Annealing control primer and the use of the same annealing control primer
A technology of annealing and primer pairs, applied in the field of application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0407] Example 1: Estimating the role of universal bases in ACP
[0408] The role of universal base residues located between the 3'- and 5'-terminal parts of ACP can be assessed by RT-PCR using mouse embryonic tissue.
[0409] Total RNA was obtained from intact embryos of murine ICR at gestational days 4.5, 11.5, and 18.5 by using Tri-reagent (Sigma) or the LiCl / urea method (Hogan et al., 1994) were extracted. Two independent cDNA amplification experiments using ACP were performed to detect the following effects of universal bases located between the 3'- and 5'-terminal parts of ACP, in particular, deoxyinosine residues: A.ACP 3' Effect of deoxyinosine residues between - and 5'-terminal parts compared with ACP and conventional primers without deoxyinosine groups; B. Deoxyinosine residues between 3'- and 5'-terminal parts of ACP The effect of xanthosine residues as a function of the number of deoxyinosines.
[0410] These experiments were conducted based on the following a...
Embodiment 2
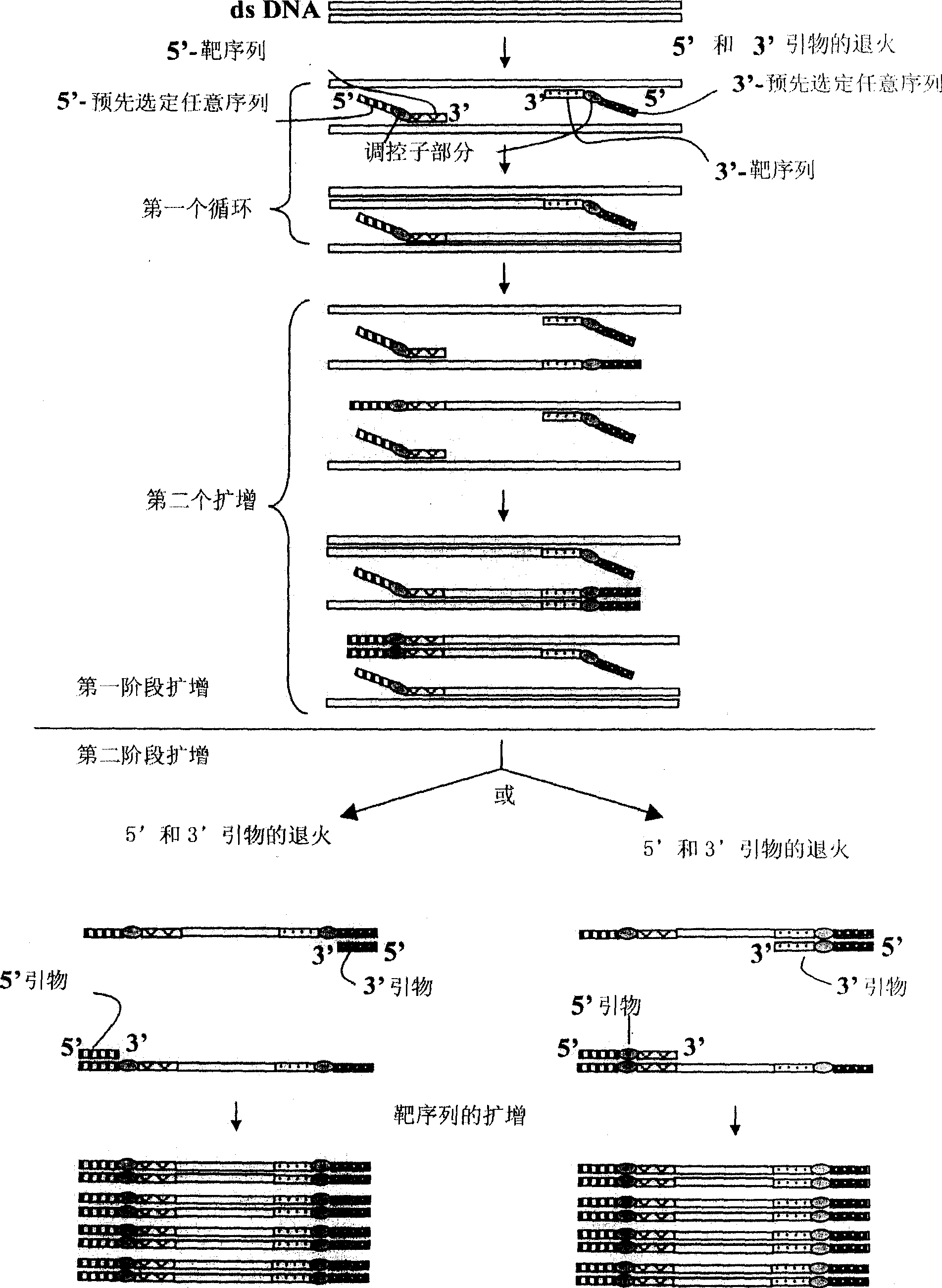
[0439] Example 2: Method for Amplifying a Target Nucleic Acid Sequence Using ACP
[0440] The ACP of the subject invention was used to amplify the target nucleotide sequence of the mouse placenta-specific homebox gene Esx1 cDNA. The procedure and results of using ACPs to amplify the target nucleotide sequence of Esx1 cDNA are described here. Total RNA (3 μg) extracted from placentas of 18.5-day-old mice was used as starting material. In addition to using oligo-dT 15 First-strand cDNAs were prepared under the same conditions as the cDNA synthesis in Example 1 as primers for first-strand cDNA synthesis.
