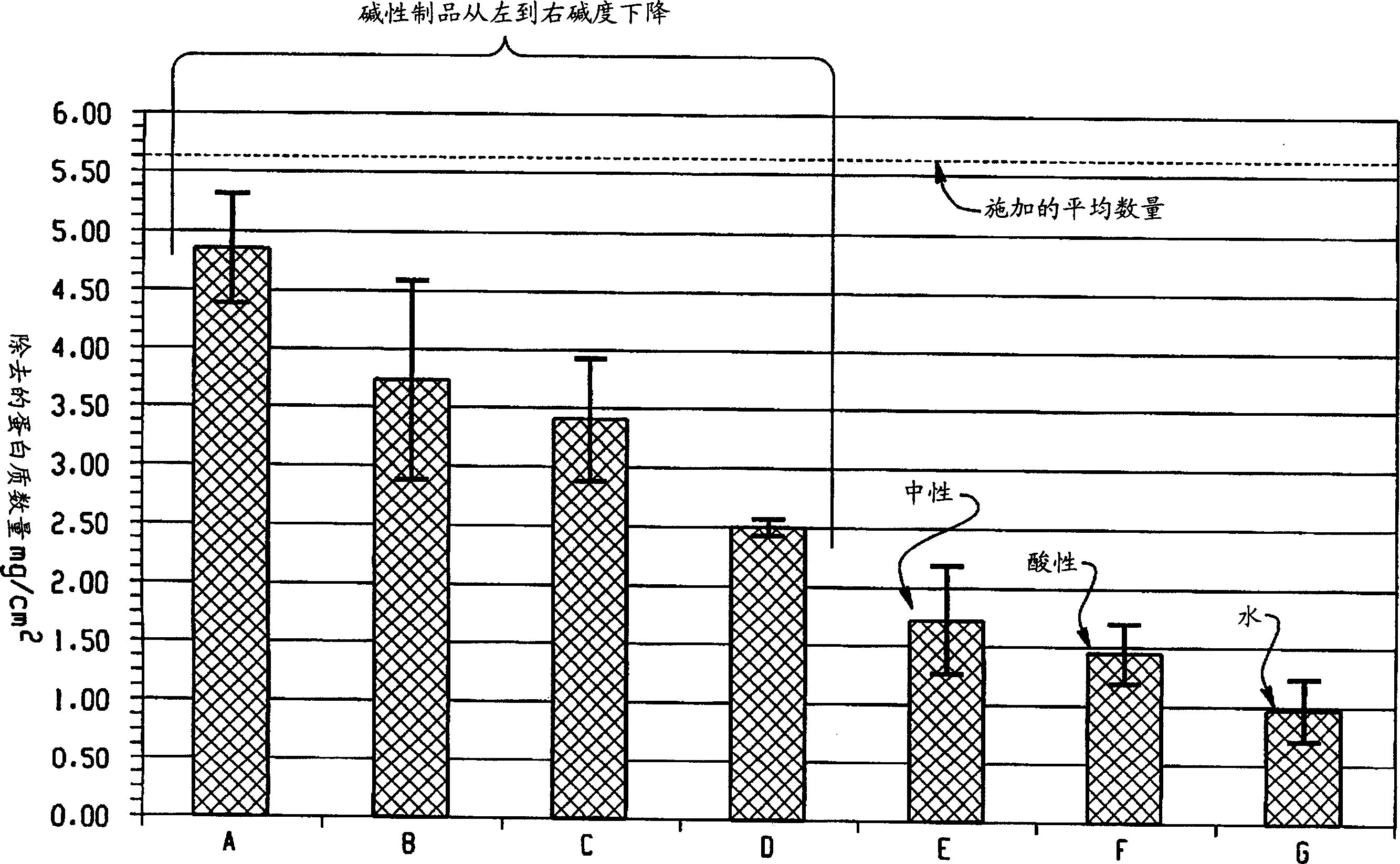
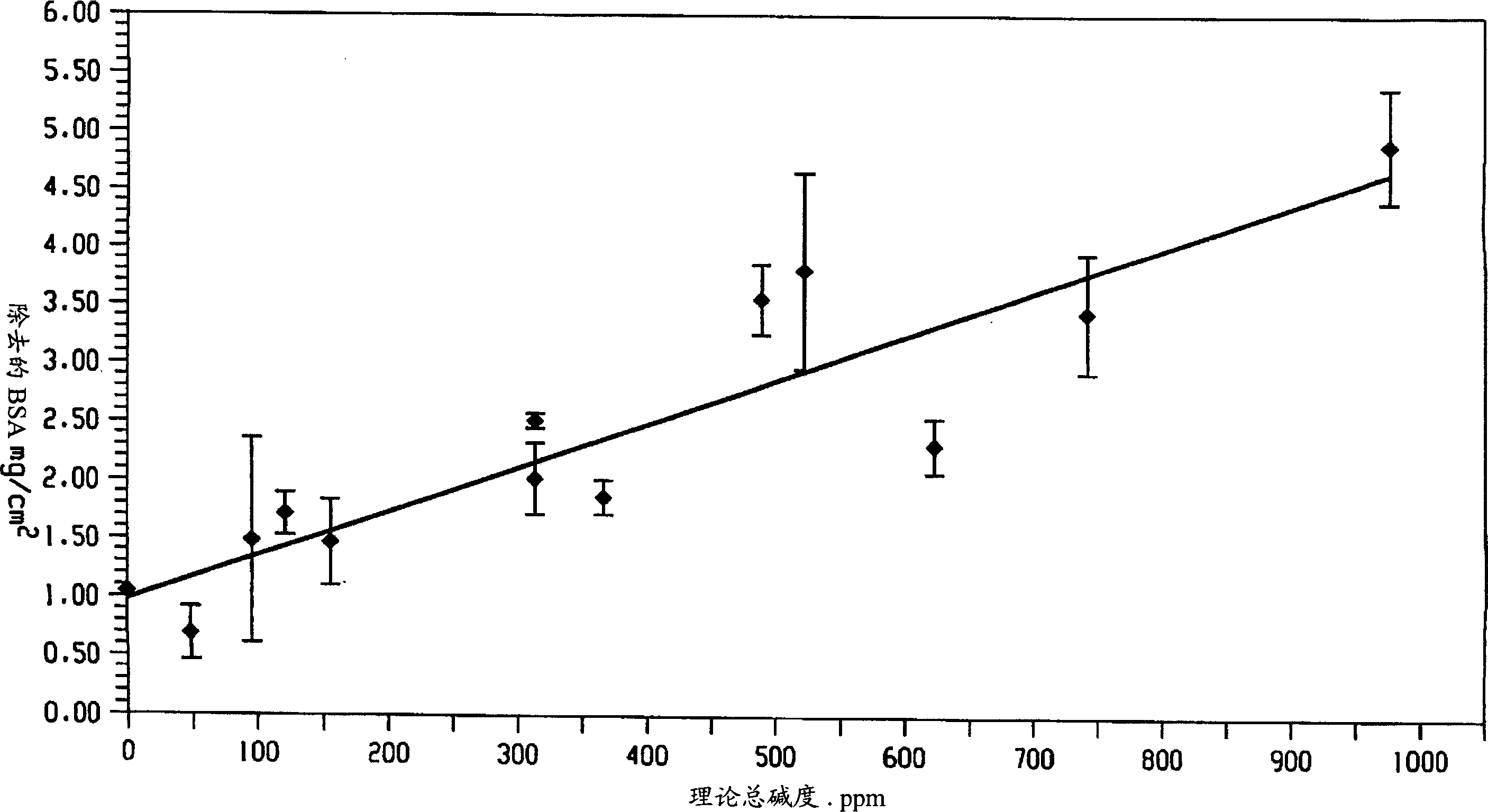
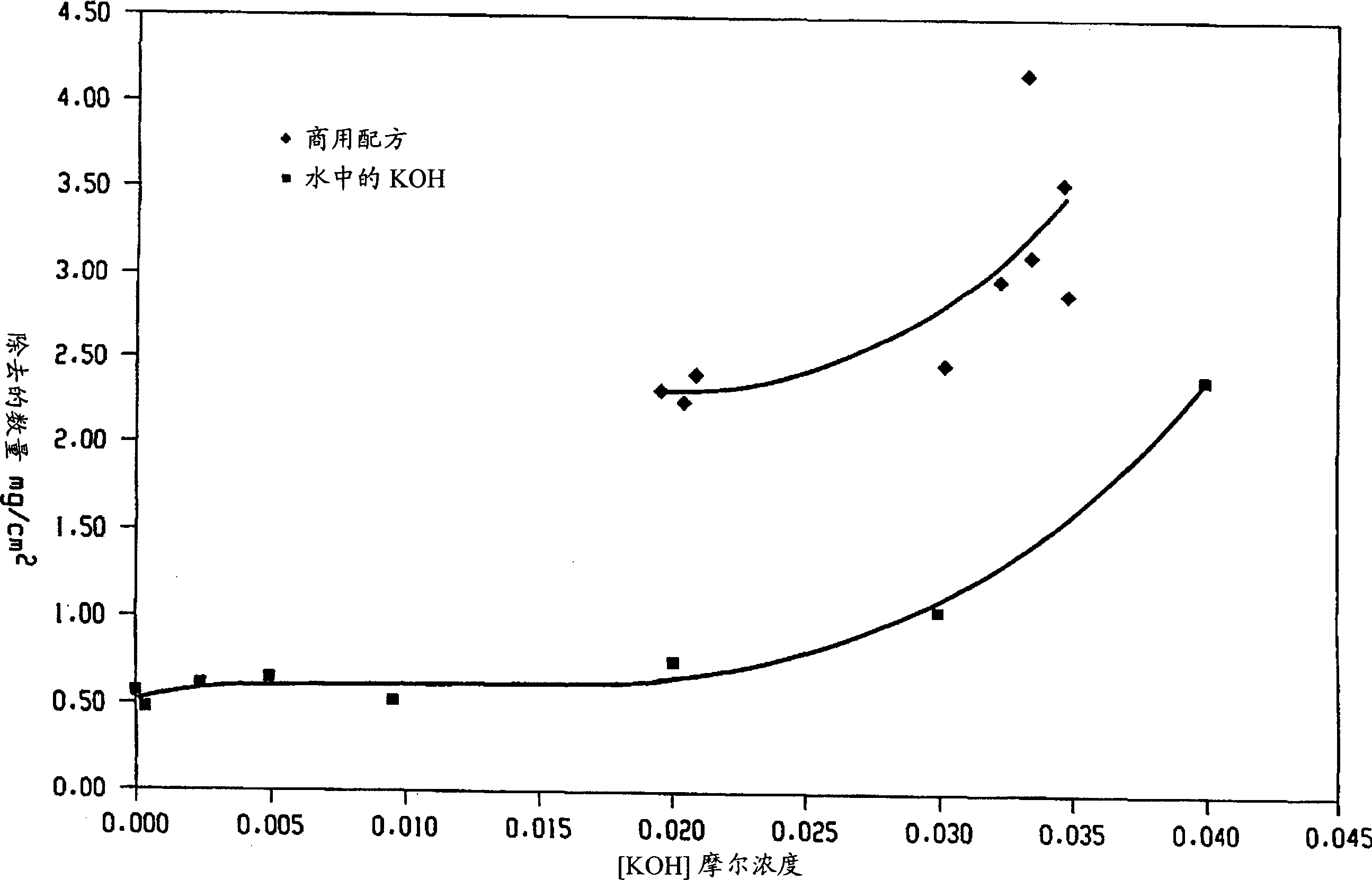
Decontamination of surfaces contaminated with prion-infected material with oxidizing agent-based formulations
A technology of prions and oxidants, applied in the direction of detergent materials, detergent compounding agents, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of damage to medical equipment, damage, etc., and achieve the effect of alleviating the effect of equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] Samples were prepared by treating it with a prion model (BSA denatured protein). The samples were then treated with a composition containing peracetic acid at a concentration of 1,000 mg / L at 40-60°C. The composition also includes a surfactant system, a phosphate buffer system, an organic corrosion inhibitor, and a chelating agent. The composition is free of heavy metals.
[0069] Table 4 summarizes the amount of BSA decomposed during 12 minutes of exposure to the composition.
