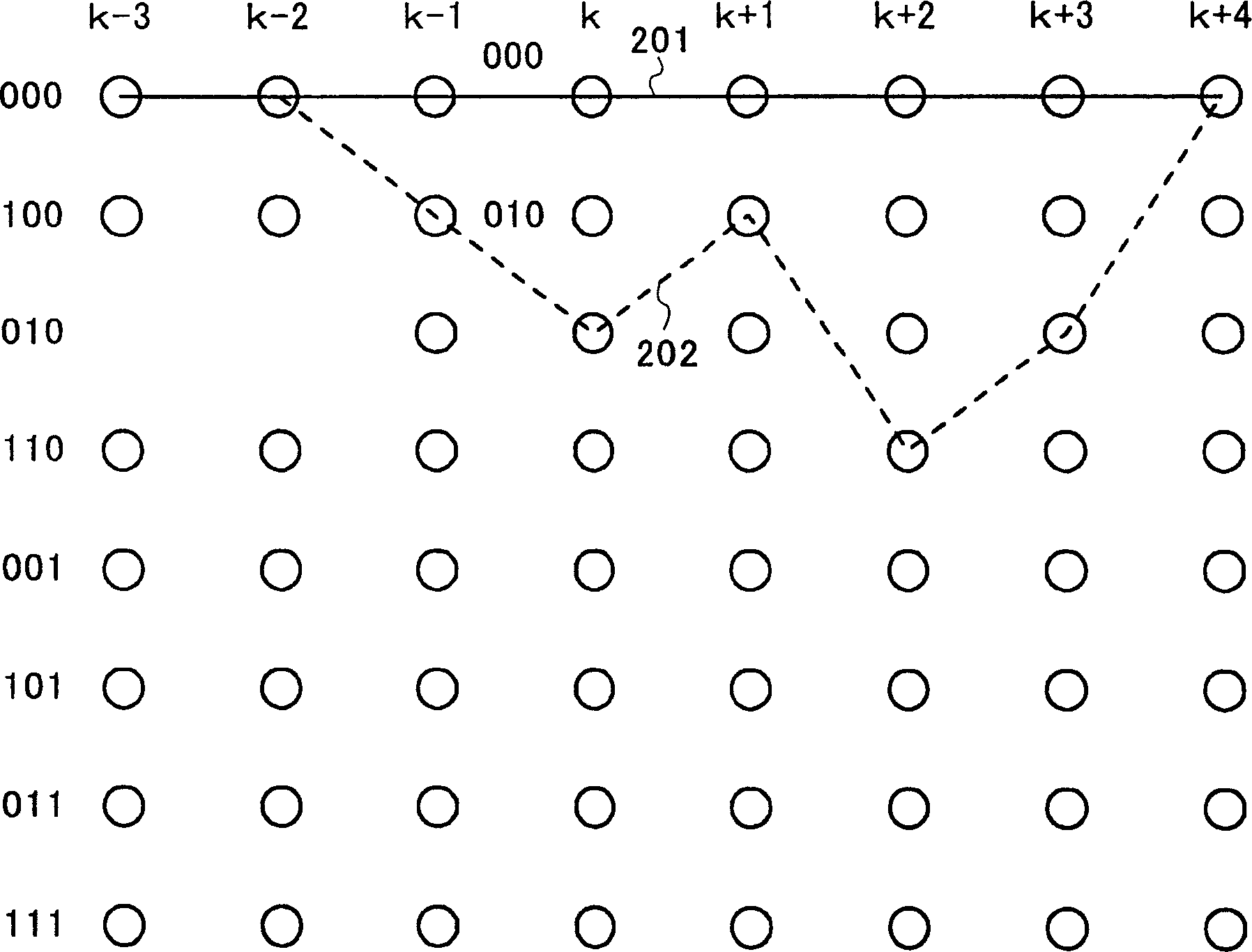
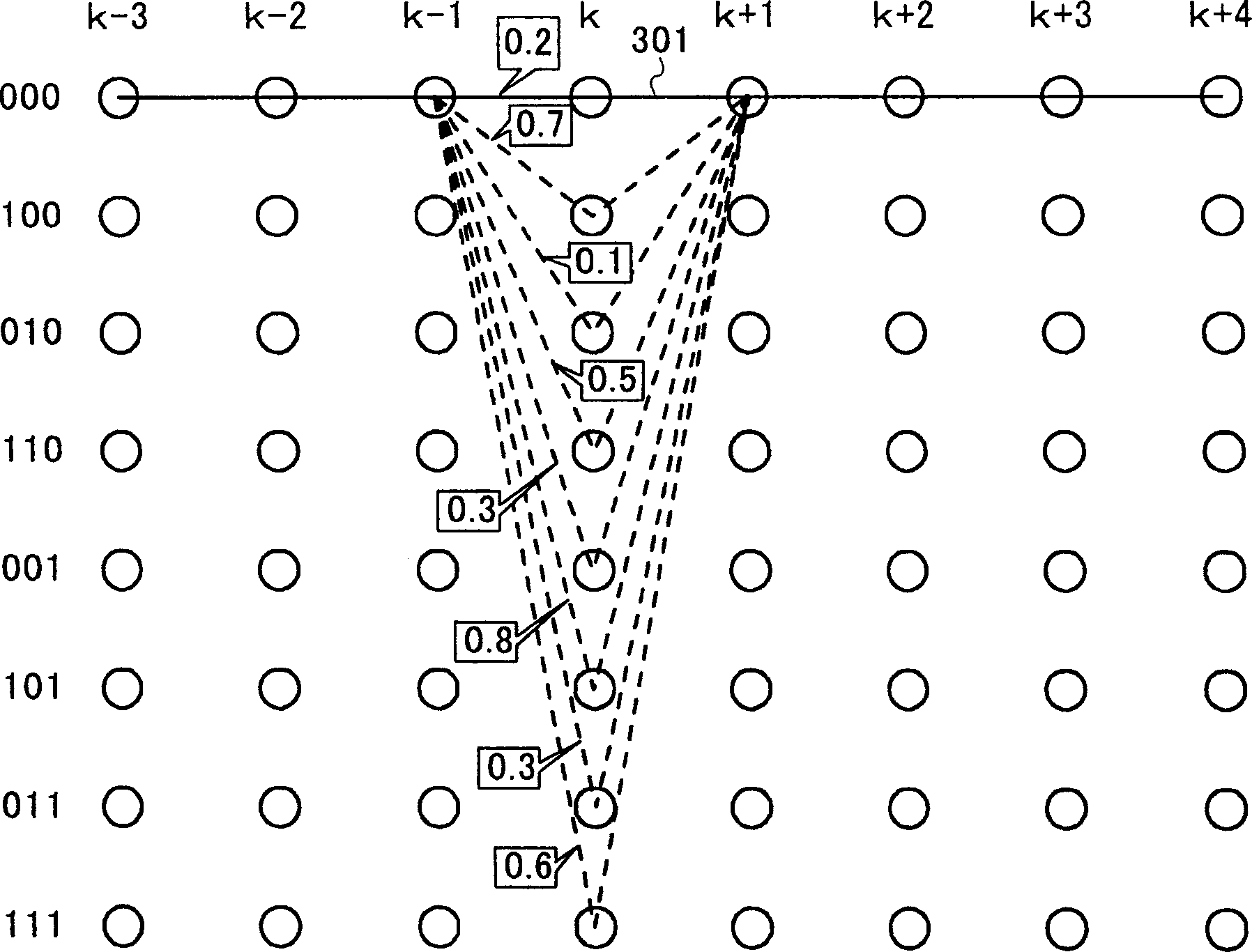
[0012] First, Viterbi equalization considering a signal delayed by only one unit time (for example, 1 symbol time) requiring constraints is explained. In realizing Viterbi equalization, a prefilter is often provided to prevent deterioration caused by timing jitter or the like. Here, when prefilter taps (taps) and replica taps (replica taps) of Viterbi equalization are determined according to the MMSE (Minimum Mean Sequence Estimator) standard, all taps become "0 ". To avoid this, the tap of the previous signal corresponding to the replica tap is fixed to 1 as a constraint. When such Viterbi equalization is used, the present invention relates to a bit likelihood calculation method.
[0013] Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
[0014] figure 1 A block diagram showing the structure of a demodulation device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
[0015] The pre-filter 101 ab...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com