[0441] oligo-dT 15 5'-TTTTTTTTTTTTTTTT-3' (SEQ ID NO: 54)
[0442] The resulting first-strand cDNAs were used as templates to amplify the target cDNA fragment of Esx1 using ACPs. These experiments performed a two-stage PCR amplification which is one of the unique features of the present invention.
[0443] The conventional primers of Esx1 used in this example are:
[...
Embodiment 3
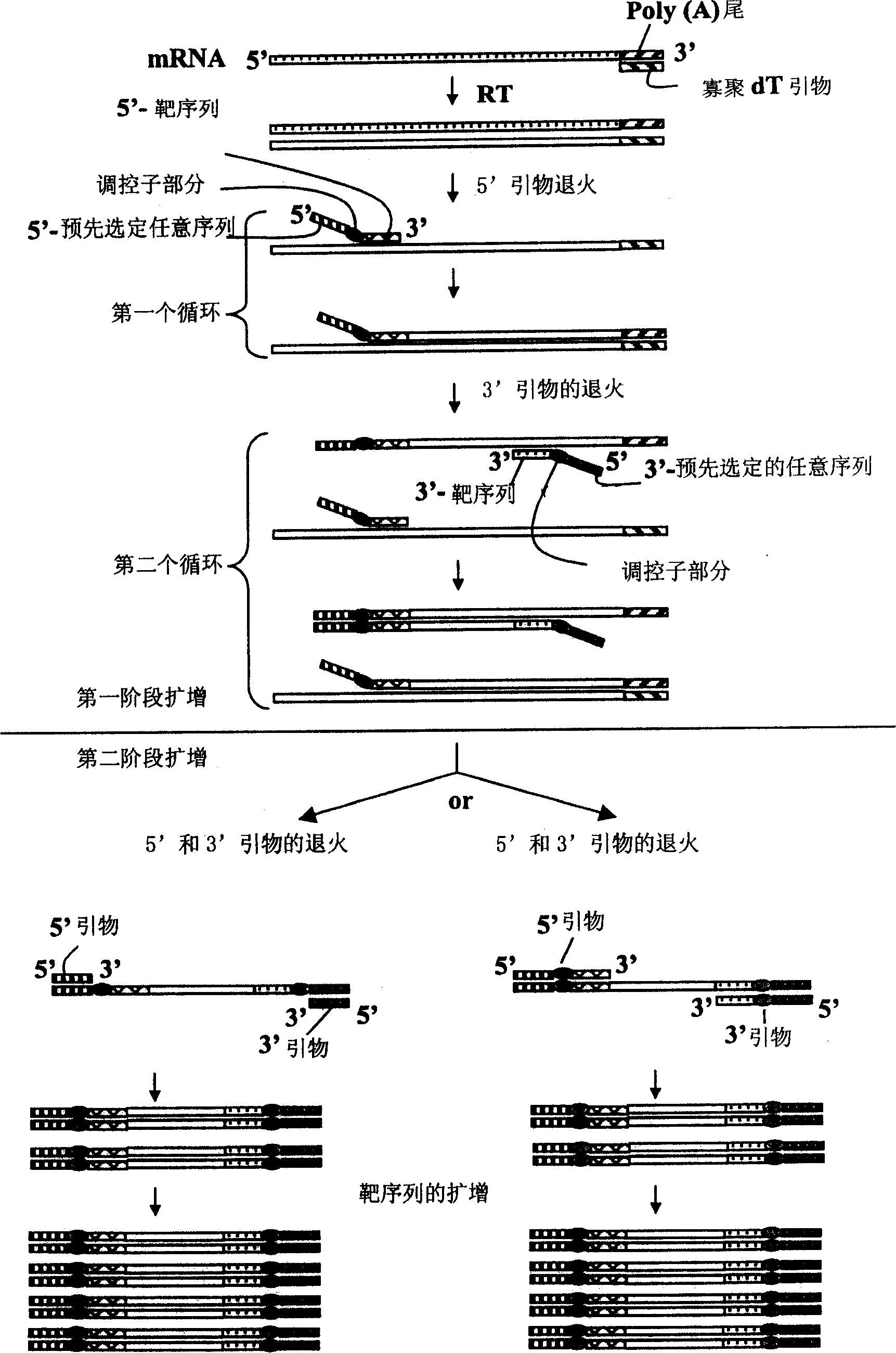
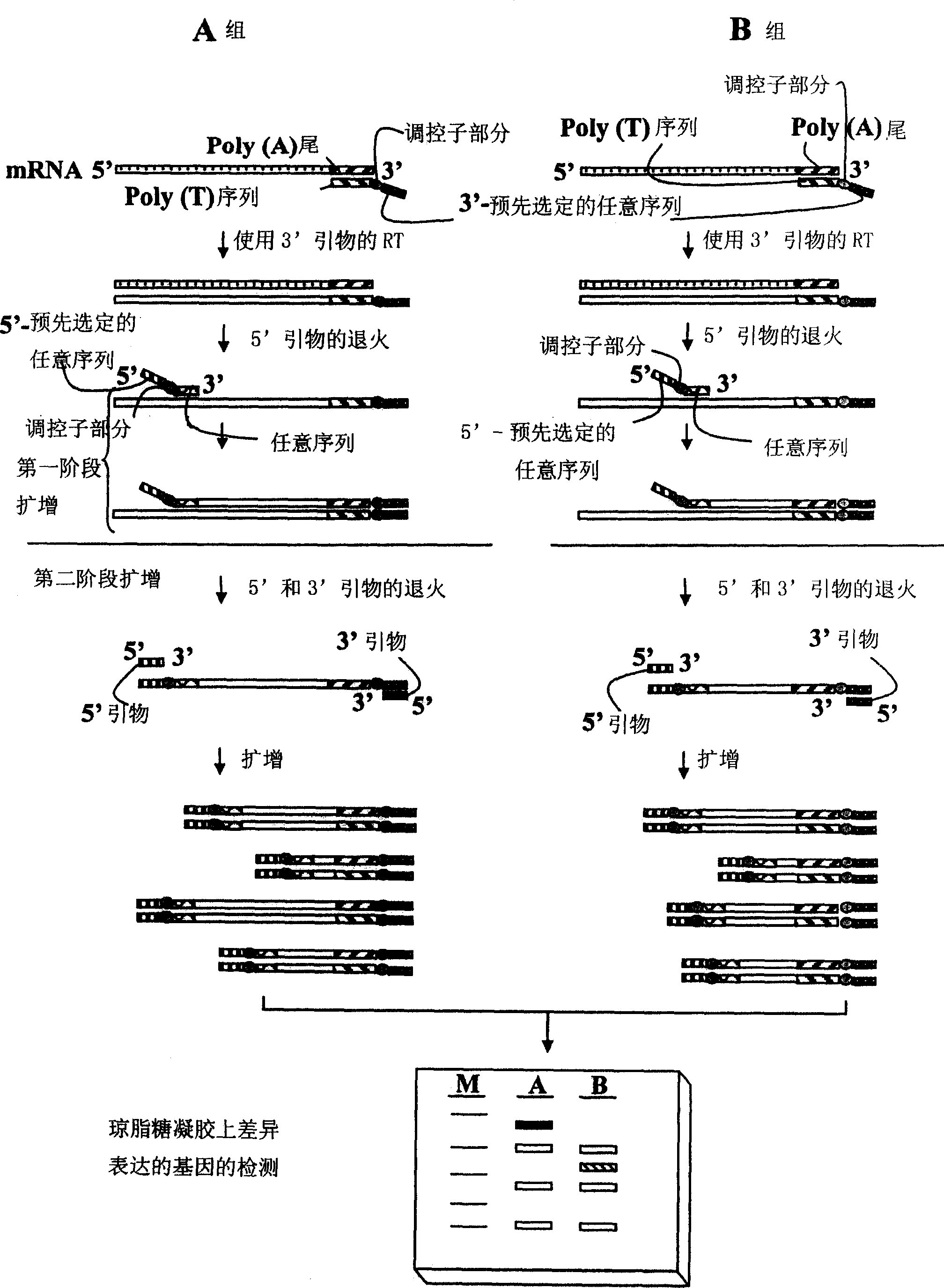
[0492] Example 3: Differentially Expressed mRNAs During Mouse Embryo Development Using ACP Identification and Characterization
[0493] The ACP of the subject invention has been used to detect differentially expressed mRNAs in embryonic development. In particular, three different protocols and results are described here using total RNAs from embryonic tissues at different developmental stages as starting material. The primers used in the subject invention are shown in Table 1.
[0494] A1. Process 1
[0495] step 1): Synthesis of first-strand cDNA
[0496] Use dT 10 -ACP1 or JYC5-T 15 -ACP as a primer for cDNA synthesis First-strand cDNAs were prepared under the same conditions as in Example 1 for cDNA synthesis. The resulting cDNAs were purified by spin column (PCR purification kit QIAGEN) to remove primers, dNTPs and the above reagents. A purification step must be performed before measuring the concentration of cDNAs absorbing at 260 nm using a UV spectrometer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com