[0070] temperature(℃)
[0071] The results showed that at 40°C and 45°C, little, if any, protein breakdown occurred. Whereas, at 50°C and 55°C, proteins were efficiently decomposed. At 60°C, some protein residue remained, suggesting protein clumping. That is, when the temperature is around and above 60°C, the protein aggregates and has a higher resistance to protect itself from attack by peracetic acid or other strong oxidants.
[0072] The effect of peracetic acid concentration o...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Ileal fluid-dependent organism (IFDO) form prion model specimens were treated with peracetic acid formulations as described in Example 1 at 50°C with peracetic acid concentrations of 0-2,000 mg / liter, and then in modified mycoplasma cultured in liquid medium. Aliquots of the IFDO suspension were added directly to 1,000 mg / liter, 1,500 mg / liter, 2,000 mg / liter, and 2,500 mg / liter peracetic acid solutions at 50°C. The models were then incubated in modified Mycoplasma liquid medium for 48 hours at 37°C. Figure 5 Shown is the logarithm versus time curve for the prion model in solutions of 0, 1,000, 1,500, 2,000, and 2,500 mg / liter. An initial concentration of 2,500 mg / liter of peracetic acid is preferred since high concentrations of material on practical devices can decompose peracetic acid.
Embodiment 3
[0078] Specimens of the prion model of ileal fluid-dependent organism (IFDO) morphology were treated with 1,500 mg / L peracetic acid formulation at various temperatures between 25-60°C and then cultured in modified mycoplasma-based agar such as as described in Example 2. Image 6 The relationship between the logarithmic decline of the prion model and the time is described when the temperature is 25, 30, 40, 45, 50, 55, and 60 °C, respectively. The formulation is optimal at temperatures above 50°C. However, since proteins may coagulate at temperatures above about 60°C (as illustrated in Table 4), the optimal temperature for prion denaturation is 50-60°C, more specifically 53-57°C.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com