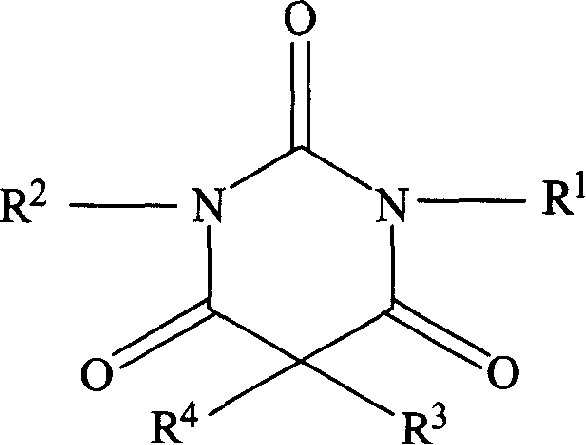
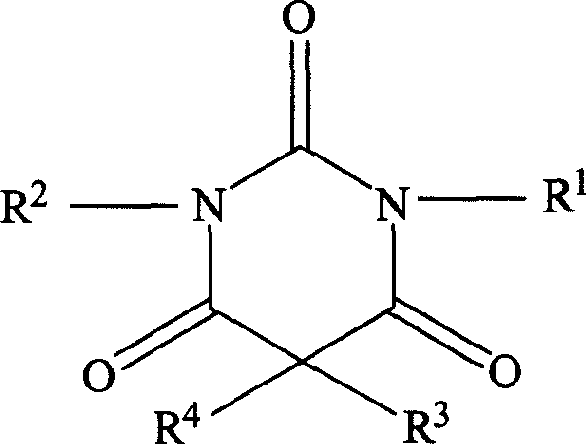
Non-sedating barbituric acid derivatives
A sedative and barbiturate technology, applied in the direction of drug combinations, organic active ingredients, nervous system diseases, etc., can solve the problems of not teaching non-sedating barbiturates, not teaching sedative barbiturates, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0123] The anticonvulsant activity of the barbituric acid derivatives of the invention can be demonstrated or tested by evaluating the prevention of maximal electroshock seizures (MES) in treated mice. The MES test is widely used to evaluate the anticonvulsant properties of compounds, mainly because of the good correlation between test results and clinical findings of effects in patients with epilepsy. In a typical MES test in which corneal electrodes are used, a current of about 150 mA and a stimulus of 60 Hz are applied for about 200 milliseconds to evaluate the anticonvulsant properties of the barbituric acid derivatives of the present invention. Mice were tested prior to dosing in order to exclude from the study any animal that did not respond to complete tonic convulsions including tonic extension of the hind limbs (THE), which served as a basis for evaluating the efficacy of the active substances used. Animals protected by THE are considered protected in the MES test.
...
Embodiment 2
[0126] The non-toxicity of the barbituric acid derivatives of the present invention can be tested by repeated high-dose administration, as follows:
[0127] The test compound is suspended in warmed polyethylene glycol 400 or other suitable solvent and administered to eg Sprague-Dawley rats via gastric tube at an initial dose of about 1500 mg / kg. A similar dose was given to the same mice 24 hours later, and a similar dose was given to the same mice again 48 hours after the first dose. Animals were checked several hours after dosing, again before the next dose, and 3 days after the last dose. Administration is monitored for toxic effects as well as behavioral effects such as locomotion, avoidance behavior, feeding or any other observable effects.
Embodiment 3
[0129] The sedative and muscle relaxant properties of the barbituric acid derivatives of the invention can be demonstrated by monitoring the behavior and locomotor effects of the treated mice.
[0130] For example, a test composition may be administered intraperitoneally, eg, in Swiss Webster rat alkalized saline. The time required for animals to receive various doses to exhibit specific motor and behavioral effects is recorded. Surveillance effects may include, for example, muscle hypotonia, locomotor activity, tranquility, and avoidance behavior. Toxic effects were also recorded.
[0131] The efficacy of the composition can be evaluated against known drugs that are primarily used as skeletal muscle relaxants and / or sedatives. The combination of sedation and not impairing the animal's ability to respond to its environment is highly desirable in an agent used to treat anxiety. The compositions of the present invention preferably do not exhibit central nervous system hypnoti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com